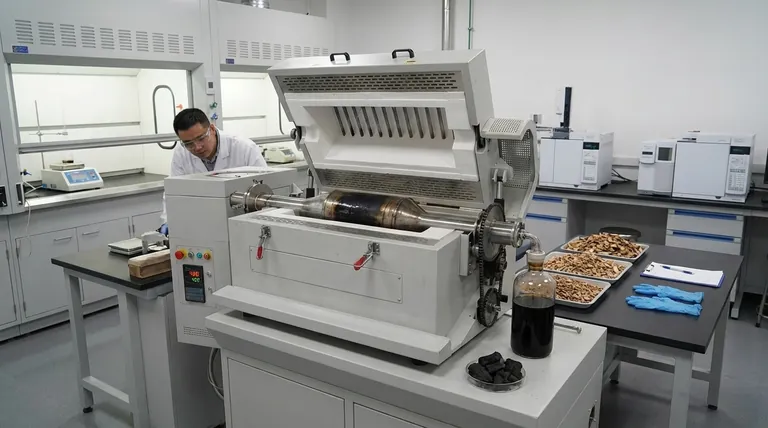
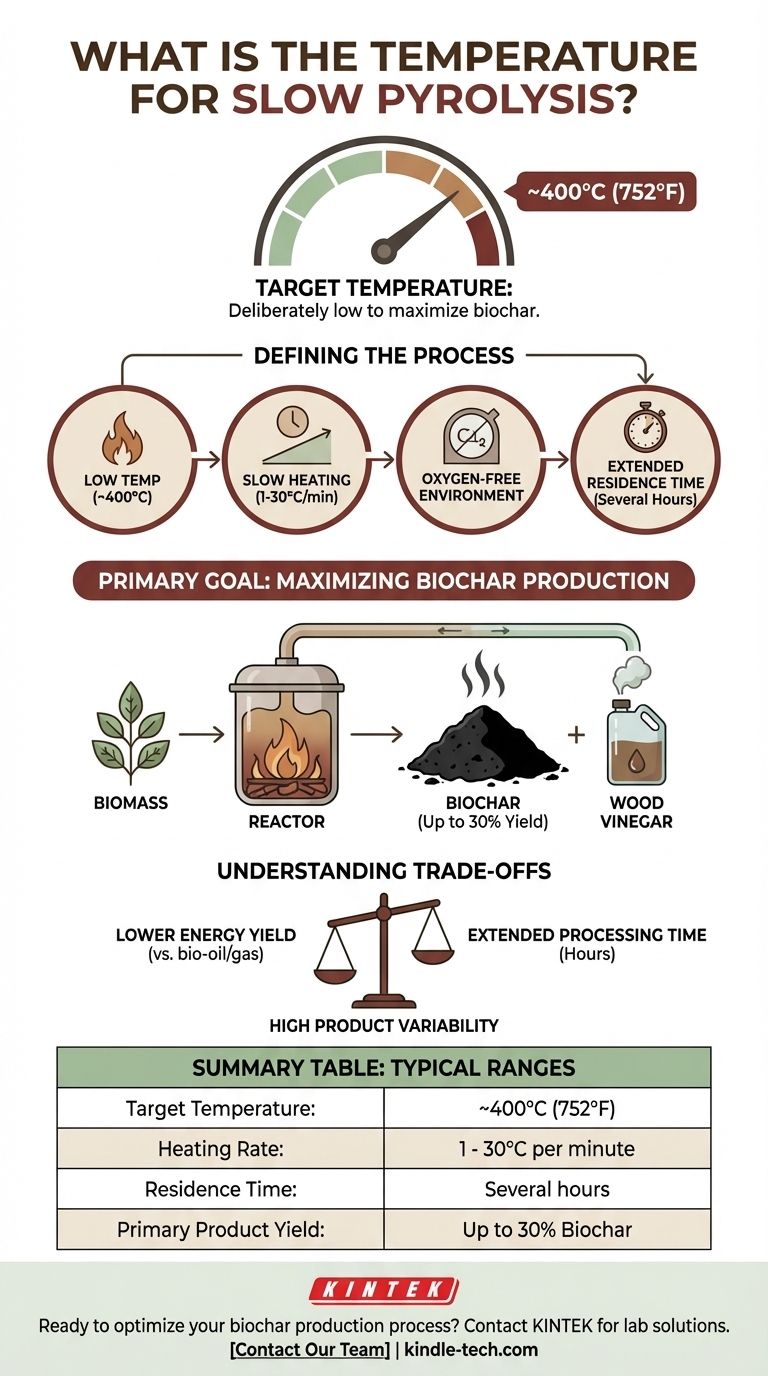
In slow pyrolysis, the target temperature for decomposition is typically around 400°C (752°F). This relatively low temperature, combined with a slow heating rate and long processing time, is deliberately chosen to maximize the production of a solid carbon-rich product known as biochar, rather than liquids or gases.
