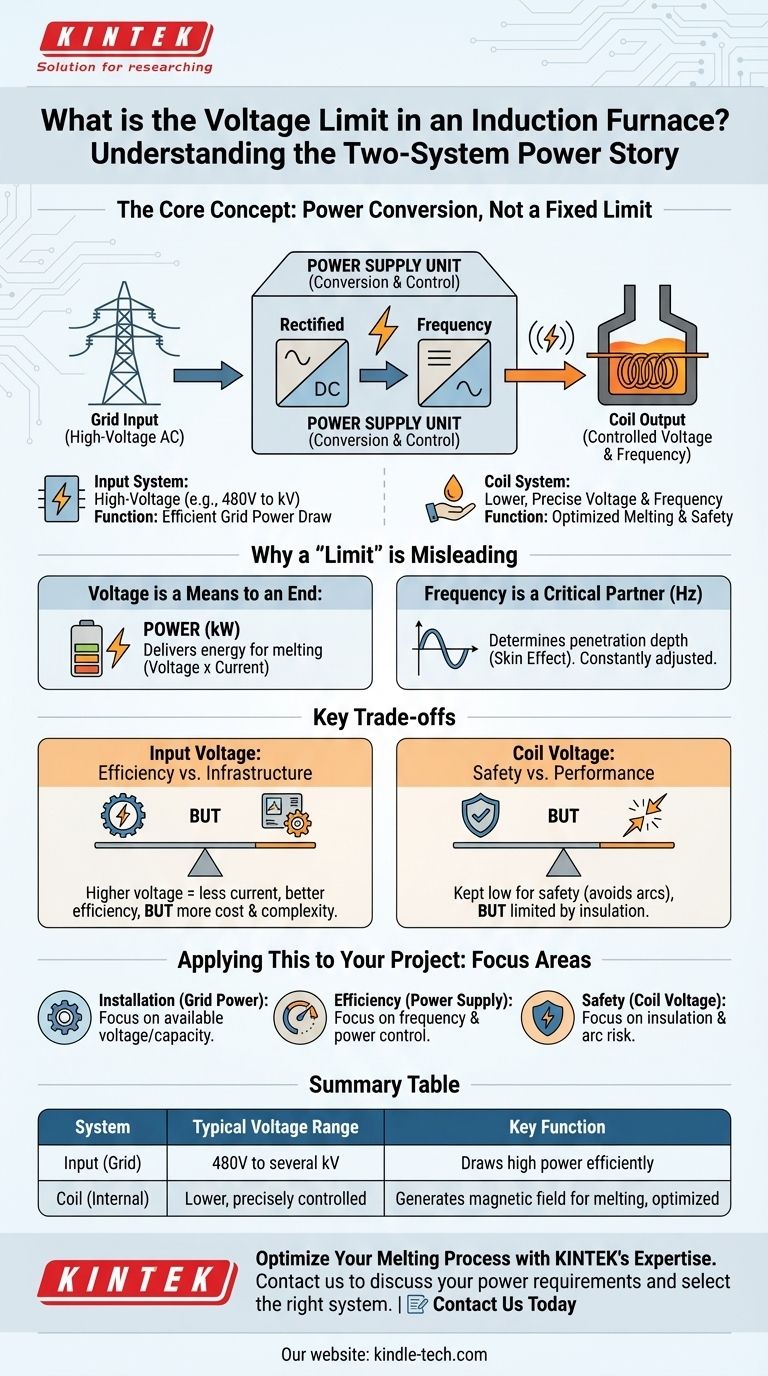
There is no single, universal voltage limit for an induction furnace. The critical voltage is not one number, but a story of two separate systems. The furnace receives high-voltage power from the electrical grid, but its internal power supply converts this into a different, precisely controlled voltage and frequency at the induction coil to perform the melting.
The concept of a voltage "limit" in an induction furnace is misleading. The crucial factor is the power conversion process: transforming high-voltage grid power into the specific voltage and frequency required at the coil to efficiently generate the intense magnetic field for melting.
