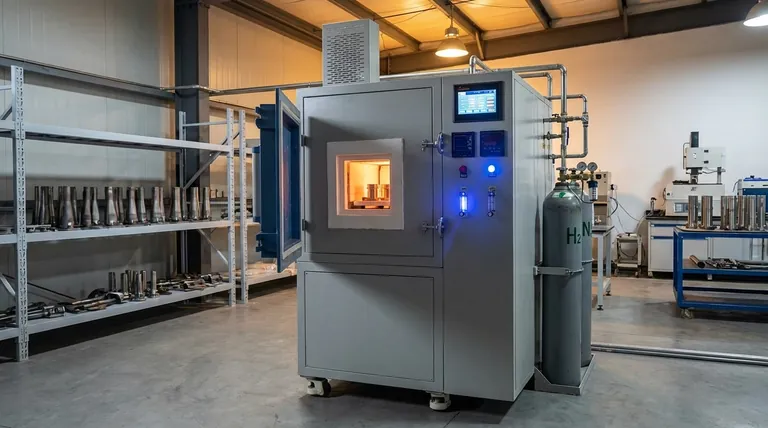
In short, hydrogen is used in annealing as an active chemical agent. It serves two primary functions: to remove surface oxides for a clean, bright finish, and to draw out trapped internal hydrogen atoms that can cause material brittleness.
The core purpose of using hydrogen in annealing is to transform the process from simple heating into a targeted chemical refinement. It actively purifies the material by deoxidizing its surface and removing internal contaminants, preventing critical failures like embrittlement.

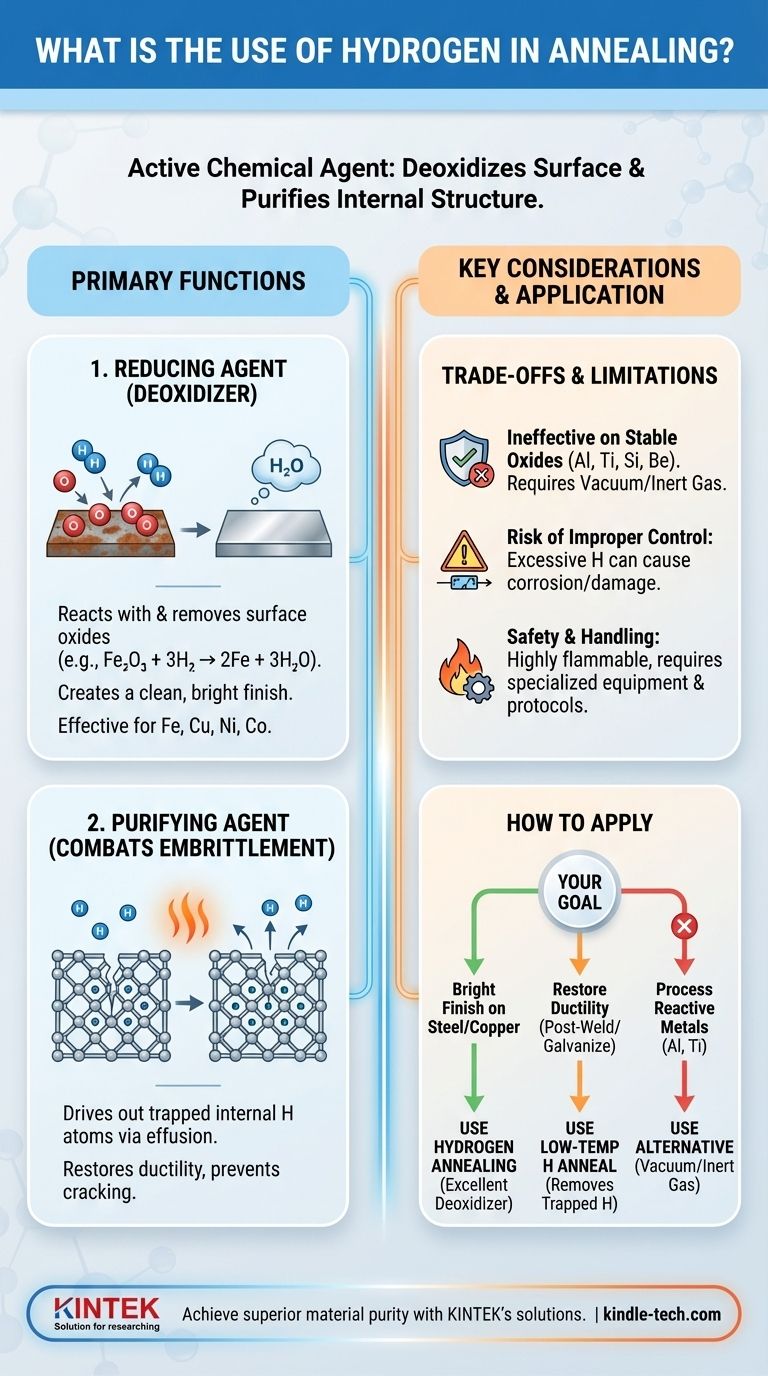
The Primary Functions of Hydrogen in Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process designed to relieve internal stresses and improve a material's ductility. Introducing hydrogen into the furnace atmosphere adds a powerful chemical component to this physical process.
