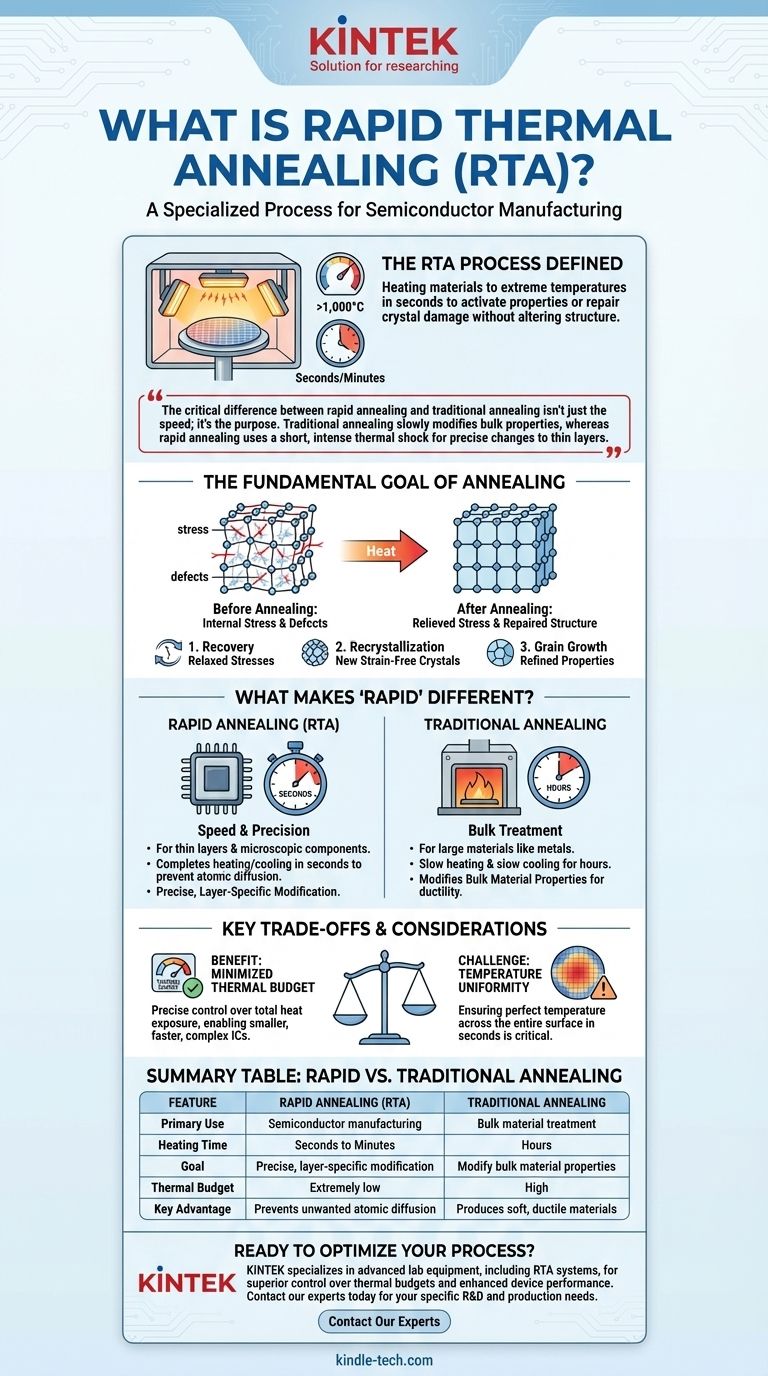
Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA), also known as Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP), is a specialized manufacturing process used primarily in the semiconductor industry. It involves heating a material, such as a silicon wafer, to extremely high temperatures (often over 1,000°C) in a matter of seconds to activate specific physical properties or repair crystal damage without altering the underlying structure.
The critical difference between rapid annealing and traditional annealing isn't just the speed; it's the purpose. Traditional annealing slowly modifies the bulk properties of a material like metal, whereas rapid annealing uses a short, intense thermal shock to make precise changes to thin layers in a complex device like a microchip.

