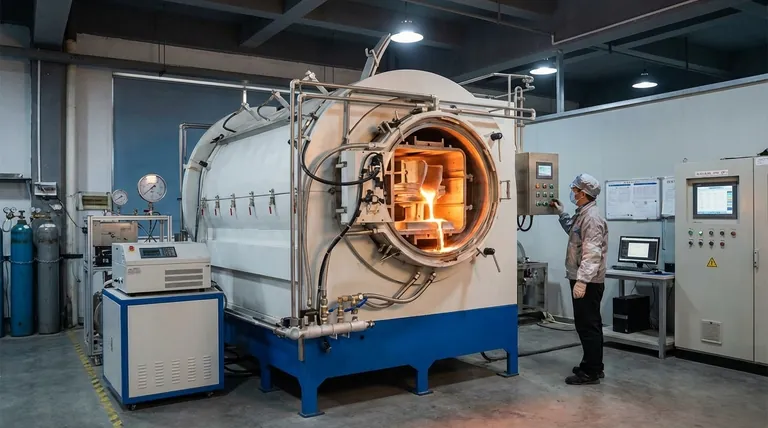
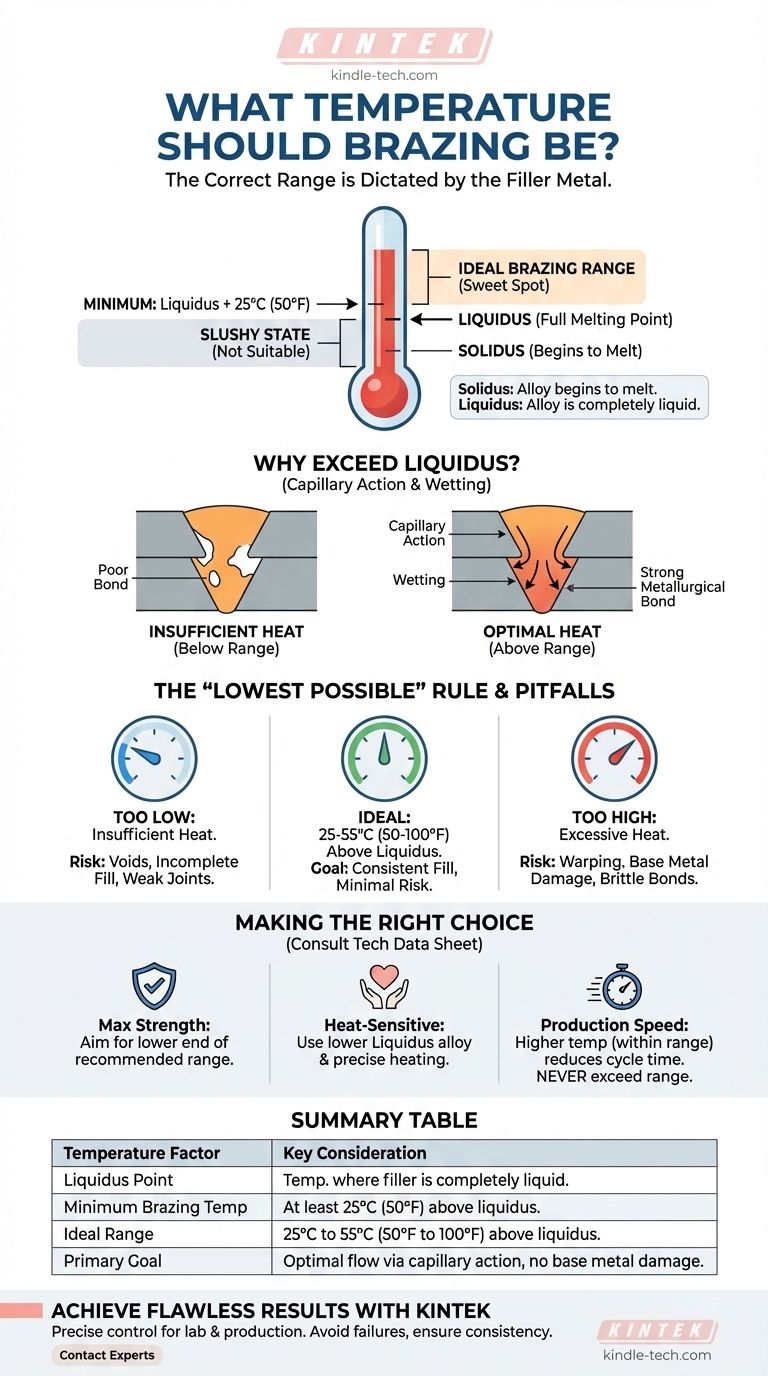
The correct brazing temperature is not a single value but a specific range dictated by the filler metal you are using. As a rule, you must heat the assembly to a temperature that is at least 25ºC (50ºF) above the full melting point (the liquidus) of your chosen brazing alloy. This ensures the filler metal is fluid enough to flow properly into the joint.
