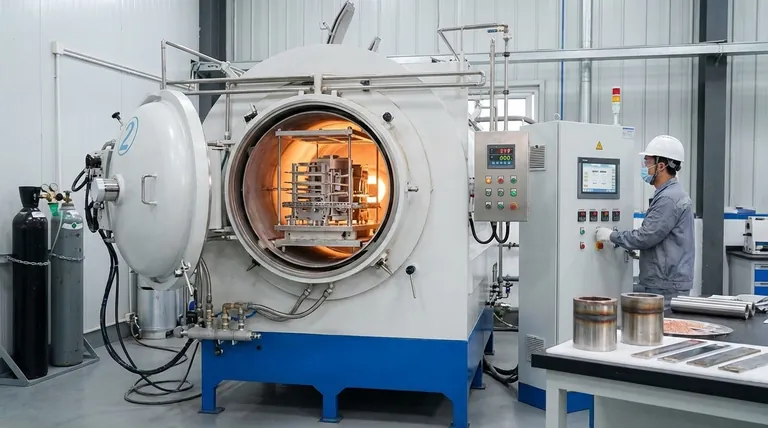
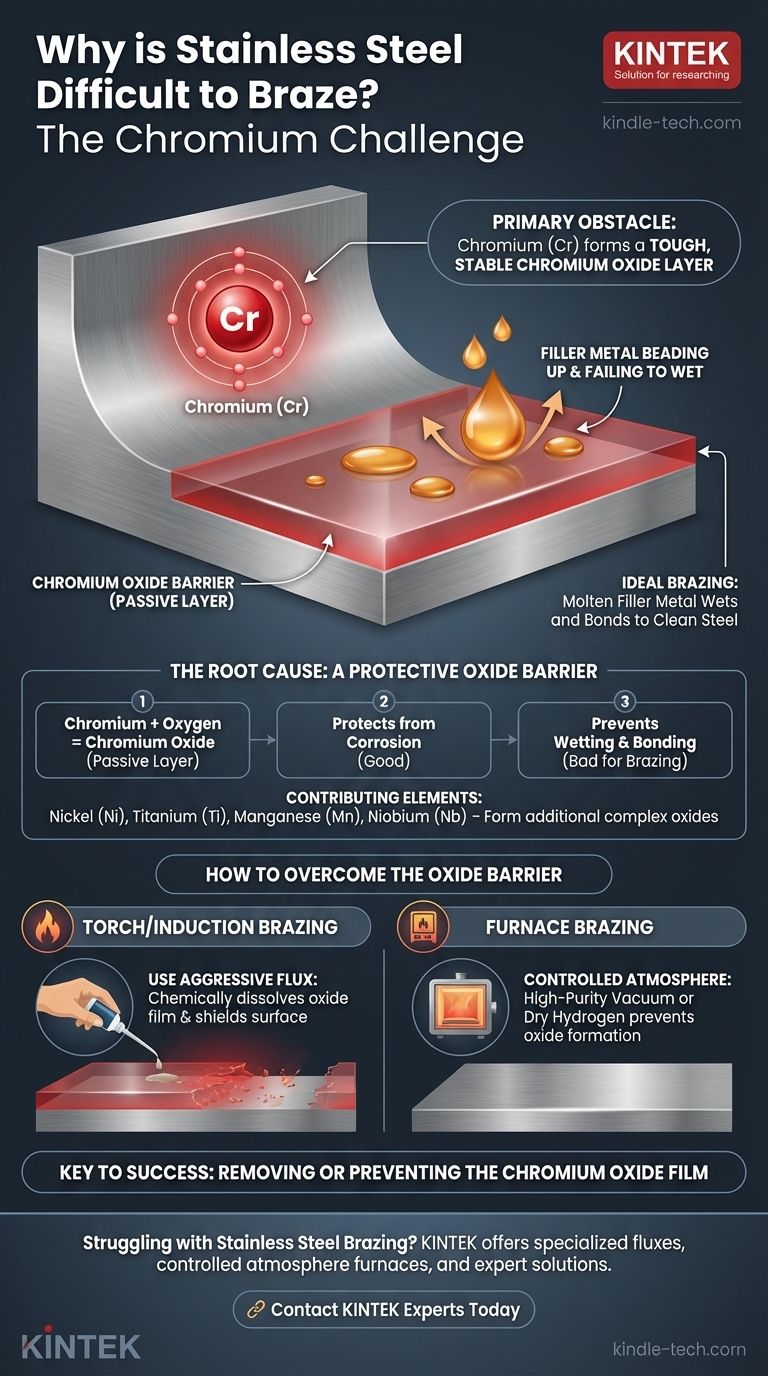
The primary element that makes stainless steel difficult to braze is Chromium (Cr). While essential for the material's signature corrosion resistance, chromium readily forms a tough, stable, and invisible layer of chromium oxide on the surface. This oxide film acts as a barrier, preventing the molten brazing filler metal from properly wetting and bonding to the steel underneath.
