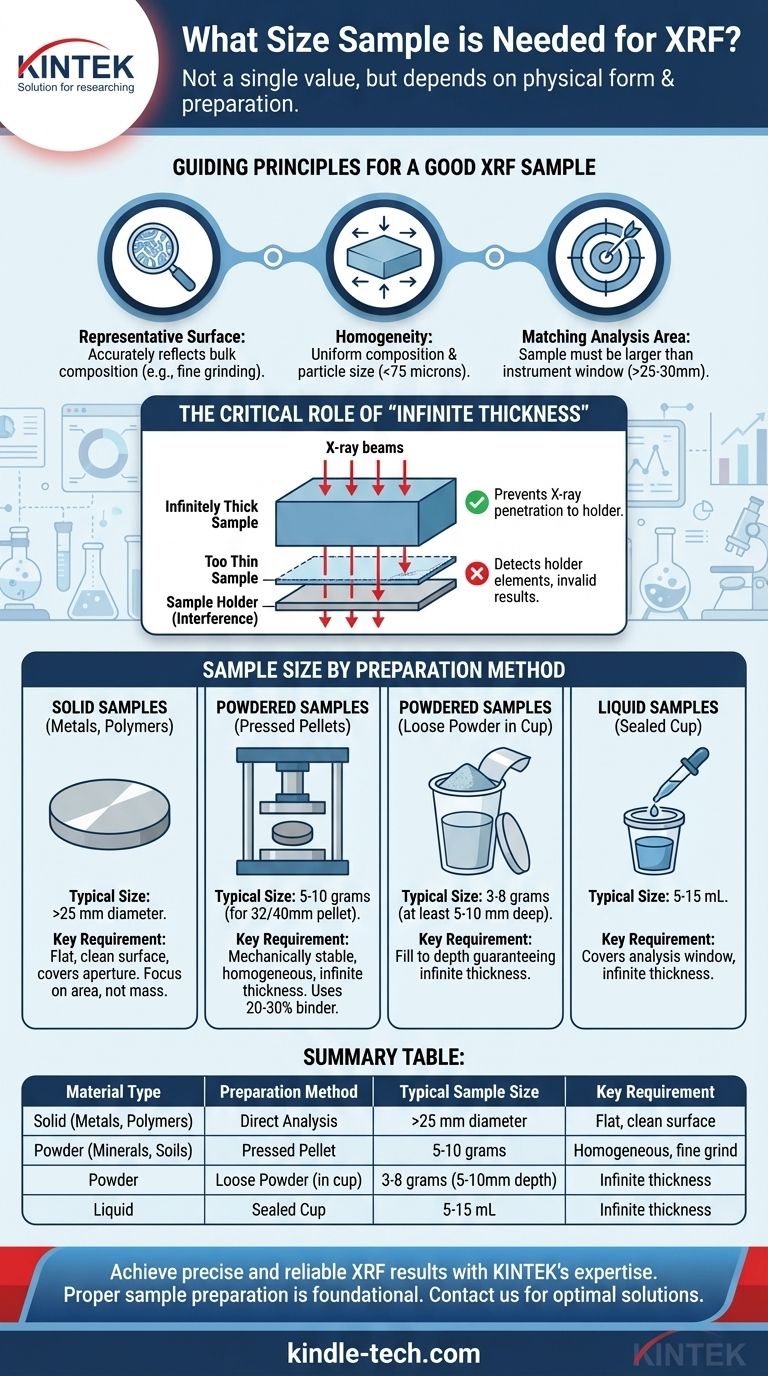
The required sample size for X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) is not a single value but depends entirely on the sample's physical form and the preparation method you choose. For solids, a flat surface area larger than the instrument's analysis window (often >25 mm diameter) is key. For powders, you typically need several grams (e.g., 5-10 g) to create a pellet or fill a sample cup to a sufficient depth.
The core principle is not about meeting a minimum weight, but about presenting a sample to the instrument that is homogeneous, representative of the bulk material, and thick enough to prevent interference from the sample holder. Your preparation technique is far more critical than the raw amount of material.

The Guiding Principles: What Makes a Good XRF Sample?
Before discussing specific quantities, it's crucial to understand the goals of sample preparation. An XRF instrument analyzes a relatively small area and depth of your material. The data from that small spot is then assumed to represent the entire sample.
The Need for a Representative Surface
The portion of the sample analyzed by the X-ray beam must accurately reflect the composition of the whole material. If you are analyzing a non-uniform alloy or a mineral, taking a sample from just one spot can be highly misleading.
Proper sampling techniques, such as grinding a larger sample into a fine powder, are essential for creating a representative average.
The Critical Role of Homogeneity
Once you have a representative sample, it must be homogeneous. This means it should be uniform in composition and particle size.
Large grains or variations in density can cause measurement errors due to shadowing effects and inconsistent X-ray absorption, leading to inaccurate results. This is why grinding materials to a fine powder (<75 microns) is a standard practice.
