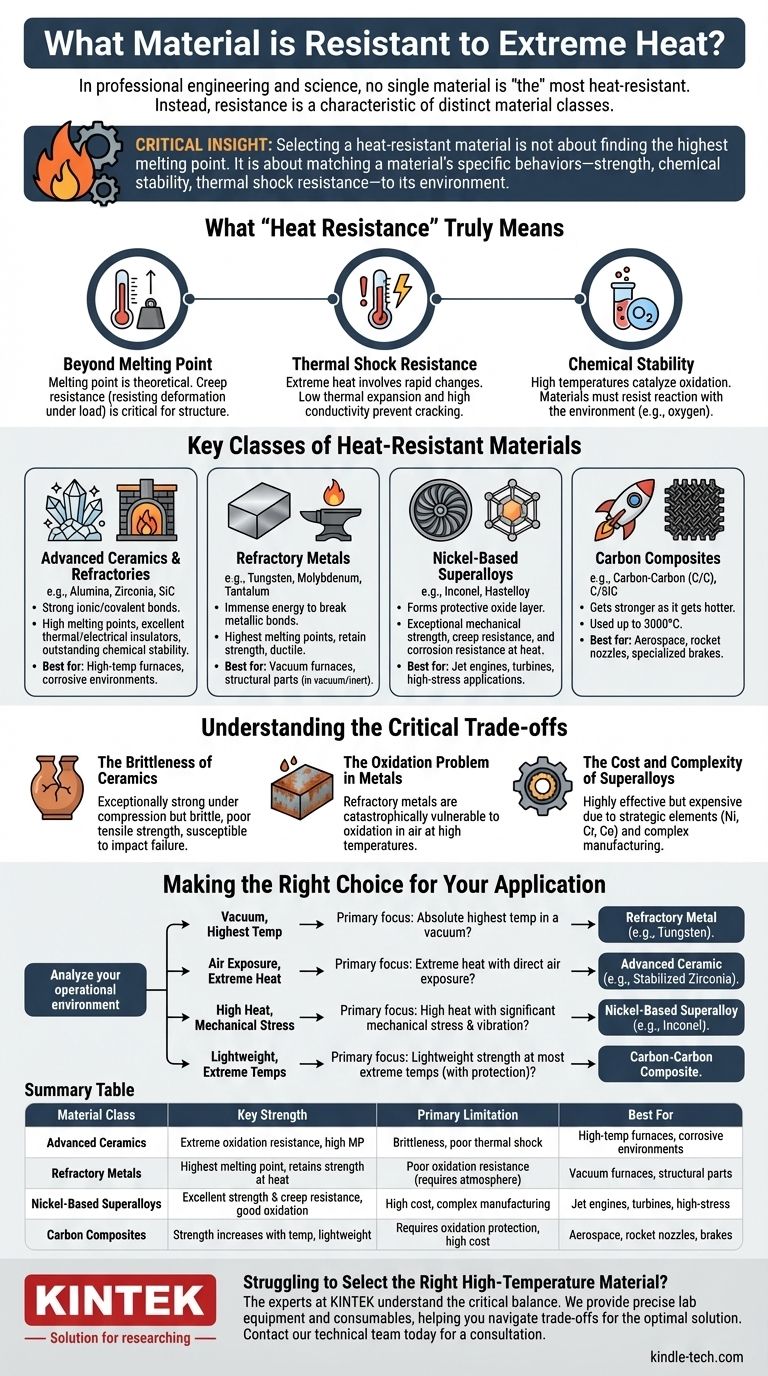
In professional engineering and science, no single material is "the" most heat-resistant. Instead, resistance to extreme heat is a characteristic of several distinct material classes, each with unique properties. The most common and effective are advanced ceramics like zirconia, refractory metals like tungsten, and nickel-based superalloys like Inconel.
The most critical insight is that selecting a heat-resistant material is not about finding the highest melting point. It is about matching a material's specific high-temperature behaviors—its strength, chemical stability, and thermal shock resistance—to the precise demands of its intended environment.

What "Heat Resistance" Truly Means
To choose the right material, you must look beyond a simple temperature rating. True heat resistance is a combination of multiple properties that dictate how a material behaves under thermal stress.
Beyond Melting Point
A material's melting point is its theoretical upper limit, but its practical limit is often much lower.
Creep resistance, or the ability to resist deformation under a constant load at high temperatures, is often the more critical factor in structural applications.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Extreme heat rarely occurs in a vacuum; it involves rapid temperature changes.
Thermal shock is the stress induced in a material when different parts expand or contract at different rates. Materials with low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity generally perform better.
Chemical Stability
High temperatures act as a catalyst for chemical reactions, most notably oxidation.
A material that performs exceptionally well in a vacuum or inert atmosphere may fail catastrophically in the presence of oxygen. Oxidation resistance is a crucial selection criterion for real-world applications.
