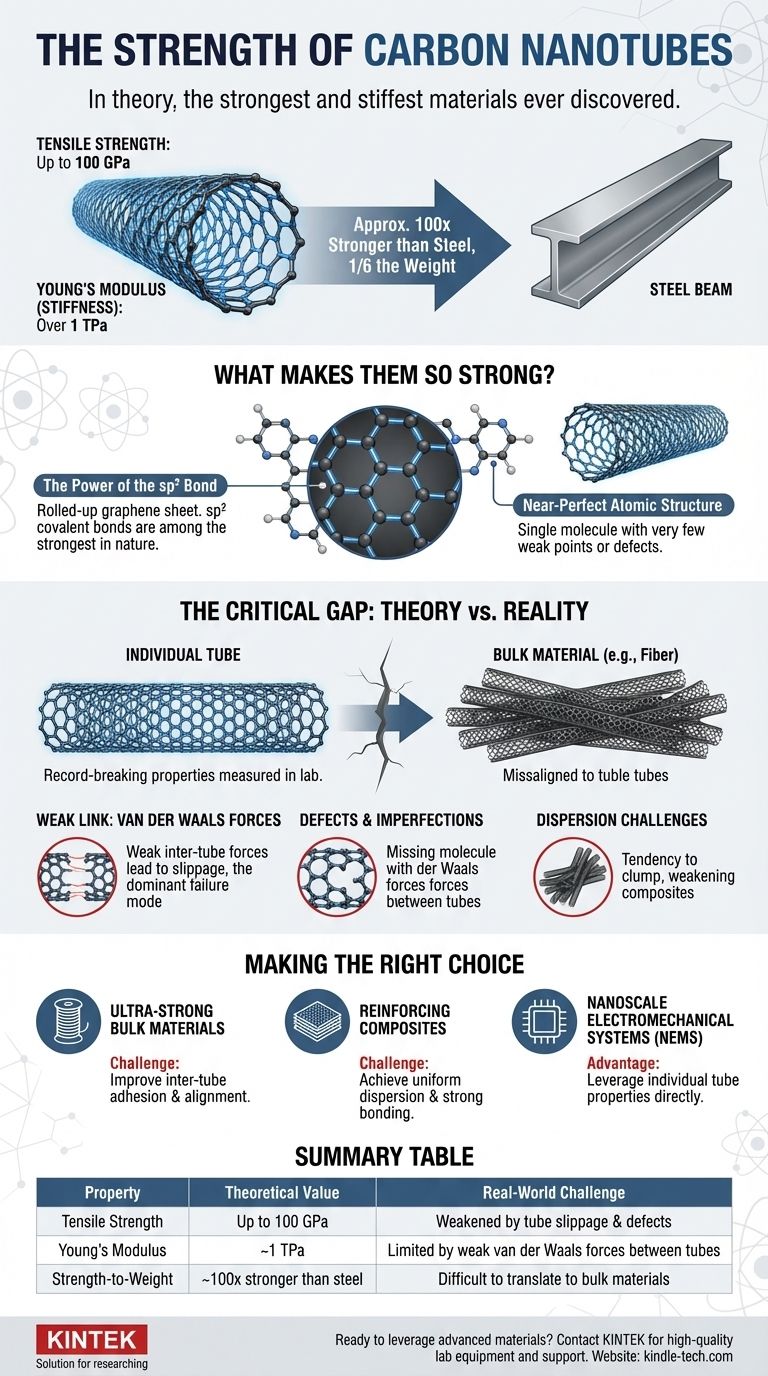
In theory, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are the strongest and stiffest materials ever discovered. A single, flawless carbon nanotube has a tensile strength estimated to be as high as 100 gigapascals (GPa) and a Young's Modulus (a measure of stiffness) of over 1 terapascal (TPa). For context, this makes them approximately 100 times stronger than steel at only one-sixth of the weight.
The unparalleled strength of a carbon nanotube exists at the individual, molecular level. The central engineering challenge is not in the nanotube itself, but in translating this nano-scale property into a macroscopic material, where weaknesses between tubes dramatically reduce the overall strength.

