Brazing relies on a carefully selected combination of materials, primarily a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the parts being joined. Common filler metals include aluminum-silicon alloys, copper-based alloys (like brass and bronze), silver alloys, and nickel-based amorphous foils. These work in conjunction with the base metals being joined and, often, a chemical flux that cleans the surfaces to ensure a strong bond.
The core principle of brazing is the interaction between three distinct materials: the base metals being joined, a filler metal with a lower melting point, and a flux that prepares the surfaces for bonding. The success of the entire process hinges on the correct selection and compatibility of these three components.
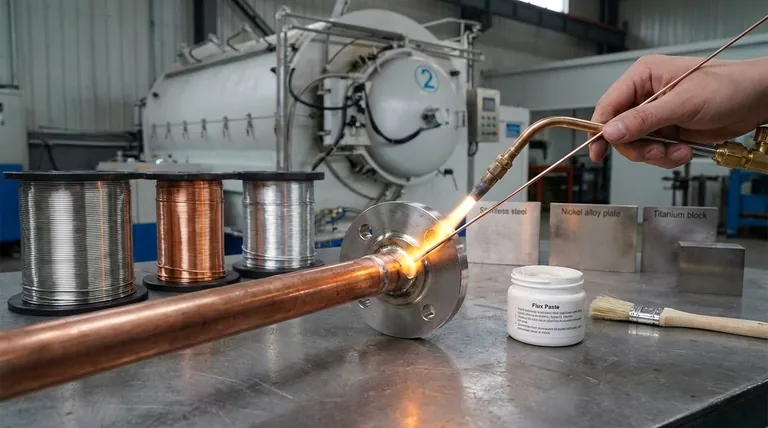

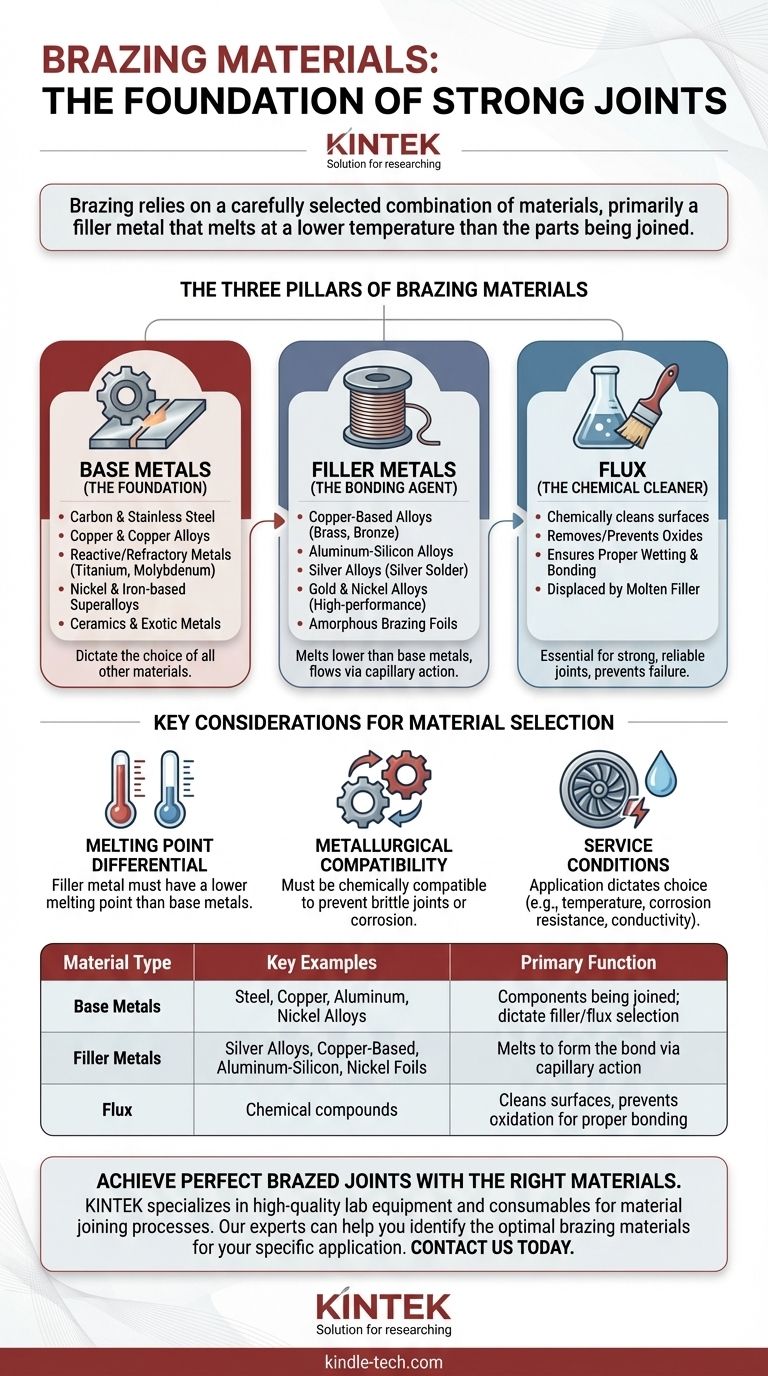
The Three Pillars of Brazing Materials
To fully understand the materials used in brazing, it's essential to look beyond just the filler wire. The process is a system involving the parts themselves, the bonding agent, and a cleaning agent.