Key Classes of Heat-Resistant Materials
Materials that operate at extreme temperatures are typically found in three primary categories, each with a different underlying mechanism for its resistance.
Advanced Ceramics & Refractories
These materials (e.g., Alumina, Zirconia, Silicon Carbide) are defined by their incredibly strong ionic and covalent bonds.
They possess some of the highest melting points and are excellent thermal and electrical insulators. Their chemical stability, particularly against oxidation, is outstanding.
Refractory Metals
This group includes tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum, and niobium. Their high melting points are due to the immense energy required to break the metallic bonds in their crystal structures.
These metals retain significant strength at temperatures where steels and superalloys would fail. They are also ductile, unlike ceramics.
Nickel-Based Superalloys
Superalloys like Inconel and Hastelloy are metallic alloys designed specifically for high-stress, high-temperature, and highly corrosive environments.
They don't have the highest melting points, but they form a stable, protective oxide layer on their surface that allows them to maintain exceptional mechanical strength and resist corrosion at elevated temperatures.
Carbon Composites
Materials like Carbon-Carbon (C/C) or Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Silicon Carbide (C/SiC) are in a class of their own.
C/C uniquely gets stronger as it gets hotter. It is used in applications like rocket nozzles and high-performance brakes, where temperatures can exceed 3000°C.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
No material is perfect. The extraordinary capabilities of heat-resistant materials come with significant limitations that you must factor into your design and selection process.
The Brittleness of Ceramics
While exceptionally strong under compression, ceramics are brittle and have poor tensile strength.
They are highly susceptible to catastrophic failure from mechanical impact or internal defects, making them unsuitable for applications requiring toughness.
The Oxidation Problem in Metals
The primary weakness of refractory metals is their catastrophic vulnerability to oxidation at high temperatures.
Tungsten and molybdenum will literally burn away in air at temperatures far below their melting points. They must be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere, or be protected with specialized coatings.
The Cost and Complexity of Superalloys
Superalloys are highly effective but are composed of expensive and often strategic elements like nickel, chromium, and cobalt.
Their manufacturing and machining processes are difficult and costly, reserving their use for critical applications like jet engine turbines and nuclear reactors where performance justifies the expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection must be driven by a clear understanding of the operational environment. Analyze the combination of heat, mechanical load, and chemical exposure your component will face.
- If your primary focus is the absolute highest temperature in a vacuum: A refractory metal like tungsten is the best choice due to its unmatched melting point.
- If your focus is extreme heat combined with direct exposure to air: An advanced ceramic like stabilized zirconia offers superior oxidation resistance and stability.
- If your focus is high heat combined with significant mechanical stress and vibration: A nickel-based superalloy like Inconel provides the necessary strength, creep resistance, and fatigue life.
- If your focus is lightweight strength at the most extreme temperatures (with protection): A carbon-carbon composite is necessary for specialized aerospace or braking applications.
Ultimately, choosing the right material is an exercise in balancing ideal properties against real-world constraints and trade-offs.
Summary Table:
| Material Class | Key Strength | Primary Limitation | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Ceramics | Extreme oxidation resistance, high melting point | Brittleness, poor thermal shock resistance | High-temperature furnaces, corrosive environments |
| Refractory Metals | Highest melting point, retains strength at heat | Poor oxidation resistance (requires protective atmosphere) | Vacuum furnaces, high-temperature structural parts |
| Nickel-Based Superalloys | Excellent strength & creep resistance, good oxidation | High cost, complex manufacturing | Jet engines, turbines, high-stress applications |
| Carbon Composites | Strength increases with temperature, very lightweight | Requires oxidation protection, high cost | Aerospace, rocket nozzles, specialized brakes |
Struggling to Select the Right High-Temperature Material for Your Lab?
Choosing the wrong material can lead to equipment failure, costly downtime, and compromised results. The experts at KINTEK understand the critical balance between temperature, mechanical stress, and chemical environment.
We specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables your research demands. Whether you need components made from advanced ceramics, refractory metals, or superalloys, we can help you navigate the trade-offs to find the optimal solution for your specific application.
Let our expertise guide you to a reliable, high-performance solution. Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is sputtering method? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Coating Technology
- What are the disadvantages of wiped film molecular still? High Cost, Complexity & Separation Limits
- What materials are used in the forging process? Choose the Right Metal for Strength & Performance
- What is direct current pulse magnetron sputtering? Achieve Superior Thin Film Deposition for Insulating Materials
- How does a mechanical propulsion system ensure HEA-NP quality? Master Fast Moving Bed Pyrolysis with Precision Control
- How many types of physical vapor deposition are there? The 4 Main PVD Processes Explained
- What are the methods used in sample preparation? A Guide to Extraction, Cleanup, and Concentration
- Why is a laboratory drying oven required for LDH powders? Achieve Precision and Structural Integrity



















