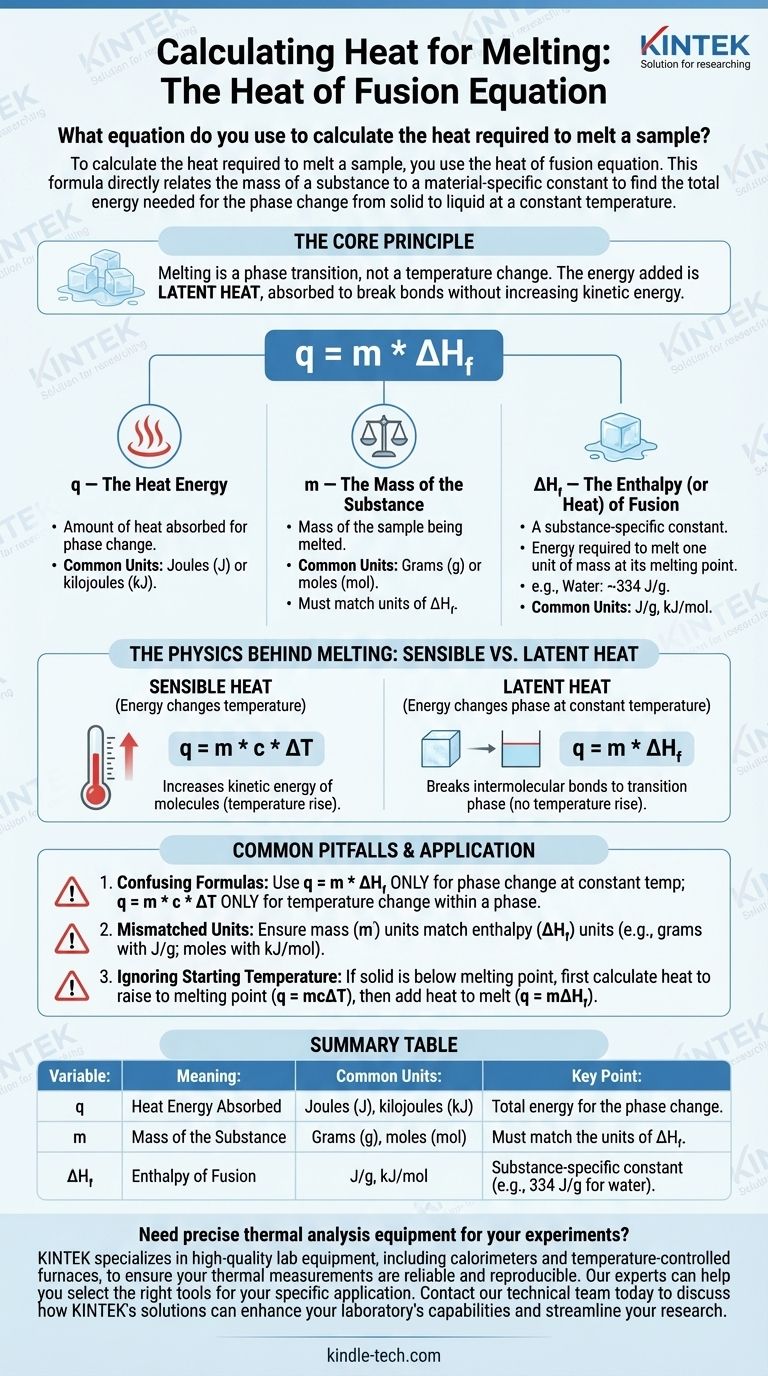
To calculate the heat required to melt a sample, you use the heat of fusion equation. This formula directly relates the mass of a substance to a material-specific constant to find the total energy needed for the phase change from solid to liquid at a constant temperature.
The core principle is that melting is a phase transition, not a temperature change. The energy you add is called latent heat, which is absorbed to break the bonds of the solid structure without increasing the kinetic energy of the molecules.
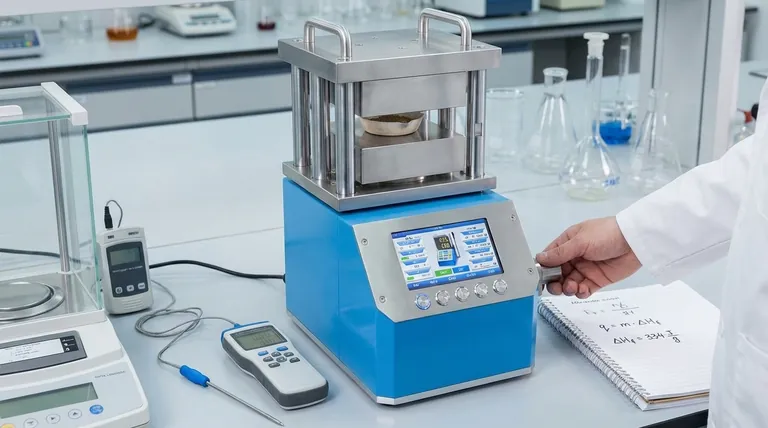

Deconstructing the Heat of Fusion Equation
The formula for calculating the heat absorbed during melting is:
q = m * ΔH_f
Each variable in this equation represents a critical piece of the physical process. Understanding them individually is key to applying the formula correctly.
