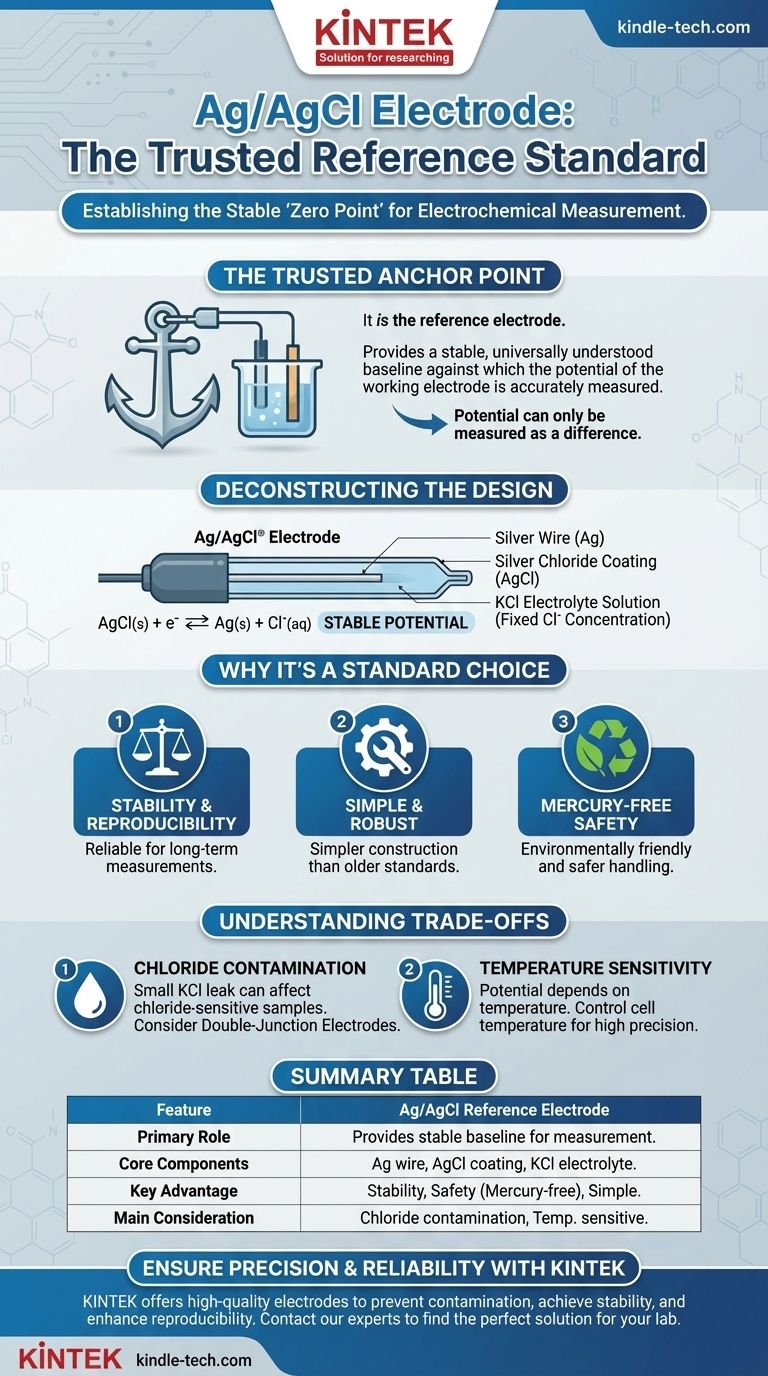
In short, the Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode is not measured against a reference electrode; it is the reference electrode. It functions as a stable, internationally recognized standard half-cell. Its purpose is to provide a constant and reliable potential baseline against which the potential of another electrode (the "working electrode") can be accurately measured.
A reference electrode is a necessary tool in electrochemistry because potential can only be measured as a difference between two points. The Ag/AgCl electrode provides a universally understood, stable "zero point" for these measurements, ensuring results are consistent and comparable across different experiments.

What Makes an Electrode a "Reference"?
To understand the role of the Ag/AgCl electrode, it's essential to grasp why a reference is needed in the first place. You cannot measure the absolute potential of a single electrode; you can only measure the voltage difference between two.
