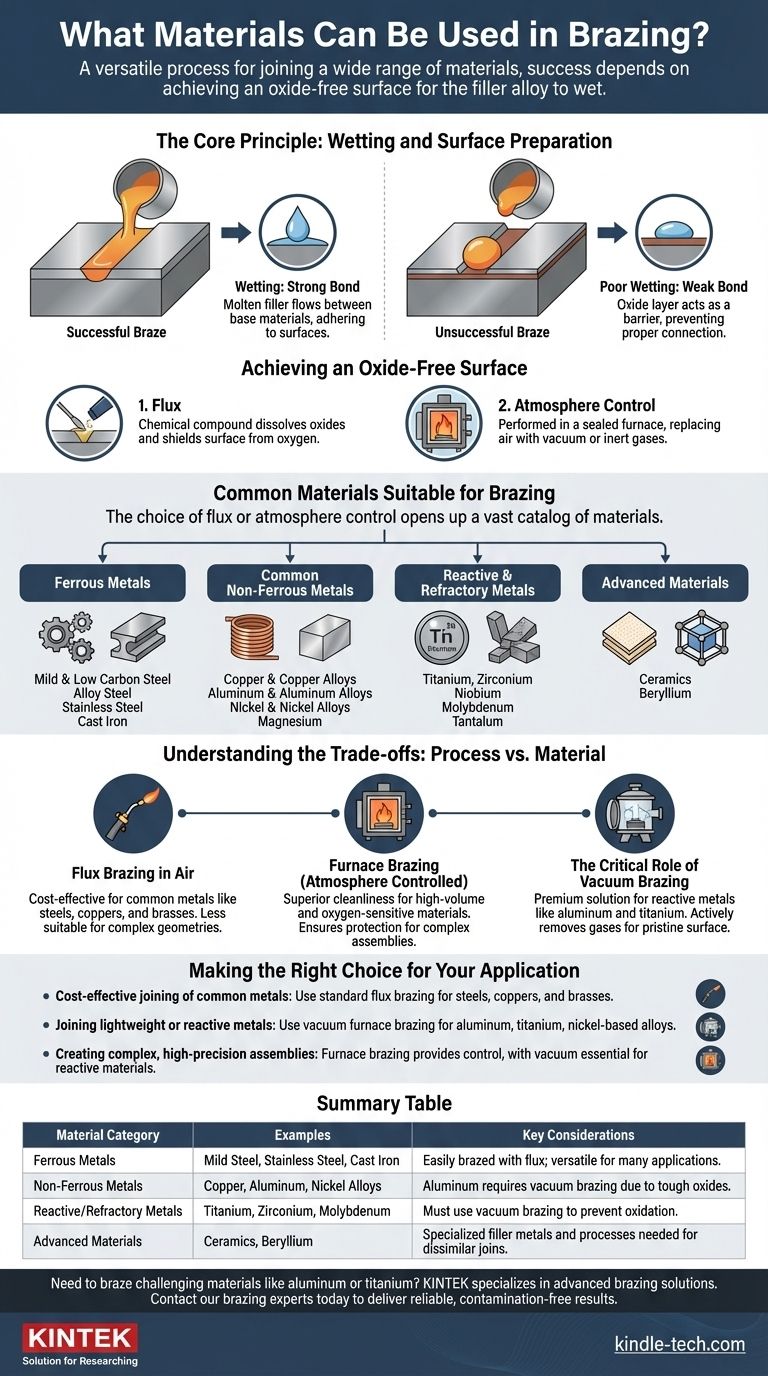
At its core, brazing is a remarkably versatile process capable of joining an extensive range of materials. Nearly any metal—from common steels and coppers to advanced alloys and reactive metals—can be brazed, as can certain ceramics. The success of the joint depends not on the material itself, but on the ability of a molten filler alloy to "wet" and bond to the surfaces being joined.
The fundamental requirement for a successful braze joint is not the specific material, but achieving a clean, oxide-free surface. If the filler metal can wet the base materials, a strong, permanent bond can be formed.
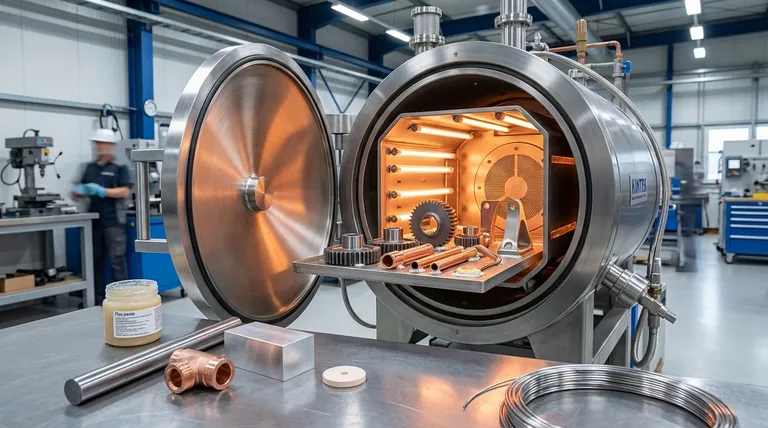

The Core Principle: Wetting and Surface Preparation
Brazing works by melting a filler metal that flows between two closely-fitted base materials. For this to happen, the molten filler must be able to spread across the base material surfaces in a process known as wetting.