The core challenge in brazing stainless steel is not the metal itself, but the tenacious and self-healing oxide layer it forms. Successfully brazing this material depends entirely on removing this chromium oxide film before and during the heating process.

The Root Cause: A Protective Oxide Barrier
The very property that makes stainless steel "stainless"—its resistance to corrosion—is what creates the primary obstacle for brazing. This property is known as passivation.
Chromium's Dual Role
Chromium, when added to steel, reacts with oxygen in the air to form a very thin, inert layer of chromium oxide.
This passive layer is extremely stable and instantly re-forms if scratched, protecting the underlying steel from rust and corrosion.
However, during brazing, this same protective layer prevents the molten filler metal from making the intimate, atomic-level contact required for a strong metallurgical bond.
How the Oxide Layer Prevents Brazing
For a braze to be successful, the filler metal must "wet" the base material, meaning it must flow and spread evenly across the surface.
The chromium oxide film has poor wettability. The molten filler metal will bead up on the oxide surface, much like water on a waxed car, rather than spreading out and adhering to the base metal.
The Influence of Other Alloying Elements
While chromium is the primary culprit, other elements found in various stainless steel grades also contribute to the problem.
Elements like nickel (Ni), titanium (Ti), manganese (Mn), and niobium (Nb) also form their own stable oxides. These can create even more complex oxide films on the surface, further complicating the brazing process.
Understanding the Practical Implications
Failing to address this oxide layer is the most common reason for brazing failures with stainless steel, leading to weak joints or a complete lack of bonding.
The Need for Aggressive Flux
Because chromium oxide is so stable and difficult to remove, standard brazing fluxes used for carbon steel or copper are ineffective.
A specialized, chemically aggressive brazing flux for stainless steel is required. Its job is to chemically dissolve the oxide film during heating and shield the surface from re-oxidizing.
The Alternative: Controlled Atmospheres
An alternative to flux is to prevent the oxide from forming in the first place. This is the principle behind furnace brazing.
By brazing in a high-purity vacuum or a dry hydrogen atmosphere, there is little to no oxygen present to react with the chromium. This keeps the surface clean and ready to accept the filler metal.
How to Approach Brazing Stainless Steel
Successfully brazing stainless steel requires a direct strategy to combat the oxide layer before and during the heating process. Your approach will depend on your method.
- If your primary focus is torch or induction brazing: You must use a specialized, aggressive flux specifically formulated for stainless steel to chemically remove the chromium oxide.
- If your primary focus is furnace brazing: You must use a controlled atmosphere, such as a high-purity vacuum or dry hydrogen, to prevent the oxide layer from forming at high temperatures.
Ultimately, understanding that the true obstacle is the oxide film, not the metal itself, is the key to achieving a successful and reliable braze.
Summary Table:
| Element | Role in Stainless Steel | Effect on Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium (Cr) | Provides corrosion resistance | Forms a stable chromium oxide layer that prevents wetting |
| Nickel (Ni), Titanium (Ti) | Enhances specific properties | Can form additional oxides, further complicating brazing |
Struggling with brazing stainless steel components? The key to a strong, reliable braze is overcoming the tenacious chromium oxide layer. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the right tools and expertise—from specialized fluxes to controlled atmosphere furnaces—to ensure your brazing process is a success. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and achieve perfect results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of heat treatment? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- What are the three types of tempering? Choose the Right Process for Hardness vs. Toughness
- How does a high-precision heating and stirring system affect the phase formation of 6-line ferrihydrite?
- What are the benefits of metallurgy? Achieve Superior Material Performance and Efficiency
- Is sputtering a deposition? Discover the PVD Technique for High-Performance Thin Films
- How does RF sputtering work? Deposit Thin Films on Insulating Materials
- What are ultra-low temperature freezers designed for? Preserving Your Most Valuable Biological Samples
- What are the applications of fused silica glass? Unlock Extreme Performance for Demanding Environments



