Matching the Instrument's Analysis Area
Every XRF spectrometer has an analysis window, or "mask," that defines the area being measured. This can range from a few millimeters to over 30 millimeters in diameter.
Your prepared sample must be larger than this window. If any part of the X-ray beam misses the sample and hits the sample holder, the results will be contaminated and invalid.
Sample Size by Preparation Method
The amount of material you need is a direct function of how you prepare it. Here are the most common scenarios.
Solid Samples (Metals, Polymers, Wafers)
For pre-formed solids, the focus is on surface area and flatness, not mass. The sample must be large enough to completely cover the analysis aperture and have a flat, clean surface to ensure consistent measurement geometry. A diameter of 30-40 mm is common.
Powdered Samples (Pressed Pellets)
This is a very common method for minerals, soils, and cements. You typically need 5 to 10 grams of finely ground powder to create a standard 32 mm or 40 mm pellet.
This amount ensures the pellet is mechanically stable and achieves "infinite thickness" (see below). To create a strong pellet, the powder is often mixed with a binder. A 20-30% binder-to-sample ratio is a good starting point for ensuring durability.
Powdered Samples (Loose Powder in a Cup)
An alternative to pellets is to use a special XRF cup with a thin film window. You need enough powder to fill the cup to a depth that guarantees infinite thickness, which is often at least 5-10 mm deep. The total mass will depend on the powder's density but is often in the range of 3-8 grams.
Liquid Samples
Liquids are analyzed in sealed sample cups. The typical volume required is between 5 and 15 mL. As with powders, the goal is to ensure the liquid is deep enough to achieve infinite thickness and completely covers the analysis window.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Sample Thickness is Key
The most common error related to sample quantity is not using enough material to achieve "infinite thickness."
The "Infinite Thickness" Concept
An XRF sample is considered "infinitely thick" when it is thick enough that the primary X-ray beam cannot penetrate through it to excite the sample holder or anything behind it.
If the sample is too thin, the instrument will detect elements from the holder, leading to significant contamination of your results. The required thickness varies depending on the material's density and the energy of the X-rays used.
The Risk of Using Too Little Sample
Using a minimal amount of sample is risky. It can lead to a thin, fragile pellet that breaks easily or a loose powder that doesn't meet the infinite thickness requirement. The result is poor data quality and non-representative analysis.
When Only a Small Sample is Available
If you have a very small or precious sample, you can still perform an analysis. You may need to use a special sample holder with a smaller aperture or rely on a micro-XRF instrument. However, you must accept that the results may not be representative of the bulk material and may have higher statistical uncertainty.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice depends on your material and your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is quick analysis of a solid object: Ensure the surface is clean, smooth, and large enough to completely cover your instrument's analysis window (typically >25mm).
- If your primary focus is high-accuracy analysis of powders: Aim for 5-10 grams to create a pressed pellet that is mechanically robust and infinitely thick.
- If your primary focus is convenience with powders or liquids: Use a sample cup and fill it with enough material (at least 5-10 mm deep or 5-15 mL for liquids) to ensure infinite thickness.
- If you have a very limited amount of material: Acknowledge the compromises and use a method designed for small spots, understanding the result reflects only that specific spot.
Ultimately, investing time in correct sample preparation is the foundation of trustworthy X-ray fluorescence analysis.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Preparation Method | Typical Sample Size | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid (Metals, Polymers) | Direct Analysis | >25 mm diameter (covers instrument window) | Flat, clean surface |
| Powder (Minerals, Soils) | Pressed Pellet | 5-10 grams | Homogeneous, fine grind (<75 microns) |
| Powder | Loose Powder (in cup) | 3-8 grams (5-10 mm depth) | Infinite thickness to avoid holder interference |
| Liquid | Sealed Cup | 5-15 mL | Infinite thickness, covers analysis window |
Achieve precise and reliable XRF results with KINTEK's expertise.
Proper sample preparation is the foundation of accurate XRF analysis. Whether you're working with solid metals, powdered minerals, or liquid samples, using the correct quantity and preparation technique is critical for data you can trust.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our team can help you select the right tools and methods to ensure your samples are homogeneous, representative, and meet the 'infinite thickness' requirement for flawless analysis.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and let our experts guide you to optimal results. Reach out via our contact form to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- What key indicators does a laboratory pressure testing machine measure? Essential T91 Alloy Steel Weld Testing
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used for PEO electrolyte membranes? Achieve Uniform, High-Performance Results
- What products are made with a hydraulic press? From Car Parts to Cosmetics, Shaping Modern Manufacturing
- How many types of presses are there? A Guide to Mechanical, Hydraulic, Servo & More
- What is the world's strongest hydraulic press? Unpacking the 80,000-Ton vs. 60,000-Ton Giants
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used for MOF-CGC pellets? Maximize Density and Encapsulation Quality
- What is the limitation of XRF? Understanding the Key Constraints for Accurate Analysis
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of a cubic press compared to a belt press? Choose the Best Synthetic Tool



