q — The Heat Energy
q represents the amount of heat absorbed by the substance to undergo the phase change. This value is typically expressed in Joules (J) or kilojoules (kJ), though older contexts may use calories (cal).
m — The Mass of the Substance
m is the mass of the sample you are melting. It's crucial that the units of mass, typically grams (g) or moles (mol), match the units used in the heat of fusion constant for that substance.
ΔH_f — The Enthalpy (or Heat) of Fusion
ΔH_f is the most important variable. It is the enthalpy of fusion, often called the latent heat of fusion.
This is a physical constant unique to each substance. It defines the amount of energy required to melt one unit of mass (e.g., 1 gram or 1 mole) of that substance at its melting point.
For example, the heat of fusion for water is approximately 334 Joules per gram (J/g). This means you must add 334 Joules of energy to melt 1 gram of ice at 0°C into 1 gram of liquid water at 0°C.
The Physics Behind Melting: Sensible vs. Latent Heat
A common point of confusion is why the temperature doesn't rise during melting. This is explained by the difference between two types of heat energy.
Sensible Heat
Sensible heat is the energy that changes the temperature of a substance. When you add sensible heat, you increase the kinetic energy of the molecules, making them move faster, which we measure as a temperature increase. The formula for this is q = m * c * ΔT.
Latent Heat
Latent heat is the energy absorbed or released during a phase change at a constant temperature. During melting, the incoming energy is used entirely to break the intermolecular bonds holding the solid's crystal lattice together, transitioning it to a liquid.
Because the energy is "hidden" in the phase change rather than causing a temperature rise, it is called latent.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Applying the wrong concept or formula is a frequent source of error in thermodynamic calculations. Be aware of these common mistakes.
Confusing Heat of Fusion with Specific Heat
The most common mistake is using the wrong formula.
- Use
q = m * ΔH_f(Heat of Fusion) ONLY for a phase change at a constant temperature (e.g., melting ice at 0°C). - Use
q = m * c * ΔT(Specific Heat) ONLY for changing the temperature of a substance within a single phase (e.g., heating solid ice from -10°C to 0°C).
Mismatched Units
Always check your units. If your mass (m) is in grams, your heat of fusion (ΔH_f) must be in Joules per gram (J/g). If ΔH_f is given in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol), you must first convert the mass of your sample to moles.
Ignoring the Starting Temperature
The heat of fusion equation only applies if the substance is already at its melting point. If you have a solid below its melting point, you must perform a two-step calculation:
- Calculate the heat needed to raise the solid to its melting point (
q = mcΔT). - Calculate the heat needed to melt the solid at its melting point (
q = mΔH_f). - Add the results for the total heat required.
Applying the Correct Formula for Your Calculation
To ensure you solve your problem correctly, identify the exact process you need to calculate.
- If your primary focus is melting a substance already at its melting point: You only need the heat of fusion equation:
q = m * ΔH_f. - If your primary focus is heating a substance without changing its phase: You only need the specific heat capacity equation:
q = m * c * ΔT. - If your primary focus is heating a solid and then completely melting it: You must calculate the heat for both steps separately and add them together:
q_total = (m * c * ΔT)_heating + (m * ΔH_f)_melting.
Understanding which physical process you are modeling is the key to selecting the right equation.
Summary Table:
| Variable | Meaning | Common Units | Key Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| q | Heat Energy Absorbed | Joules (J), kilojoules (kJ) | Total energy for the phase change |
| m | Mass of the Substance | Grams (g), moles (mol) | Must match the units of ΔH_f |
| ΔH_f | Enthalpy of Fusion | J/g, kJ/mol | Substance-specific constant (e.g., 334 J/g for water) |
Need precise thermal analysis equipment for your experiments?
Accurately calculating heat requirements is fundamental in materials science, chemistry, and pharmaceuticals. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including calorimeters and temperature-controlled furnaces, to ensure your thermal measurements are reliable and reproducible.
Our experts can help you select the right tools for your specific application, whether you're studying phase changes, material synthesis, or reaction kinetics.
Contact our technical team today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and streamline your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Lab Infrared Press Mold
People Also Ask
- What is a hydraulic hot press? A Guide to Precision Heat and Pressure for Manufacturing
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production


