What is "Wetting"?
Think of wetting like water spreading on a clean glass surface, rather than beading up on a waxed car. For a strong braze, the molten filler alloy must flow smoothly into the joint, adhering to the base materials.
Poor wetting results in a weak, incomplete bond, as the filler metal fails to properly connect the two pieces.
The Barrier: Surface Oxides
Almost all metals form a thin layer of oxide when exposed to air. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the molten filler metal from making direct contact with the pure base material and blocking the wetting process.
A successful braze is impossible without first removing this oxide layer and preventing it from re-forming during the heating cycle.
Achieving an Oxide-Free Surface
Two primary methods are used to manage oxides:
- Flux: A chemical compound applied to the joint area. When heated, the flux melts, dissolves existing oxides, and shields the surface from oxygen, allowing the filler metal to wet the clean material underneath.
- Atmosphere Control: Performed inside a sealed furnace. By replacing the air with a specific atmosphere—such as a vacuum or inert gases—oxygen is removed, preventing oxides from forming in the first place. This is essential for materials that form very tough or rapid-forming oxides.
Common Materials Suitable for Brazing
The choice of flux or atmosphere control opens up a vast catalog of materials that can be reliably joined.
Ferrous Metals
These are among the most commonly brazed materials due to their wide use in manufacturing. They include:
- Mild and Low Carbon Steel
- Alloy Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Cast Iron
Common Non-Ferrous Metals
Copper and aluminum alloys are frequently brazed for their excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
- Copper and Copper Alloys (Brass, Bronze)
- Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys
- Nickel and Nickel Alloys (Inconel)
- Magnesium
Reactive and Refractory Metals
These advanced materials require more sophisticated process control, typically vacuum brazing, to manage their high reactivity with oxygen.
- Titanium
- Zirconium
- Niobium
- Molybdenum
- Tantalum
Advanced Materials
Brazing is not limited to metals. With the correct filler alloy and process, it is possible to join dissimilar materials.
- Ceramics: Can be brazed to themselves or to metals.
- Beryllium: A specialized, high-performance material joined with brazing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process vs. Material
The right brazing process is dictated by the base material's properties. This is a critical decision with direct trade-offs in complexity and cost.
Flux Brazing in Air
This is the most straightforward method, often done with a torch. It is ideal for robust, common materials like steels, coppers, and brasses whose oxides are easily removed by standard fluxes. It is cost-effective but less suitable for complex geometries or reactive metals.
Furnace Brazing (Atmosphere Controlled)
This method provides superior cleanliness and is essential for high-volume production and for materials sensitive to oxygen. By controlling the atmosphere, it ensures every part of a complex assembly is protected from oxidation.
The Critical Role of Vacuum Brazing
Vacuum brazing is the premium solution for the most demanding applications. It is non-negotiable for reactive metals like aluminum and titanium, whose aggressive oxide layers cannot be managed by flux. The vacuum actively removes all gases, ensuring a pristine surface for perfect wetting.
This process is chosen for high-value components, such as aerospace parts, precision assemblies, and complex geometries where joint failure is not an option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material choice is inseparable from the brazing process you intend to use. Base your decision on the final requirements of the component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective joining of common metals: Use standard flux brazing for steels, coppers, and brasses, as it offers a strong bond without the need for specialized equipment.
- If your primary focus is joining lightweight or reactive metals: You must use vacuum furnace brazing for materials like aluminum, titanium, or nickel-based superalloys to ensure a contamination-free joint.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, high-precision assemblies: Furnace brazing provides the control needed for intricate parts, with a vacuum process being essential if any of the materials are reactive.
Understanding the relationship between the material, its surface chemistry, and the brazing process is the key to creating a reliable and effective joint.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Examples | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Mild Steel, Stainless Steel, Cast Iron | Easily brazed with flux; versatile for many applications. |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Copper, Aluminum, Nickel Alloys | Aluminum requires vacuum brazing due to tough oxides. |
| Reactive/Refractory Metals | Titanium, Zirconium, Molybdenum | Must use vacuum brazing to prevent oxidation. |
| Advanced Materials | Ceramics, Beryllium | Specialized filler metals and processes needed for dissimilar joins. |
Need to braze challenging materials like aluminum or titanium? KINTEK specializes in advanced brazing solutions, including vacuum furnace brazing, to ensure oxide-free, high-strength joints for your most critical components. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables means we understand the precision required for aerospace, medical, and R&D applications. Contact our brazing experts today to discuss how we can enhance your joining process and deliver reliable, contamination-free results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
People Also Ask
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy



















