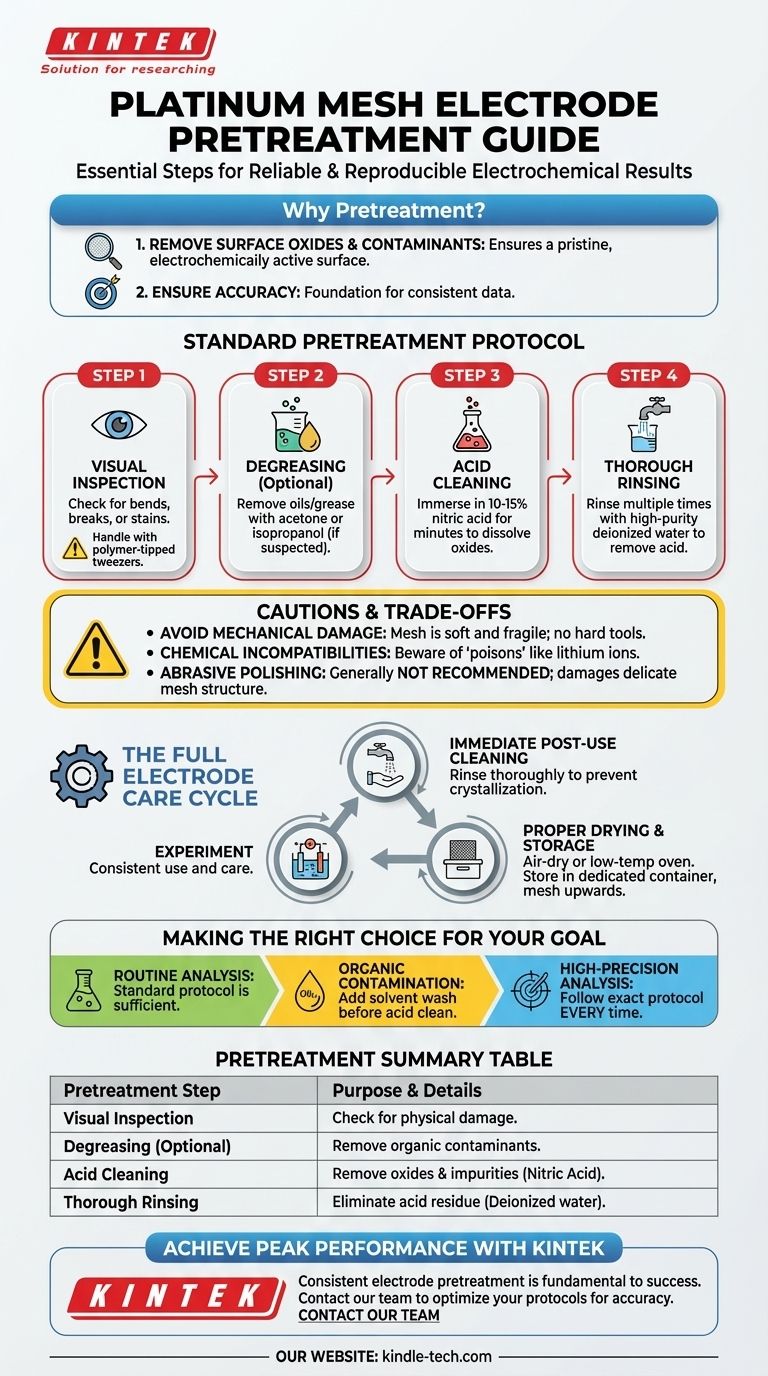
To properly pretreat a platinum mesh electrode, you should begin with a visual inspection for any physical damage. The standard chemical cleaning procedure involves soaking the electrode in a dilute acid, such as nitric acid, to remove surface oxides and impurities, followed by a thorough rinse with deionized water.
The goal of pretreatment is not a one-time cleaning, but the first step in a disciplined cycle of care. This ensures the platinum surface remains electrochemically active and free of contaminants, which is the foundation for obtaining accurate and reproducible experimental results.
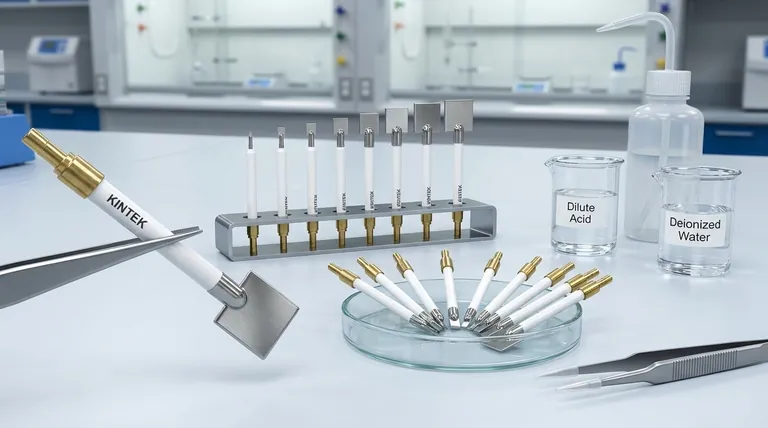

The Purpose of Pretreatment: A Pristine Surface
The primary objective of any electrode pretreatment is to create a clean, well-defined, and electrochemically active surface. A platinum electrode that appears clean to the naked eye can still have invisible layers of contamination that interfere with your experiment.
