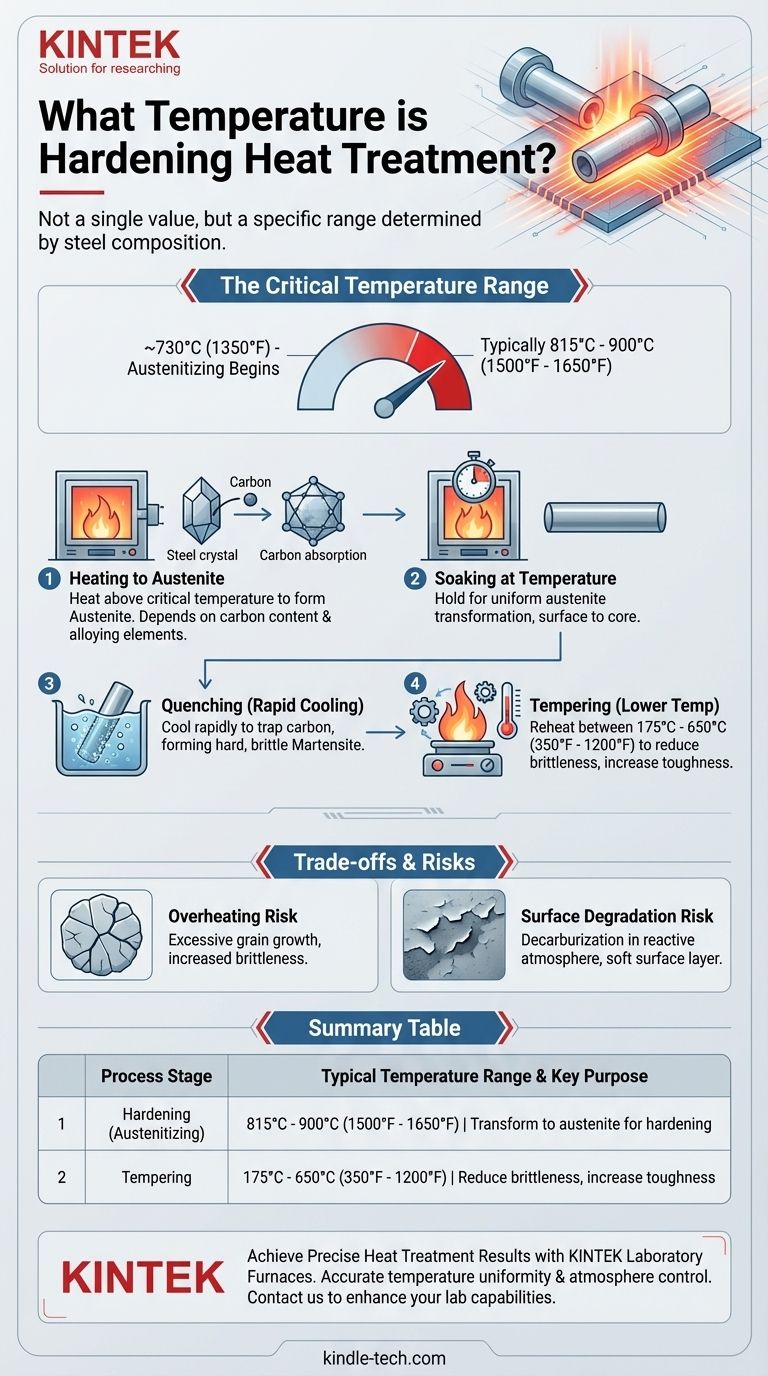
The temperature for hardening heat treatment is not a single value but a specific range determined by the steel's composition. For most common carbon and alloy steels, this process, known as austenitizing, requires heating to a temperature typically above 730°C (1350°F) to induce a critical internal phase transformation. The exact temperature is crucial for dissolving carbon into the iron structure, which is the foundational step for achieving hardness.
