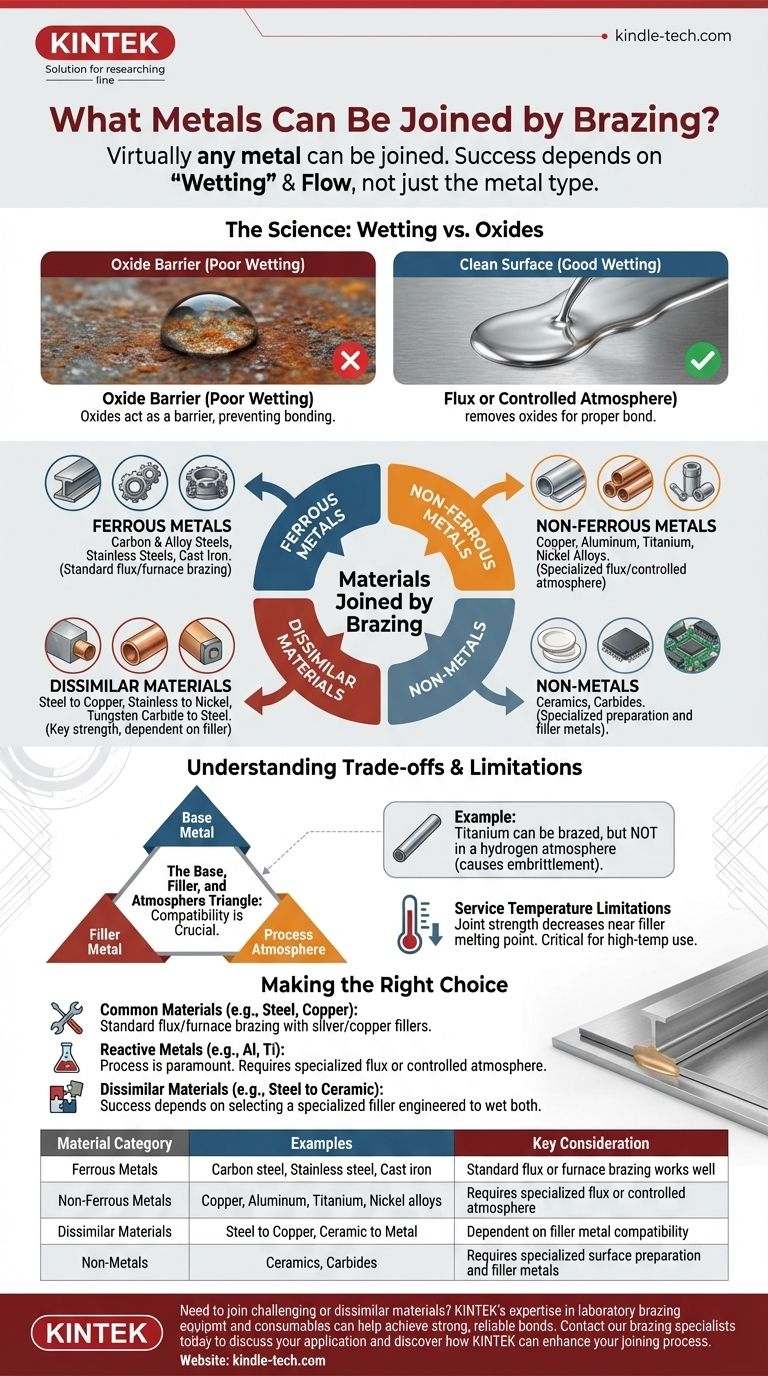
Virtually any metal can be joined by brazing, provided the correct process and filler material are used. This includes common materials like steels, stainless steels, aluminum, and copper, as well as more specialized metals like titanium, nickel-based superalloys, and even non-metals like ceramics. The success of the joint depends less on the specific metal and more on the underlying chemical principles of the brazing process.
The critical factor in brazing is not the metal itself, but the ability of the liquid braze filler to "wet" and flow across the surfaces being joined. This requires a chemically clean, oxide-free surface, which is achieved through the use of a flux or a controlled furnace atmosphere.

The Fundamental Principle: It's About "Wetting," Not a List of Metals
Brazing is a process of adhesion and metallurgical bonding. To understand which materials can be joined, you must first understand the core requirement for a successful bond.
