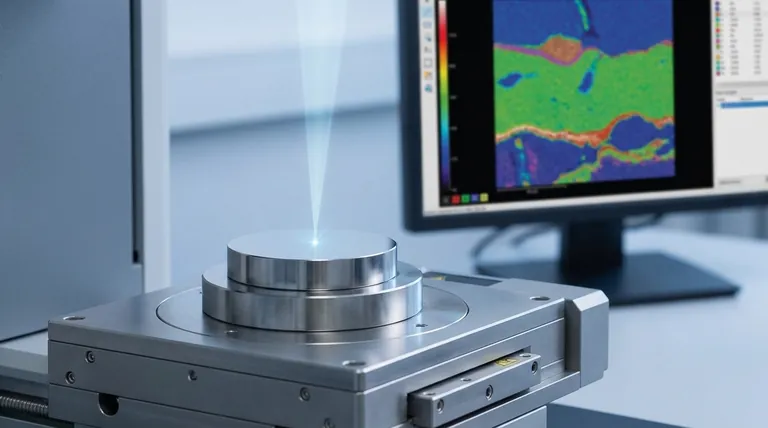
For micro-XRF analysis, there is no required sample size in the traditional sense of mass or volume. Instead, the limitations are defined by the physical dimensions of the instrument's sample stage and, more importantly, the microscopic spot size of the X-ray beam, which can be as small as a few micrometers.
The critical question for micro-XRF is not "how much sample is required," but rather "can the sample fit on the stage, and is its surface suitable for analysis?" The technique is defined by its small analysis spot size and mapping capabilities, not a required sample volume.

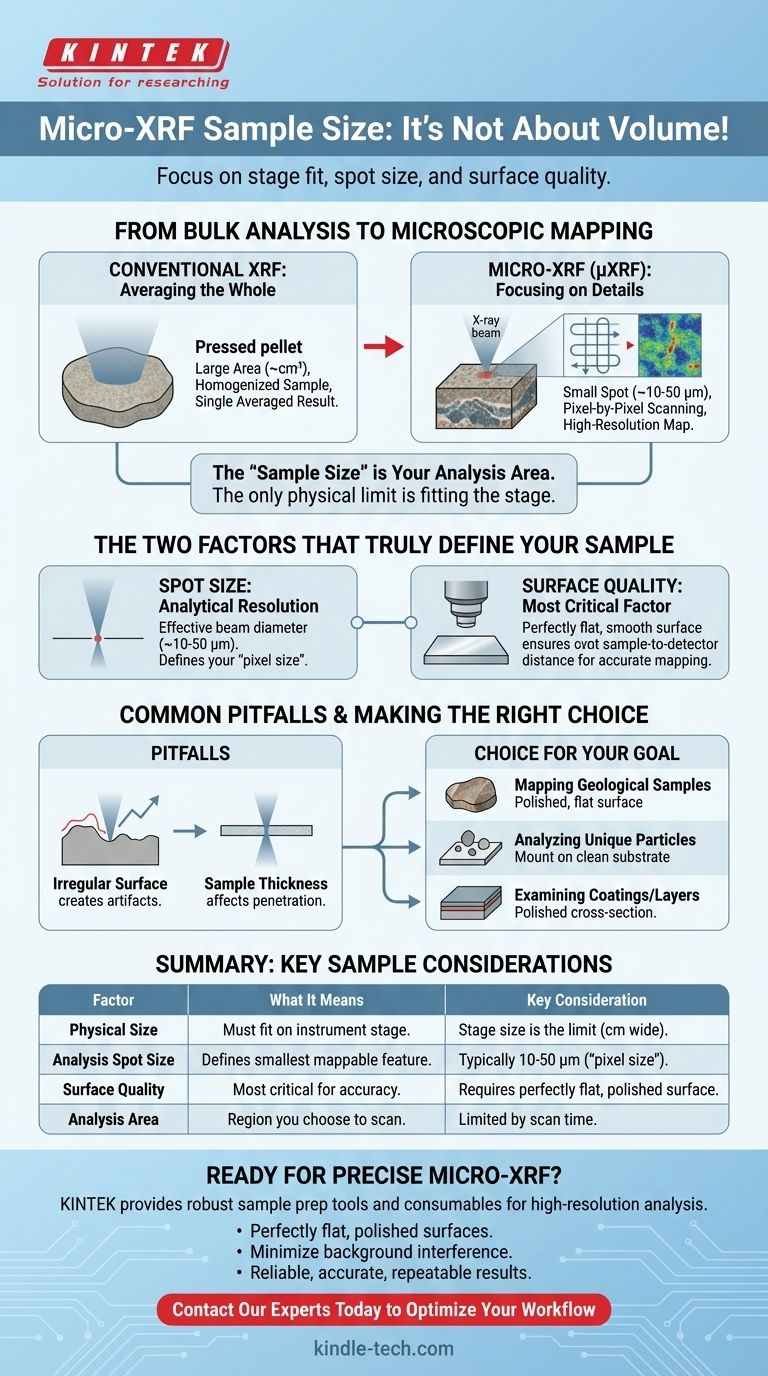
From Bulk Analysis to Microscopic Mapping
Understanding the sample requirements for micro-XRF begins with understanding how it differs from conventional, or "bulk," X-ray Fluorescence.