The goal of hardening is not simply to heat the metal, but to heat it to a precise "critical temperature." This specific temperature transforms the steel's internal crystal structure into a state called austenite, which is the necessary prerequisite for creating a hard material upon rapid cooling.

The Role of Critical Temperature in Hardening
The entire hardening process hinges on reaching and maintaining the correct temperature. This target temperature is directly linked to the steel's chemical makeup and the structural changes required to increase its hardness and strength.
The Austenitic Phase Transformation
The primary purpose of heating is to transform the steel's microstructure into austenite. Austenite is a specific crystal structure of iron that has the unique ability to absorb a significant amount of carbon into its matrix. This is the essential first step; without a complete transformation to austenite, the steel cannot be fully hardened.
Why Temperature Varies by Steel Type
The precise austenitizing temperature depends heavily on the steel's carbon content and other alloying elements. As a general rule, higher carbon content can slightly lower the required temperature. Specific material data sheets for each alloy provide the exact temperature range needed for optimal results.
A General Temperature Range
For the majority of common carbon and alloy steels, the hardening or "austenitizing" temperature falls between 815°C and 900°C (1500°F and 1650°F). This is significantly above the lower critical temperature of approximately 730°C (1350°F) where the transformation to austenite begins.
Hardening is More Than Just Heating
Reaching the target temperature is only one part of a multi-stage process. The subsequent steps are just as critical for achieving the desired final properties of the component.
Step 2: Soaking at Temperature
Once the steel reaches its target austenitizing temperature, it must be held there for a specific period. This "soaking" time ensures that the entire part, from its surface to its core, has fully and uniformly transformed into austenite.
Step 3: Quenching for Hardness
True hardness is not achieved at high temperatures. It is created by cooling the steel rapidly from its austenitic state in a process called quenching. This rapid cooling traps the dissolved carbon atoms, forming a new, extremely hard and brittle microstructure known as martensite.
Step 4: Tempering for Toughness
After quenching, the steel is often too brittle for most practical applications. A subsequent, lower-temperature heat treatment called tempering is performed to reduce brittleness and restore some toughness. Tempering temperatures typically fall within the range of 175°C to 650°C (350°F to 1200°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right temperature and process involves balancing competing factors. A misunderstanding of these trade-offs can lead to failed components.
The Risk of Overheating
Exceeding the recommended austenitizing temperature can cause excessive grain growth within the steel's microstructure. This can make the final product brittle and prone to cracking, even after tempering.
The Problem of Surface Degradation
At these high temperatures, the steel's surface is highly reactive. The protective atmosphere within the furnace is critical. As noted in technical processes, the carbon potential of the furnace atmosphere must match the steel's carbon composition to prevent decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface), which would result in a soft outer layer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct temperature is dictated entirely by your material and your desired outcome. The terms "hardening" and "tempering" refer to distinct processes with different temperature ranges and goals.
- If your primary focus is hardening the steel: You must heat the material above its critical transformation temperature, typically into the 815-900°C (1500-1650°F) range, to form austenite before quenching.
- If your primary focus is increasing toughness after hardening: You must use a lower-temperature tempering process, typically between 175-650°C (350-1200°F), to relieve internal stresses.
Ultimately, consulting the material specification sheet for your specific steel alloy is the only way to ensure you are using the precise temperature required for optimal results.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Typical Temperature Range | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening (Austenitizing) | 815°C - 900°C (1500°F - 1650°F) | Transform steel to austenite for hardening |
| Tempering | 175°C - 650°C (350°F - 1200°F) | Reduce brittleness and increase toughness |
Achieve precise and consistent heat treatment results with KINTEK's laboratory furnaces.
Whether you are hardening, tempering, or conducting other thermal processes, precise temperature control is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment designed for the exacting demands of metallurgy and materials science.
Our solutions ensure accurate temperature uniformity and atmosphere control, helping you prevent issues like grain growth or decarburization. Trust KINTEK to provide the reliable equipment you need to meet your material specifications and quality goals.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your specific steel hardening and heat treatment applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation



















