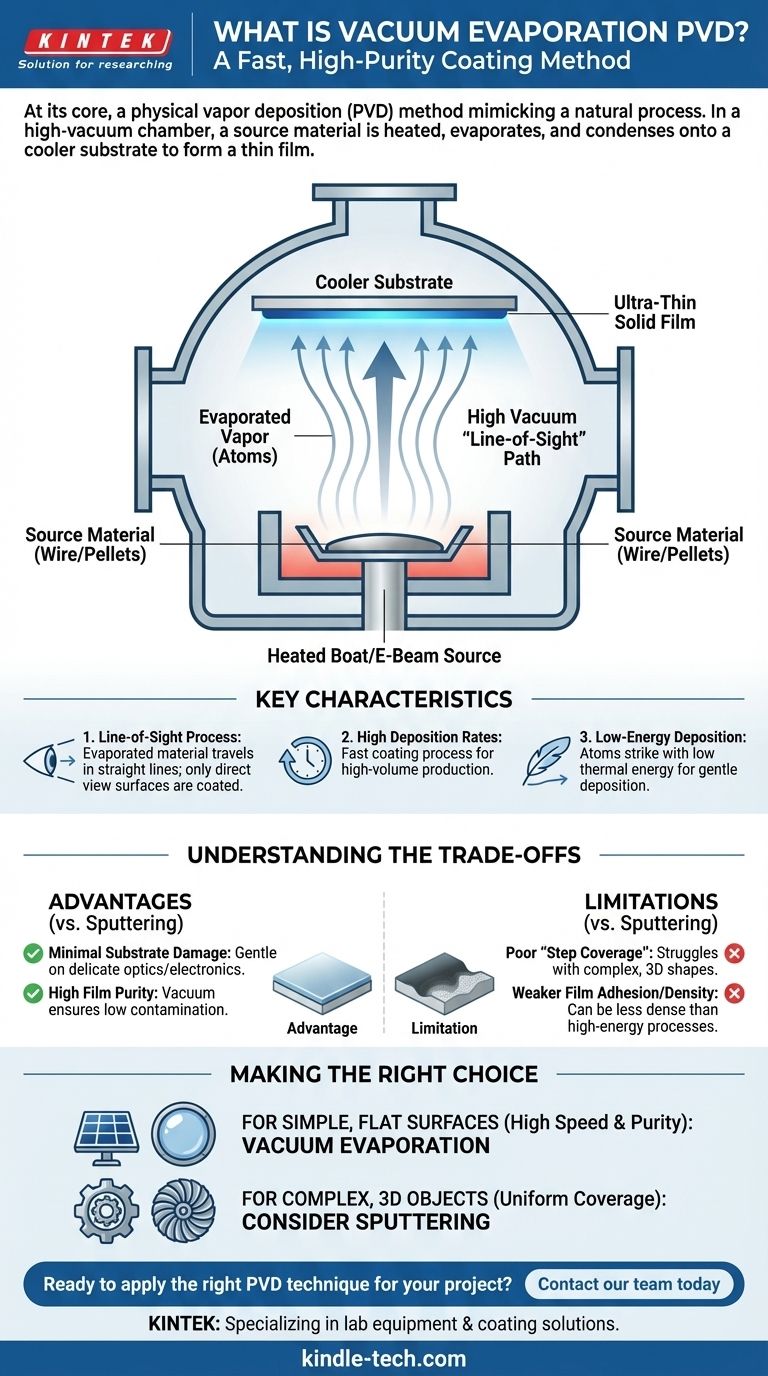
At its core, vacuum evaporation is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method that mimics a natural process. In a high-vacuum chamber, a source material is heated until it evaporates into a gaseous vapor. This vapor then travels unimpeded through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler target object, known as the substrate, forming an ultra-thin, solid film.
The central concept to grasp is that vacuum evaporation is a fast, high-purity coating process defined by its direct "line-of-sight" nature. It excels at coating simple surfaces with minimal damage but struggles with complex, three-dimensional shapes.