Removing Surface Oxides
Platinum naturally forms a thin layer of oxides on its surface when exposed to air. This oxide layer can alter the electrode's behavior and must be removed to expose the pure metal for consistent electrochemical reactions.
Eliminating Organic and Inorganic Contaminants
Impurities from previous experiments, handling (like oils from fingerprints), or storage can adsorb onto the platinum surface. These contaminants can block active sites, introduce unwanted side reactions, and lead to unreliable data.
Standard Pretreatment Protocol
Follow these steps in sequence to ensure your electrode is ready for use. Always handle the delicate mesh with care, preferably with polymer-tipped tweezers.
Step 1: Visual Inspection
Before any chemical treatment, carefully examine the electrode. Look for any signs of physical damage, such as bends, breaks in the mesh, or stains. A deformed electrode may produce an inconsistent electric field.
Step 2: Degreasing (If Necessary)
If you suspect contamination from oils, grease, or other organic materials, an initial cleaning with an organic solvent is recommended. Submerging the electrode in a solvent like acetone or isopropanol for a few minutes can effectively remove these films.
Step 3: Acid Cleaning
This is the most critical step for removing surface oxides and inorganic residues. Immerse the platinum mesh in a dilute solution of nitric acid (e.g., 10-15% solution) for several minutes. This will dissolve the oxide layer and other acid-soluble impurities.
Step 4: Thorough Rinsing
After the acid bath, it is absolutely essential to rinse the electrode thoroughly with high-purity deionized or distilled water. Rinse multiple times to ensure all traces of acid are removed, as any residual acid will contaminate your electrolyte.
Understanding the Cautions and Trade-offs
Proper care extends beyond the initial preparation. Understanding what to avoid is as important as knowing what to do.
Avoid Mechanical Damage at All Costs
Platinum mesh is extremely soft and fragile. Never use hard tools to handle it, and avoid letting it scrape against the sides of your glassware. Physical stress can easily deform the mesh, altering its surface area and performance.
Be Aware of Chemical Incompatibilities
Certain chemical species can permanently damage or "poison" a platinum electrode. For example, lithium ions are known to be corrosive to platinum and should be strictly avoided. Always verify the chemical compatibility of your electrolyte with platinum before starting an experiment.
The Role of Abrasive Polishing
You may see protocols for other electrode types, like platinum disks, that involve polishing with alumina powder. This is an aggressive method meant to create a mirror-smooth surface and is generally not recommended or necessary for a platinum mesh electrode. The high surface area of the mesh is its key feature, and abrasive polishing can damage its delicate structure.
The Full Electrode Care Cycle
Effective use of your electrode requires a consistent routine before, during, and after your experiment.
Immediate Post-Use Cleaning
As soon as your experiment is complete, remove the electrode from the electrolyte. Immediately rinse it thoroughly with deionized water to prevent salts and other species from crystallizing on the surface as it dries.
Proper Drying and Storage
After its final rinse, allow the electrode to air-dry completely or place it in a low-temperature oven. Store the dry electrode in a clean, dedicated container, such as its original box. Placing it with the mesh facing upwards helps prevent stress on the connection point.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is routine analysis or general-purpose electrolysis: The standard protocol of inspection, dilute acid wash, and a deionized water rinse is perfectly sufficient.
- If you suspect oil or organic contamination from handling or the sample: Add a preliminary wash with a solvent like acetone before proceeding with the acid cleaning step.
- If your primary focus is high-precision quantitative analysis: Consistency is paramount. Follow the exact same rigorous pretreatment and cleaning protocol every single time to ensure your results are comparable from one experiment to the next.
Adopting this complete cycle of care will protect your investment and ensure your platinum mesh electrode provides reliable service for years.
Summary Table:
| Pretreatment Step | Purpose | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Check for physical damage | Look for bends, breaks, or stains in the mesh. |
| Degreasing (Optional) | Remove organic contaminants | Use acetone or isopropanol if oils are suspected. |
| Acid Cleaning | Remove surface oxides & impurities | Soak in 10-15% nitric acid for several minutes. |
| Thorough Rinsing | Eliminate acid residue | Rinse multiple times with high-purity deionized water. |
Achieve Peak Performance in Your Lab
Consistent and reliable electrode pretreatment is fundamental to successful electrochemical experiments. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable platinum electrodes, designed to meet the rigorous demands of your research.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment and optimize your protocols for unparalleled accuracy and reproducibility. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Gold Disc Electrode
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
People Also Ask
- What is the expected lifespan of a platinum sheet electrode? Maximize Your Electrode's Service Life
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be operated during an experiment? Ensure Accurate and Reproducible Results
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What is the proper post-treatment procedure for a platinum sheet electrode? Ensure Long-Term Accuracy & Protect Your Investment
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be pretreated before use? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements



