As a Reducing Agent (Deoxidizer)
Many metals, especially iron, copper, and nickel, form oxides on their surface when exposed to air. These oxide layers can be detrimental to the final product's quality and appearance.
Hydrogen acts as a reducing agent, meaning it chemically reacts with and removes these oxides. At the high temperatures of the annealing furnace, hydrogen bonds with the oxygen atoms in the metal oxide, forming water vapor (H₂O) which is then carried away. This leaves behind a pure, clean, and bright metallic surface.
As a Purifying Agent to Combat Embrittlement
Certain manufacturing processes like welding, electroplating, or galvanizing can introduce atomic hydrogen into the metal's internal structure. These trapped atoms can cause a serious condition known as hydrogen embrittlement.
Hydrogen embrittlement significantly reduces the ductility of the metal, making it brittle and prone to cracking under stress. Annealing in a hydrogen-rich atmosphere helps reverse this. The process, known as effusion, uses heat to give the trapped hydrogen atoms the energy to diffuse out of the material, restoring its integrity.
The Chemical Mechanisms at Work
Understanding how hydrogen accomplishes these tasks requires looking at the reactions driven by the thermal energy of the annealing process.
The Deoxidization Reaction
The fundamental reaction for removing an oxide, such as iron oxide (rust), is straightforward. The hydrogen gas (H₂) reacts with the metal oxide to produce the pure metal and water.
For iron oxide, the reaction is: Fe₂O₃ + 3H₂ → 2Fe + 3H₂O. This process is highly effective for the oxides of iron, copper, nickel, and cobalt.
Driving Out Trapped Hydrogen
The removal of internal hydrogen operates on the principle of diffusion. By heating the material in a hydrogen atmosphere, the trapped hydrogen atoms gain enough thermal energy to move through the metal's crystal lattice.
They migrate to the surface, where they can escape, effectively purging the material of the contaminant that causes embrittlement. This is most often performed at temperatures between 200 °C and 300 °C.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, hydrogen annealing is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is dependent on the material and the precise control of the process.
Ineffectiveness on Stable Oxides
Hydrogen is not strong enough to reduce the highly stable oxides formed by certain metals. Materials like aluminum, titanium, silicon, and beryllium have oxides that do not react with hydrogen under typical annealing conditions.
For these materials, alternative methods such as annealing in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon) are required.
The Risk of Improper Control
The concentration and flow rate of hydrogen are critical variables. As seen in advanced material synthesis like graphene production, hydrogen is used to remove unwanted amorphous carbon.
However, excessive hydrogen can begin to corrode and damage the desired material itself. This principle applies to metal annealing as well; the process must be carefully optimized to purify without causing harm.
Safety and Handling
As a highly flammable gas, hydrogen requires specialized equipment and strict safety protocols. This operational complexity and cost is a significant consideration when choosing an annealing atmosphere.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The decision to use hydrogen annealing depends entirely on the material you are working with and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is a bright, oxide-free finish on steel or copper parts: Hydrogen annealing is an excellent choice for its effective deoxidizing properties.
- If your primary focus is restoring ductility after welding or galvanizing: A low-temperature hydrogen anneal is the specific remedy for removing trapped hydrogen and preventing embrittlement.
- If your primary focus is processing aluminum, titanium, or other reactive metals: You must use an alternative like vacuum or inert gas annealing, as hydrogen will not reduce their stable oxides.
Ultimately, using hydrogen correctly elevates annealing from a simple heat treatment to a precise chemical purification process.
Summary Table:
| Function | Mechanism | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing Agent | Reacts with surface oxides (e.g., Fe₂O₃) to form water vapor. | Creates a bright, oxide-free finish. |
| Purifying Agent | Heat drives trapped internal hydrogen atoms out of the metal (effusion). | Prevents hydrogen embrittlement, restoring ductility. |
Achieve superior material purity and performance with KINTEK's hydrogen annealing solutions.
Our specialized lab equipment is designed for precise control of the hydrogen atmosphere, ensuring effective deoxidization and hydrogen removal for metals like steel, copper, and nickel. This prevents embrittlement and delivers the clean, bright finish your application demands.
Contact us today to discuss how our annealing systems can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and material quality.
Get in touch with our experts →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is hydrogen annealing? Achieve Superior Material Properties with Bright Annealing
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance
- What are the effects of hydrogen (H2) in a controlled furnace environment? Mastering Reduction and Risk
- Why is a hydrogen atmosphere furnace necessary for W-Cu composite? Unlock Superior Infiltration and Density



