What is Wetting?
Wetting describes the ability of a liquid to spread across a solid surface. Think of water beading up on a waxy car finish (poor wetting) versus spreading out evenly on a clean glass pane (good wetting). For a strong braze joint, the molten filler metal must exhibit good wetting on the base metals.
The Role of Oxides: The Primary Barrier
Almost all metals form a thin, invisible layer of oxide on their surface when exposed to air. This oxide layer acts like the wax on the car, preventing the molten filler metal from making direct contact with the pure base metal beneath it. This prevents wetting and a proper bond.
How Brazing Overcomes Oxides
The entire brazing process is designed to overcome this oxide barrier in one of two ways:
- Flux: A chemical compound applied to the joint area that melts before the braze filler. The molten flux dissolves existing oxides and shields the surface from forming new ones, allowing the filler metal to wet the clean metal.
- Controlled Atmosphere: In furnace brazing, the parts are heated in a controlled environment, such as a vacuum or a specific gas (like hydrogen or nitrogen). This atmosphere actively removes oxides or prevents them from forming in the first place.
Common Materials Joined by Brazing
Because the process is designed to prepare the surface, brazing is applicable to an exceptionally broad range of materials, often in combinations that are impossible to weld.
Ferrous Metals
This category includes the most common engineering materials. The process is extremely effective for joining carbon steels, alloy steels, stainless steels, and cast iron.
Non-Ferrous Metals
Brazing is widely used for non-ferrous applications. This includes copper and its alloys (like brass and bronze), nickel and its high-performance alloys, aluminum, titanium, and magnesium.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
This is a key strength of brazing. Because the base metals are not melted, you can easily join materials with vastly different melting points. Common examples include joining steel to copper, stainless steel to nickel alloys, or tungsten carbide to steel for cutting tools.
Non-Metals
With the correct filler metal and surface preparation, brazing can even be used to join metals to non-metals. Ceramics are routinely brazed to metals for electronic and high-wear applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, brazing is not a universal solution. Success depends on a compatible system of the base metal, filler metal, and process atmosphere.
The Base, Filler, and Atmosphere Triangle
These three components must be compatible. For example, the references note that titanium alloys can be brazed, but they cannot be brazed in a hydrogen atmosphere, which would cause embrittlement. This highlights that the process must be matched to the material.
Filler Metal Selection is Critical
The filler metal must have two key properties. First, its melting point must be lower than the base metals being joined. Second, it must be chemically capable of wetting the specific base metals in the joint. This is why different fillers exist, such as aluminum-silicon for aluminum parts and silver-based alloys for steels and copper.
Service Temperature Limitations
A brazed joint's mechanical strength decreases as the service temperature approaches the filler metal's melting point. The joint will always be weaker than the base metal at elevated temperatures, a critical design consideration for high-temperature applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine your brazing strategy.
- If your primary focus is joining common materials like steel, stainless steel, or copper: Standard flux-based or simple furnace brazing with common silver or copper fillers is highly effective.
- If your primary focus is joining reactive metals like aluminum or titanium: The process is paramount; you will likely need a specialized flux or controlled atmosphere furnace brazing to manage the aggressive oxide layers.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials (e.g., steel to ceramic): Your success depends almost entirely on selecting a specialized filler metal engineered to wet both distinct surfaces.
Ultimately, brazing's versatility comes from respecting the fundamental need to create a clean, oxide-free surface for the filler metal to bond with.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Examples | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Carbon steel, Stainless steel, Cast iron | Standard flux or furnace brazing works well |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Copper, Aluminum, Titanium, Nickel alloys | Requires specialized flux or controlled atmosphere |
| Dissimilar Materials | Steel to Copper, Ceramic to Metal | Dependent on filler metal compatibility |
| Non-Metals | Ceramics, Carbides | Requires specialized surface preparation and filler metals |
Need to join challenging or dissimilar materials? KINTEK's expertise in laboratory brazing equipment and consumables can help you achieve strong, reliable bonds. Whether you're working with reactive metals like titanium and aluminum or joining metals to ceramics, our specialized furnaces and filler materials are designed for optimal wetting and joint integrity. Contact our brazing specialists today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your joining process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds



