Base Metals: The Foundation
The base metals are the components you are trying to join together. The choice of all other brazing materials is dictated by the properties of these metals.
Brazing is exceptionally versatile and can be used to join a wide range of materials, from common steels to highly specialized alloys used in demanding industries like aerospace and defense.
Examples of base metals frequently joined by brazing include:
- Carbon steel, cast iron, and stainless steel
- Copper and copper alloys
- Reactive and refractory metals like titanium, zirconium, and molybdenum
- Nickel and iron-based superalloys
- Ceramics and exotic metals like beryllium
Filler Metals: The Bonding Agent
The filler metal is the heart of the brazing process. It is designed to melt at a temperature lower than the base metals, allowing it to be drawn into the tight-fitting joint by capillary action before solidifying to form the bond.
The composition of the filler metal determines the final joint's strength, conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
Common Filler Metal Families:
- Copper-Based Alloys: Widely used for joining steels, cast iron, and copper alloys. These fillers, including copper-zinc (brass) and copper-tin (bronze), offer excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
- Aluminum-Silicon Alloys: The standard choice for brazing aluminum components, common in automotive and HVAC applications.
- Silver Alloys: Often referred to as "silver solder," these fillers offer high strength and ductility and are used for joining a wide variety of metals.
- Gold and Nickel Alloys: Used in high-performance applications where extreme corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, or specific metallurgical compatibility is required, such as in aerospace or medical devices.
- Amorphous Brazing Foils: Modern materials made of elements like nickel, iron, boron, and silicon. These foils provide precise, uniform joints and are common in advanced engineering sectors.
Flux: The Chemical Cleaner
Flux is the unsung hero of many brazing operations. Its role is to chemically clean the base and filler metals by removing and preventing the formation of surface oxides during heating.
Without flux, these oxides would prevent the filler metal from wetting and bonding with the base metals, resulting in a weak or failed joint. The flux melts before the filler metal, preparing the surface and is then displaced by the molten filler as it flows into the joint.
Key Considerations for Material Selection
Choosing the right combination of materials is not arbitrary; it's a technical decision based on metallurgy and the intended application of the final component.
Melting Point Differential
The most fundamental rule of brazing is that the filler metal's melting point must be lower than that of the base metals. This ensures the components being joined do not melt or deform during the process.
Metallurgical Compatibility
The filler metal must be chemically and metallurgically compatible with the base metals. An incompatible combination can lead to brittle joints, corrosion, or other forms of premature failure.
Service Conditions
The final application dictates material choice. A hydraulic fitting for a tractor requires different properties than a turbine blade for a jet engine. Factors like operating temperature, exposure to corrosive elements, and required electrical conductivity must guide the selection of the filler metal.
Selecting Materials for Your Application
Your choice of materials should be driven by the base metal you are joining and the performance requirements of the final assembly.
- If your primary focus is general fabrication of steel or copper: Copper-based fillers offer a cost-effective and reliable solution with good strength and conductivity.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum components: An aluminum-silicon filler metal, paired with the appropriate flux, is the standard and correct choice.
- If your primary focus is high-performance or specialized applications: Nickel, silver, or gold-based alloys provide the superior strength, temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance required for aerospace, defense, or medical components.
Understanding the distinct roles of the base metal, filler metal, and flux is the key to creating strong, reliable brazed joints.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Base Metals | Steel, Copper, Aluminum, Nickel Alloys | Components being joined; dictate filler/flux selection |
| Filler Metals | Silver Alloys, Copper-Based, Aluminum-Silicon, Nickel Foils | Melts to form the bond via capillary action |
| Flux | Chemical compounds (various formulations) | Cleans surfaces, prevents oxidation for proper bonding |
Achieve perfect brazed joints with the right materials. Selecting the correct combination of base metal, filler alloy, and flux is critical for joint strength and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for material joining processes. Our experts can help you identify the optimal brazing materials for your specific application, whether you're working with common steels or advanced alloys. Contact us today to discuss your project needs and ensure a reliable, high-strength bond. #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Vacuum Cold Trap Chiller Indirect Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance



