The core principle of slow pyrolysis is using a lower temperature (around 400°C) and extended residence times to intentionally favor the creation of solid biochar over the volatile liquids and gases that are prioritized in higher-temperature pyrolysis methods.

What Defines the Slow Pyrolysis Process?
Slow pyrolysis is a specific method of thermal decomposition characterized by a unique set of operating conditions designed to achieve a very particular outcome. It is not merely about heating a material, but about controlling that heat to dictate the final product.
The Critical Role of Low Temperature
The process operates at the lower end of the pyrolysis spectrum, generally around 400°C. This temperature is hot enough to break down the complex organic polymers in biomass like cellulose and lignin, but it is not so extreme that it violently fractures them into volatile gases and aerosols. This controlled decomposition is key to preserving a solid carbon structure.
A Deliberately Slow Heating Rate
The heating rate is carefully managed, typically between 1 and 30°C per minute. This gradual increase in temperature ensures that the biomass decomposes uniformly and gently. Unlike the thermal shock of fast pyrolysis, this slow "cooking" process gives the material time to carbonize thoroughly, maximizing the solid residue.
An Oxygen-Free Environment
Like all pyrolysis processes, this occurs in an oxygen-limited or oxygen-free environment. This is the fundamental requirement that separates pyrolysis from combustion (burning). Without oxygen, the biomass thermally decomposes into new products instead of simply burning away into ash and flue gas.
The Primary Goal: Maximizing Biochar Production
The specific conditions of slow pyrolysis are chosen with one primary objective in mind: to produce the highest possible yield of high-quality solid char.
Prioritizing Solids Over Liquids and Gases
The combination of low temperature and slow heating minimizes the production of volatile compounds. While some gases and liquids are inevitably produced, the process is optimized to yield up to 30% biochar by weight from the initial dry feedstock. The produced bio-gas is often captured and combusted to provide the energy needed to sustain the reaction.
The Resulting Products: Biochar and Wood Vinegar
The two main outputs from this process are distinct and valuable. The primary product is biochar (or biocoal), a stable, carbon-rich solid. The secondary product is wood vinegar (pyroligneous acid), an aqueous liquid condensed from the limited vapors produced during the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing slow pyrolysis comes with a clear set of advantages and disadvantages tied directly to its operational parameters.
Lower Energy Yield
If the goal is to produce energy, slow pyrolysis is inefficient. It is not designed to maximize the creation of energy-dense bio-oil or flammable syngas. The majority of the carbon and energy potential remains locked within the solid biochar.
Extended Processing Time
As the name implies, the process is slow. The residence time for the feedstock inside the reactor can last for several hours. This significantly impacts the total throughput of a facility compared to fast pyrolysis, which can complete its reaction in seconds.
High Product Variability
The final properties of the biochar are highly dependent on the specific feedstock used and the precise process conditions. This can make it challenging to produce a consistently uniform product, which is a critical consideration for developing stable market applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if slow pyrolysis is the correct approach, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the ideal method due to its unmatched solid yield and quality.
- If your primary focus is generating liquid biofuels (bio-oil) or synthesis gas for energy: You should investigate fast pyrolysis or gasification, which use higher temperatures to maximize these volatile products.
Ultimately, slow pyrolysis is a material-focused process, chosen when the solid carbon product itself is the most valuable output.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range for Slow Pyrolysis |
|---|---|
| Target Temperature | ~400°C (752°F) |
| Heating Rate | 1 - 30°C per minute |
| Residence Time | Several hours |
| Primary Product Yield | Up to 30% Biochar (by weight) |
Ready to optimize your biochar production process?
Choosing the right pyrolysis method is critical to achieving your product goals. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development.
Whether you are scaling up biochar production or need precise temperature control for your experiments, our solutions are designed to meet the demanding needs of laboratory professionals.
Contact our team today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific pyrolysis application and help you achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process



