Conventional XRF: Averaging the Whole
Conventional XRF analyzes a large area of a sample, often several square centimeters.
Methods like creating pressed pellets, as mentioned in the references, are used to homogenize a sample. This process provides a single, averaged elemental composition for the entire sample volume being measured.
Micro-XRF: Focusing on the Details
Micro-XRF (µXRF) uses advanced optics to focus the X-ray beam down to a very small spot.
Instead of providing one average result, the instrument scans this small spot across the sample surface. It collects data pixel-by-pixel to create a high-resolution map showing the spatial distribution of different elements.
The "Sample Size" is Your Analysis Area
Because micro-XRF is a mapping technique, the concept of sample size is replaced by analysis area. The only physical limitation is that your object must fit onto the sample stage, which can often accommodate samples many centimeters wide.
The practical limit is the time it takes to scan your desired region of interest at a specific resolution.
The Two Factors That Truly Define Your Sample
Instead of worrying about volume or weight, your focus should be on the analytical resolution and the physical preparation of the sample surface.
Spot Size: Your Analytical Resolution
The spot size is the effective diameter of the focused X-ray beam. This is the true "pixel size" of your elemental map and defines the smallest feature you can accurately identify.
Modern instruments typically offer spot sizes ranging from about 10 to 50 micrometers (µm).
Surface Quality: The Most Critical Factor
The quality of the sample surface is paramount for accurate micro-XRF results.
An ideal sample must have a perfectly flat and smooth surface. This ensures the distance between the X-ray source, the sample, and the detector remains constant for every single pixel in the map.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
An improperly prepared sample is the most common source of error in micro-XRF analysis.
The Impact of an Irregular Surface
As the references correctly point out, an irregular surface creates variations in the sample-to-detector distance.
On a microscopic scale, even tiny bumps or pits can cause significant errors. A pixel on a "peak" will show an artificially high signal, while a pixel in a "valley" will show an artificially low signal, creating a false elemental map that reflects topography, not chemistry.
The Influence of Sample Thickness
The X-ray beam penetrates the sample to a certain depth, which varies depending on the material and the energy of the X-rays.
For very thin samples (e.g., films, biological sections), the beam may pass entirely through, requiring special considerations. For most solid samples, the analysis is considered surface-sensitive, analyzing the top tens to hundreds of micrometers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Proper sample preparation depends entirely on your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is mapping a geological or metallurgical sample: Your goal is to create a polished, flat surface or cross-section to reveal the true elemental distribution without topographic artifacts.
- If your primary focus is analyzing small, unique particles: Mount the particles on a clean, flat substrate (like a polycarbonate film) that produces minimal background signal.
- If your primary focus is examining coatings or layers: Prepare a polished cross-section of the material to ensure the beam can cleanly scan across the distinct layers.
By focusing on surface quality and analytical area, you ensure your micro-XRF results are accurate and truly representative of your material's microscopic world.
Summary Table:
| Factor | What It Means for Your Sample | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Size | Must fit on the instrument's stage. | Stage size is the only physical limit; samples can be many centimeters wide. |
| Analysis Spot Size | Defines the smallest feature you can map. | Typically 10-50 micrometers (µm); this is your effective "pixel size." |
| Surface Quality | Most critical factor for accurate results. | Requires a perfectly flat, polished surface to avoid topographic artifacts. |
| Analysis Area | The region you choose to scan. | Limited by the time required to map the area at your desired resolution. |
Ready to Achieve Precise Micro-XRF Analysis?
Understanding the nuances of sample preparation is the first step to unlocking high-resolution elemental maps. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and expert support you need to ensure your micro-XRF analysis is a success.
We help our laboratory customers by:
- Providing robust sample preparation tools for creating perfectly flat, polished surfaces.
- Offering consumables that minimize background interference for sensitive analyses.
- Delivering the reliable performance required for accurate, repeatable results.
Let's discuss your specific application. Whether you're mapping geological samples, analyzing unique particles, or examining coatings, we have the solutions to meet your laboratory's needs.
Contact our experts today to optimize your micro-XRF workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Battery Lab Equipment Battery Capacity and Comprehensive Tester
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the five key considerations when designing a sample preparation recipe for pressed pellets in XRF analysis?
- What is the difference between EDS and XRF? EDS for Microanalysis, XRF for Bulk Analysis
- What is the size range of pellets? From 1mm to 25mm, Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What are pellet dies made of? Choose the Right Material for Accurate XRF Analysis
- What are the samples for XRF analysis? A Guide to Preparing Solids, Powders, and Liquids


