The goal is not simply to melt the filler metal, but to achieve a temperature that enables optimal flow and metallurgical bonding without damaging the base metals. Your filler metal's technical data sheet is the ultimate authority on its required temperature range.

The Science Behind Brazing Temperature
To achieve a strong brazed joint, you must understand the key properties of your filler metal. The entire process hinges on reaching a temperature that allows the filler to work as designed.
Defining Liquidus and Solidus
Every brazing alloy has two critical temperature points:
- Solidus: The temperature at which the alloy begins to melt.
- Liquidus: The temperature at which the alloy is completely liquid.
Between these two points, the alloy exists in a slushy, semi-solid state which is not suitable for proper flow.
Why You Must Exceed the Liquidus Temperature
The joint must be heated to a temperature above the liquidus point of the filler. This superheat provides the thermal energy necessary for two critical actions to occur.
First, it makes the molten filler metal extremely fluid. This allows it to be drawn deep into the tight gap between the base metals through a process called capillary action.
Second, this fluidity enables proper wetting, where the filler metal spreads evenly over the surfaces of the base metals, creating a strong, permanent metallurgical bond.
The "Lowest Possible" Temperature Rule
The standard recommendation is to use a temperature approximately 25ºC to 55°C (50°F to 100°F) above the filler's liquidus point. This is the sweet spot.
Heating within this range ensures the filler is fully liquid and flows correctly, but it minimizes the risk of overheating the assembly. The ideal temperature is the lowest one that still provides consistent, complete joint fill.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Selecting the wrong temperature—either too low or too high—is the most common cause of brazing failure. Each error creates a distinct set of problems.
The Risk of Insufficient Heat
If the base metals are not hot enough, the filler metal will freeze before it can fully penetrate the joint.
This results in voids and incomplete fill, creating a weak and unreliable connection that is prone to cracking and failure under stress. The filler will not properly wet the base metals, leading to a poor bond.
The Danger of Excessive Heat
Overheating the assembly is just as damaging, if not more so.
Excessive heat can melt or warp the base metals, compromising their structural integrity. It can also degrade the brazing filler metal, cause it to flow too thinly out of the joint, or create brittle intermetallic compounds that weaken the final bond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Always begin by consulting the technical data sheet provided by the manufacturer of your brazing filler metal. It will specify the exact solidus, liquidus, and recommended brazing temperature range.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength: Strictly adhere to the manufacturer's recommended range, aiming for the lower end that still gives you complete, consistent filler flow.
- If you are working with delicate or heat-sensitive materials: Select a filler alloy with a lower liquidus temperature and use a precise heating method to avoid overheating and damaging the base metals.
- If your primary focus is production speed: While higher temperatures can reduce cycle time, never exceed the recommended range, as this will compromise joint quality and lead to failures.
Ultimately, selecting the correct brazing temperature is about precisely controlling the filler metal's flow to create a flawless metallurgical bond.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Factor | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Liquidus Point | Temperature at which filler metal is completely liquid. |
| Minimum Brazing Temp | At least 25°C (50°F) above the liquidus. |
| Ideal Range | 25°C to 55°C (50°F to 100°F) above liquidus. |
| Primary Goal | Achieve optimal flow via capillary action without damaging base metals. |
Achieve flawless brazing results with precision equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you are working on R&D prototypes or high-volume production, the right temperature control is critical for joint integrity. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and heating systems that deliver the precise, uniform heat necessary for successful brazing operations.
Our solutions help you:
- Precisely control temperatures to stay within the optimal brazing range.
- Avoid costly failures caused by overheating or insufficient heat.
- Ensure consistent, high-quality bonds batch after batch.
Ready to perfect your brazing process? Contact our experts today to find the ideal heating solution for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is oxidation in brazing? How to prevent it for strong, durable joints
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