The Fundamental Goal of Annealing
To understand what makes rapid annealing unique, we must first understand the purpose of annealing in general. It's a form of heat treatment designed to change a material's internal structure.
Relieving Internal Stress
Many fabrication processes, especially casting or cold working, introduce significant stress into a material's crystalline structure. Annealing relieves these internal stresses, making the material more stable and less prone to failure.
Repairing the Crystalline Structure
At a microscopic level, materials are made of a crystal lattice. Defects in this lattice can negatively impact mechanical and electrical properties. The heat from annealing gives the atoms enough energy to move and rearrange themselves into a more orderly, defect-free structure.
The Three Stages of Transformation
As a material is heated, its structure transforms through three distinct stages:
- Recovery: Internal stresses are relaxed.
- Recrystallization: New, strain-free crystals (grains) form, replacing the deformed ones.
- Grain Growth: The new grains grow, which can further refine the material's properties.
What Makes "Rapid" Annealing Different?
While both traditional and rapid annealing use heat to modify materials, their methods and goals are fundamentally different, driven by the materials they are designed to treat.
The Need for Speed and Precision
In semiconductor manufacturing, engineers work with incredibly thin layers and microscopic components. A long, slow heating process would allow atoms (like dopants that control electrical conductivity) to diffuse, or spread out, ruining the precise architecture of the microchip.
RTA solves this by completing the entire heating and cooling cycle in seconds or minutes. This provides just enough energy to achieve the desired effect—like repairing damage from ion implantation—without giving the rest of the structure time to change.
The Contrast in Heating and Cooling
Traditional annealing uses a furnace to slowly heat a material for hours, holds it at temperature, and then cools it down very slowly. This slow cooling is essential for producing a soft, ductile final product.
Rapid annealing uses high-intensity lamps to heat the surface of a wafer almost instantly. The process is over so quickly that only the top layers are significantly affected, and the rapid cooling that follows "locks in" the desired changes before they can spread.
Key Trade-offs and Considerations
Choosing RTA is a deliberate engineering decision with specific benefits and challenges.
The Benefit: A Minimized Thermal Budget
The primary advantage of RTA is the precise control over the thermal budget—the total amount of heat a wafer is exposed to over time. By keeping this budget extremely low, RTA enables the creation of smaller, faster, and more complex integrated circuits that would be impossible with slow furnace heating.
The Challenge: Temperature Uniformity
Heating a wafer from room temperature to 1000°C in a few seconds creates a significant engineering challenge: ensuring the temperature is perfectly uniform across the entire surface. Even a tiny variation of a few degrees can lead to inconsistent device performance, making process control absolutely critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use rapid versus traditional annealing is dictated entirely by the material and the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is bulk material properties, such as making a large piece of steel softer and more workable, traditional furnace annealing is the correct and necessary process.
- If your primary focus is precise, layer-specific modification, such as activating dopants in a semiconductor wafer without diffusion, Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) is the essential technique.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal process is about applying the precise amount of energy needed to achieve a specific engineering goal without causing unintended consequences.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rapid Annealing (RTA) | Traditional Annealing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Semiconductor manufacturing, microchip fabrication | Bulk material treatment (e.g., metals) |
| Heating Time | Seconds to minutes | Hours |
| Goal | Precise, layer-specific modification | Modify bulk material properties |
| Thermal Budget | Extremely low | High |
| Key Advantage | Prevents unwanted atomic diffusion | Produces soft, ductile materials |
Ready to optimize your semiconductor manufacturing process with precision thermal solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including RTA systems, to help you achieve superior control over your thermal budget and enhance device performance. Our expertise in laboratory equipment and consumables ensures you get the right tools for your specific R&D and production needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your semiconductor fabrication goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- How does an industrial tube furnace ensure the required process conditions for supercritical fluid experimental devices?
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry



















