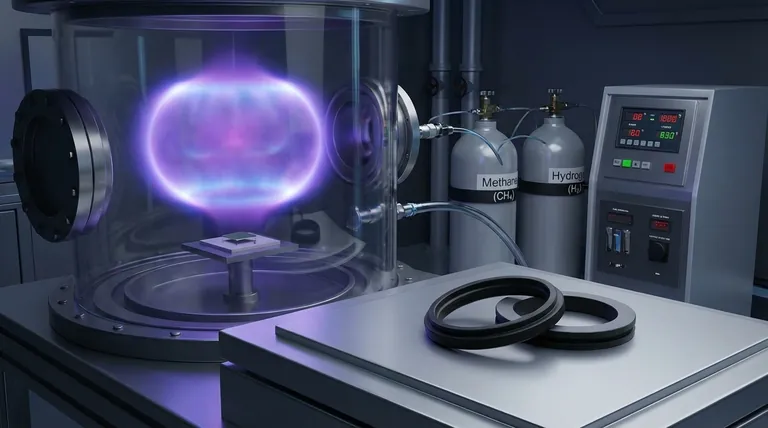
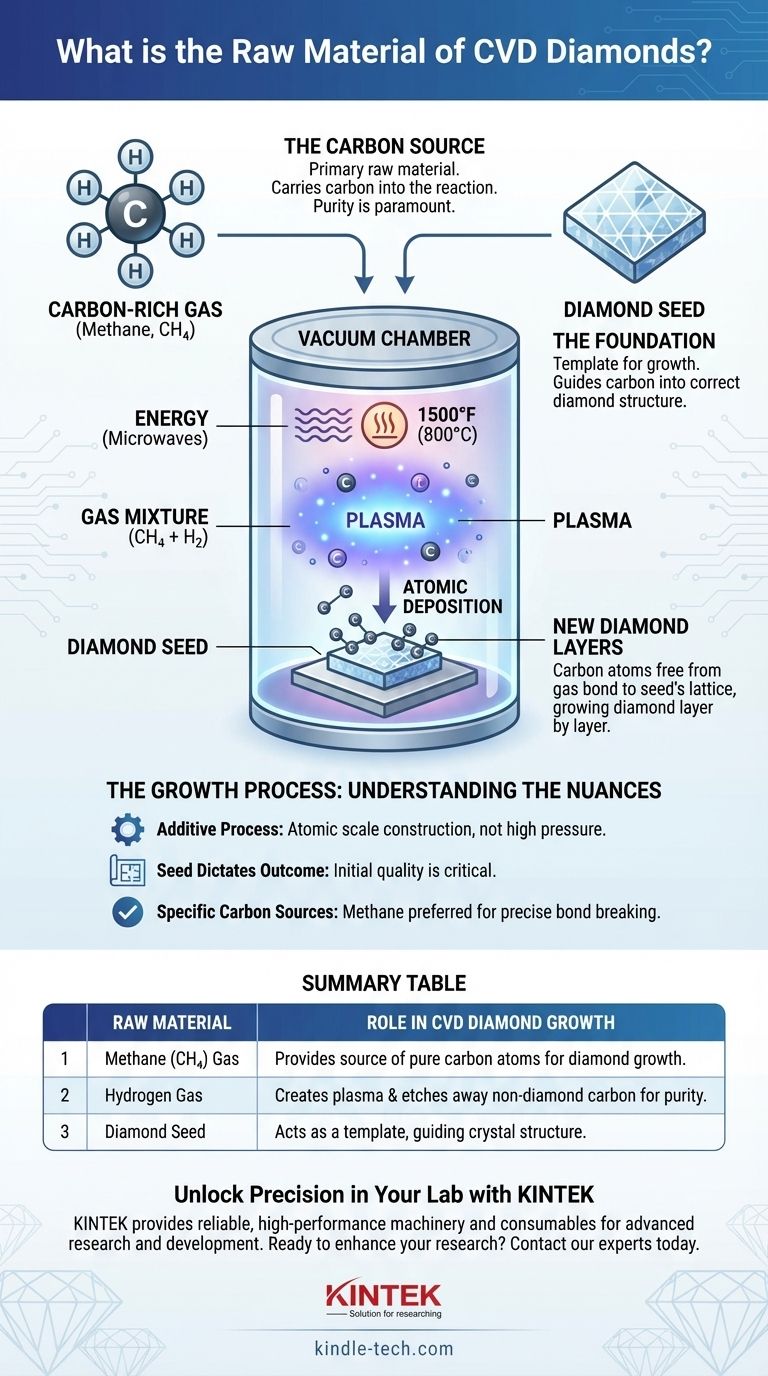
The primary raw materials for creating a CVD diamond are a high-purity, carbon-rich gas (typically methane) and a small, pre-existing slice of a diamond known as a "seed." These materials are placed inside a vacuum chamber where intense energy is used to break down the gas, allowing carbon atoms to deposit onto the seed and grow a new diamond, layer by atomic layer.