The Fundamental Principle: Phase Change in a Vacuum
Vacuum evaporation is one of the oldest and conceptually simplest PVD techniques. The entire process hinges on controlling the transition of a material from a solid to a gas and back to a solid again.
The Source Material and Heating
The process begins with the solid coating material, often in the form of wires or pellets. This source is heated within the vacuum chamber using methods like resistively heated "boats" or high-energy electron beams.
The Role of High Vacuum
The process occurs in a high vacuum, typically at pressures between 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁹ Torr. This extreme vacuum is critical because it removes virtually all air and other gas molecules that could collide with the vaporized atoms.
This ensures the evaporated material can travel directly from the source to the substrate without interference, which is essential for creating a pure, uncontaminated film.
Condensation on the Substrate
The vaporized atoms travel through the chamber until they strike the comparatively cool substrate. Upon contact, they lose their energy and condense back into a solid state, gradually building up a thin, uniform layer on the substrate's surface.
Key Characteristics of the Evaporation Method
Understanding the defining traits of this process helps clarify where it is most effectively applied.
A "Line-of-Sight" Process
This is the most critical characteristic of vacuum evaporation. The evaporated material travels in straight lines from the source. Consequently, only the surfaces of the substrate with a direct, unobstructed view of the source will be coated.
High Deposition Rates
Compared to other PVD methods like sputtering, vacuum evaporation can deposit films very quickly. This makes it efficient for high-volume production of certain components.
Low-Energy Deposition
The atoms arriving at the substrate have relatively low kinetic energy. They are driven by thermal energy, not by high-velocity impact. This results in a gentler deposition process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single coating method is perfect for every application. The value of vacuum evaporation is best understood by examining its inherent advantages and limitations, especially when compared to a method like sputtering.
Advantage: Minimal Substrate Damage
Because the depositing atoms have low energy, they cause very little surface damage to the substrate. This is a significant advantage when coating delicate materials used in sensitive optical or electronic applications.
Advantage: High Film Purity
The high-vacuum environment ensures that very few impurities from residual gases are incorporated into the film, resulting in excellent material purity.
Limitation: Poor "Step Coverage"
The line-of-sight nature means vacuum evaporation is poor at coating complex geometries with trenches, steps, or hidden surfaces. The coating will be thick on surfaces facing the source and thin or non-existent on others.
Limitation: Film Adhesion and Density
The low energy of the arriving particles can sometimes result in films that are less dense and have weaker adhesion to the substrate compared to films created by high-energy processes like sputtering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct PVD process requires matching the method's characteristics to your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is coating a simple, flat surface with high speed and purity: Vacuum evaporation is an excellent, efficient choice for applications like optical lenses or solar cells.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex, three-dimensional object uniformly: You should investigate alternative PVD methods like sputtering, which provide superior coverage on intricate shapes.
- If your primary focus is maximizing film durability, density, and adhesion: Sputtering is often the superior choice, as the higher-energy particle bombardment creates a denser, more strongly bonded coating.
Ultimately, recognizing the simple, direct nature of vacuum evaporation is the key to leveraging its speed and purity for the right applications.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal evaporation of a source material in a high vacuum, followed by condensation on a substrate. |
| Key Trait | Line-of-sight deposition; excellent for surfaces with direct view of the source. |
| Best For | High-purity coatings on simple, flat surfaces (e.g., optical lenses, solar cells). |
| Limitation | Poor coverage on complex, 3D shapes due to its line-of-sight nature. |
Ready to apply the right PVD technique for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment, including vacuum evaporation and sputtering systems, to meet your specific coating requirements. Whether you need high-purity films for optics or durable coatings for complex components, our experts can help you select the perfect solution.
Contact our team today to discuss how our PVD systems can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and achieve your project goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films



