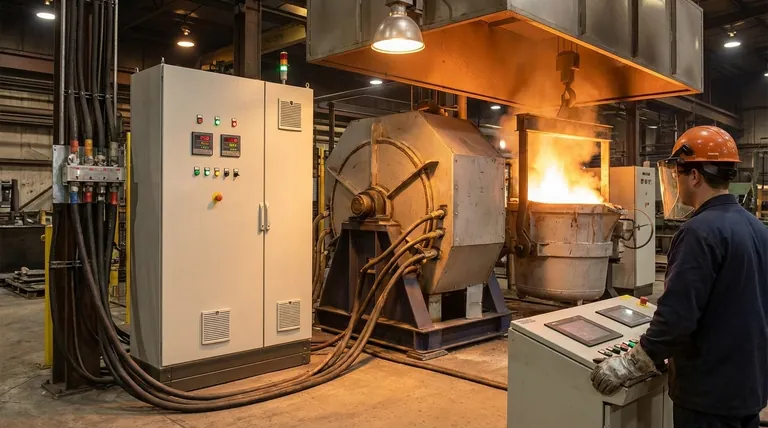

The Two Electrical Systems of an Induction Furnace
To understand the voltage, you must first understand that a modern induction furnace operates with two distinct electrical systems. This separation is fundamental to its design and operation.
The High-Voltage Input System
The furnace's power supply unit connects to a main electrical line from the grid. This is typically a three-phase, high-voltage supply.
The actual voltage level can vary significantly based on the furnace's size and the industrial site's infrastructure, often ranging from 480 volts for smaller units to several thousand volts (kilovolts) for large industrial smelters. This system is designed to draw a large amount of power efficiently from the grid.
The Coil Power System
This is the "business end" of the furnace. The power supply takes the high-voltage input and converts it into the power used by the induction coil.
The voltage at the coil itself is often significantly different from the input voltage. The power supply's primary job is to act as a sophisticated translator, changing both the voltage and, critically, the frequency of the electricity to optimize the melting process.
The Role of the Power Supply
The power supply is the heart of the furnace. It is not just a simple transformer. It's a complex piece of power electronics that rectifies the incoming AC power to DC and then inverts it back to a new, single-phase AC current.
This process gives operators precise control over the two factors that determine heating performance: power (kilowatts) and operating frequency (hertz).
Why a Fixed "Limit" is Misleading
Focusing on a single voltage number misses the point of how an induction furnace works. The voltage is a variable that is managed to achieve a specific outcome, not a fixed operational limit.
Voltage is a Means to an End: Power
The ultimate goal is to deliver a specific amount of power (energy per second) into the metal charge. Power is a product of voltage and current.
The power supply adjusts voltage and current to deliver the kilowatts needed to melt the metal in a desired timeframe. The "limit" is therefore defined by the power capacity of the supply unit, not a static voltage.
Frequency is a Critical Partner to Voltage
The frequency of the current in the coil is just as important as the voltage. Frequency determines the "skin effect," or how deeply the induced eddy currents penetrate the metal.
Lower frequencies are used for melting larger pieces of metal, while higher frequencies are more efficient for smaller pieces or holding metal at temperature. The power supply constantly adjusts both voltage and frequency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The voltages chosen for the input and the coil are the result of critical engineering trade-offs between efficiency, safety, and cost.
Input Voltage: Efficiency vs. Infrastructure
Using a higher input voltage from the grid allows the furnace to draw the same amount of power with less current. Lower current reduces resistive heat losses in the supply lines, increasing overall electrical efficiency.
The trade-off is cost and complexity. High-voltage switchgear, transformers, and cabling are more expensive and require more stringent safety protocols.
Coil Voltage: Safety vs. Performance
The voltage across the induction coil is kept as low as is practical to achieve the desired power. This minimizes the risk of a dangerous electrical arc between the coil and the metal charge or the furnace shell.
An arc can cause catastrophic damage to the coil and refractory lining. Therefore, the physical insulation and spacing within the furnace body impose a practical upper limit on the coil's operating voltage.
Applying This to Your Project
Your focus should be on the furnace as a complete power system, not a single voltage rating.
- If your primary focus is specifying a new furnace installation: Concentrate on the available grid power (voltage and capacity), as this will determine the required transformer and power supply unit.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Pay attention to the power supply's ability to control frequency and power output, as this has a greater impact on melt times and energy use than a raw voltage number.
- If your primary focus is safety and maintenance: Understand that the coil's voltage is a critical design parameter that dictates insulation requirements and the risk of potentially catastrophic electrical faults.
Ultimately, viewing the furnace as a complete power conversion system is the key to its effective and safe operation.
Summary Table:
| System | Typical Voltage Range | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Input (Grid) | 480V to several kV | Draws high power efficiently from the grid |
| Coil (Internal) | Lower, precisely controlled | Generates magnetic field for melting, optimized for safety and performance |
Optimize Your Melting Process with the Right Power System
Understanding the interplay between voltage, frequency, and power is key to efficient and safe furnace operation. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including advanced melting systems.
We can help you select the right induction furnace for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance, energy efficiency, and safety. Contact us today to discuss your project's power requirements and let our expertise work for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