The core principle is not to melt and reform carbon, but to use a specialized gas as a source of individual carbon atoms. These atoms are then meticulously layered onto a diamond template, essentially "growing" a gemstone with the exact same crystal structure as a natural one.

The Core Ingredients of a Lab-Grown Diamond
Understanding the CVD process requires looking at its two essential components: the source of the carbon atoms and the foundation upon which they are assembled.
The Carbon Source: A Specialized Gas
The primary raw material is a hydrocarbon gas, most commonly methane (CH4), mixed with hydrogen.
This gas is the vehicle that carries the carbon into the reaction. Using a gas, rather than a solid like graphite, allows for extreme precision and control over the growth environment.
The purity of these gases is paramount, as any contaminants, such as nitrogen, can be incorporated into the diamond's crystal structure, affecting its final color and clarity.
The Foundation: The Diamond Seed
The process begins with a diamond seed, which is a very thin, flat slice of a previously grown high-quality diamond (either natural or lab-grown).
This seed is not a raw material in the sense of being consumed, but rather a template. Its existing crystal lattice provides the blueprint that guides the new carbon atoms into the correct, rigid diamond structure.
Without this seed, the carbon atoms would bond chaotically, forming graphite or amorphous carbon (soot) instead of a gemstone.
How Gas and Seed Become a Gemstone
The transformation from simple gas to a flawless diamond occurs within a highly controlled environment through a process of atomic deposition.
Creating the Environment: The Vacuum Chamber
The diamond seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. All air is removed to prevent contamination from atmospheric gases.
The carbon-rich gas mixture is then introduced into the chamber at very low pressure.
Activating the Carbon: Plasma Formation
Energy, typically in the form of microwaves, is used to heat the gas mixture to extreme temperatures—often around 1500°F (approximately 800°C).
This intense energy breaks the molecular bonds of the gas (e.g., separating methane into carbon and hydrogen), creating a glowing cloud of chemically reactive ions and atoms known as plasma.
The Growth Process: Atomic Deposition
Within this plasma, individual carbon atoms are freed from their original gas molecules.
These free carbon atoms are then drawn down to the slightly cooler surface of the diamond seed. They bond directly to the seed's crystal lattice, extending its structure atom by atom.
Over hundreds of hours, these layers build upon one another, growing the diamond vertically until the desired size is achieved. The accompanying hydrogen gas plays a crucial role by selectively etching away any non-diamond carbon that may try to form, ensuring the purity of the growing crystal.
Understanding the Key Nuances
While the process is straightforward in principle, the quality of the final product depends entirely on precision and control.
It's an Additive Process
CVD is fundamentally a form of additive manufacturing at the atomic scale. It doesn't mimic the brute-force pressure of natural diamond formation. Instead, it carefully constructs a diamond with incredible control.
The Seed Dictates the Outcome
The quality of the initial diamond seed is critical. Any imperfections or stresses within the seed's structure can be propagated into the new diamond as it grows, impacting its final quality.
Not All Carbon Sources Work
You cannot simply use any carbon-containing gas. Methane is favored because the chemical bonds are relatively easy to break in the plasma, and the accompanying hydrogen is essential for the quality control part of the process, ensuring only a pure diamond lattice forms.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the raw materials provides insight into the nature of the final gemstone itself.
- If your primary focus is on the science: Remember that CVD is an atomic construction process that builds a diamond crystal directly from the atoms in a carefully selected gas.
- If your primary focus is on quality: The purity of the carbon-source gas and the perfection of the diamond seed are the most critical factors determining the final gem's clarity and color.
- If your primary focus is on the "raw material" itself: The true starting ingredients are a hydrocarbon gas, hydrogen, and a diamond template, all meticulously controlled by energy within a vacuum.
This remarkable process transforms simple gas into one of the hardest and most brilliant materials known to man.
Summary Table:
| Raw Material | Role in CVD Diamond Growth |
|---|---|
| Methane (CH₄) Gas | Provides the source of pure carbon atoms for diamond growth. |
| Hydrogen Gas | Creates plasma and etches away non-diamond carbon, ensuring purity. |
| Diamond Seed | Acts as a template, guiding the crystal structure for the new diamond to grow upon. |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK
Understanding the intricate process of CVD diamond growth highlights the importance of precision, purity, and control—the same principles we apply to all our lab equipment. Whether you are researching advanced materials or developing new applications, KINTEK provides the reliable, high-performance machinery and consumables your laboratory needs to innovate with confidence.
Ready to enhance your research capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's unique challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
People Also Ask
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer



