The Need for a Stable Baseline
In any electrochemical measurement, you are interested in the changing potential of your working electrode as it interacts with your sample. To measure this change accurately, you need a second electrode that has a constant, non-fluctuating potential. This stable partner is the reference electrode.
How Stability is Achieved
A reference electrode's stability comes from a carefully controlled electrochemical equilibrium. It is a half-cell reaction whose components are fixed, resulting in a potential that does not change as long as conditions like temperature and component concentrations are maintained.
Deconstructing the Ag/AgCl Electrode
The Ag/AgCl electrode is an elegant and robust design that achieves a highly stable potential through a specific chemical equilibrium.
Core Components
The electrode itself is remarkably simple. It consists of a high-purity silver wire (Ag) that has been coated with a layer of silver chloride (AgCl), a salt that is sparingly soluble in water.
The Crucial Electrolyte
This coated wire is then immersed in a solution with a fixed concentration of chloride ions (Cl⁻). This is almost always a solution of potassium chloride (KCl), typically at a high concentration (e.g., 3M or saturated).
The Reversible Reaction
The stable potential is generated by a reversible chemical reaction at the electrode surface:
AgCl(s) + e⁻ ⇌ Ag(s) + Cl⁻(aq)
Because the silver and silver chloride are solid, and the concentration of the chloride ions in the filling solution is fixed, the potential of this half-reaction remains constant.
Why Ag/AgCl is a Standard Choice
The Ag/AgCl electrode has become the most common reference in modern labs for several practical reasons.
Stability and Reproducibility
The electrode provides a highly stable and reproducible potential over long periods, making it a reliable standard for both routine and research-grade measurements.
Simple, Robust Construction
Compared to older standards like the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE), the Ag/AgCl electrode is simpler to manufacture and less fragile, contributing to its widespread adoption.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Crucially, the Ag/AgCl electrode is mercury-free. This makes it significantly safer to handle and dispose of than mercury-based electrodes, which are now restricted in many labs due to environmental and health concerns.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While it is the industry standard, no reference electrode is perfect for every situation. It's important to be aware of its limitations.
Chloride Contamination
The electrode is designed with a porous frit that allows electrical contact with the sample solution. Over time, a small amount of the KCl filling solution can leak into your sample. This is problematic if your sample contains species that react with chloride, such as silver ions.
Temperature Sensitivity
The potential of the Ag/AgCl electrode is dependent on temperature. For highly precise work, the temperature of the cell must be controlled and reported, or a temperature correction must be applied to the data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Measurement
Your choice of reference electrode depends entirely on the chemical nature of your experiment and the level of precision you require.
- If your primary focus is general lab analysis: The Ag/AgCl electrode is the default choice for its excellent balance of stability, safety, and cost.
- If your sample is sensitive to chloride ions: You must consider a "double-junction" Ag/AgCl electrode or an alternative like the Mercury/Mercurous Sulfate (Hg/Hg₂SO₄) electrode, which uses a non-chloride filling solution.
- If you require the highest precision across a range of temperatures: You must actively control the temperature of your electrochemical cell, regardless of which reference you use.
Ultimately, the Silver/Silver Chloride electrode serves as the trusted, stable anchor point essential for accurate and meaningful electrochemical analysis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode |
|---|---|
| Primary Role | Provides a stable potential baseline for measuring a working electrode. |
| Core Components | Silver wire coated with AgCl, immersed in KCl electrolyte solution. |
| Key Advantage | Excellent stability, safety (mercury-free), and simple construction. |
| Main Consideration | Potential chloride contamination; temperature-sensitive potential. |
Ensure your electrochemical measurements are precise and reliable. The right reference electrode is critical for your lab's success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of reference electrodes tailored to your specific experimental needs.
Our experts can help you select the ideal electrode to:
- Prevent sample contamination.
- Achieve superior measurement stability.
- Enhance the reproducibility of your results.
Contact our team today via our secure form to discuss your application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
People Also Ask
- Why and how should the electrodes of an electrolytic cell be calibrated? Ensure Reliable Results
- Why is a Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) used as a reference electrode in microbial fuel cell research?
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercury chloride? Discover the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE)
- What are the characteristics of a saturated calomel electrode for neutral solutions? Understanding its stability and limitations.
- Which type of electrode can be used as a reference point? Select the Right One for Accurate Measurements
