What Makes Carbon Nanotubes So Strong?
The extraordinary mechanical properties of CNTs are not magical; they arise directly from their unique atomic structure and the fundamental physics of chemical bonds.
The Power of the sp² Bond
The walls of a carbon nanotube are essentially a rolled-up sheet of graphene, a one-atom-thick lattice of carbon atoms. These atoms are linked by sp² covalent bonds, which are among the strongest and most stable chemical bonds in nature. This robust hexagonal lattice is what gives a CNT its intrinsic strength.
Near-Perfect Atomic Structure
In macroscopic materials like steel, strength is often limited by the presence of microscopic defects, dislocations, or grain boundaries. A high-quality, single-walled carbon nanotube is a single molecule with a near-perfect atomic arrangement, leaving very few weak points where a fracture could initiate.
Stiffness vs. Strength
It is important to distinguish between two key metrics:
- Young's Modulus (Stiffness): This measures resistance to being deformed elastically. With a modulus of ~1 TPa, CNTs are incredibly rigid and resist stretching.
- Tensile Strength (Strength): This measures the maximum stress a material can withstand before fracturing. The theoretical value of up to 100 GPa means it takes an immense amount of force to actually break the covalent bonds in the tube.
The Critical Gap: Theory vs. Reality
While the figures for a single nanotube are staggering, these properties do not automatically transfer to materials you can hold in your hand. This disconnect is the primary hurdle in CNT applications.
Individual Tube vs. Bulk Material
The record-breaking strength values are measured for individual, often short nanotubes under laboratory conditions. A real-world material, like a fiber spun from CNTs, is composed of trillions of tubes held together. The overall strength is then dictated by the weakest link in the system.
The "Slippage" Problem
The forces holding adjacent nanotubes together in a bundle or yarn are van der Waals forces. These are exceptionally weak compared to the covalent bonds within the tubes themselves. When you pull on a CNT fiber, the tubes will almost always slide past one another long before the tubes themselves actually break. This slippage is the dominant failure mode.
The Inevitability of Defects
The synthesis methods used to produce CNTs on a large scale inevitably create defects in the atomic structure (e.g., vacancies, different ring sizes). These defects act as stress concentrators and dramatically lower the real-world fracture strength compared to the theoretical maximum of a perfect tube.
The Challenge of Dispersion
When used as an additive to create composites (e.g., in a polymer or metal matrix), CNTs tend to clump together due to the same van der Waals forces. These agglomerates act as defects within the host material, often weakening the composite instead of strengthening it. Achieving a uniform, well-bonded dispersion is a significant manufacturing challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying the strength of CNTs effectively requires understanding whether your application depends on the properties of a single tube or a collective structure.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-strong bulk materials (e.g., fibers or sheets): Your main engineering challenge is improving inter-tube adhesion and alignment to prevent slippage and maximize load transfer between tubes.
- If your primary focus is reinforcing composites (e.g., CNT-epoxy): The key is achieving uniform dispersion and creating strong chemical bonding between the CNT surface and the host matrix material.
- If your primary focus is nanoscale electromechanical systems (NEMS): You can more directly leverage the properties of individual tubes as structural elements, making their theoretical strength more attainable.
Harnessing the full potential of carbon nanotubes requires shifting focus from the tube's inherent strength to the engineering of the interfaces that connect them.
Summary Table:
| Property | Theoretical Value | Real-World Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 100 GPa | Weakened by tube slippage & defects |
| Young's Modulus | ~1 TPa | Limited by weak van der Waals forces between tubes |
| Strength-to-Weight | ~100x stronger than steel | Difficult to translate to bulk materials |
Ready to leverage the strength of advanced materials in your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need for cutting-edge materials research, including applications involving carbon nanotubes. Our experts can help you select the right tools to overcome engineering challenges and achieve your project goals. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries



















