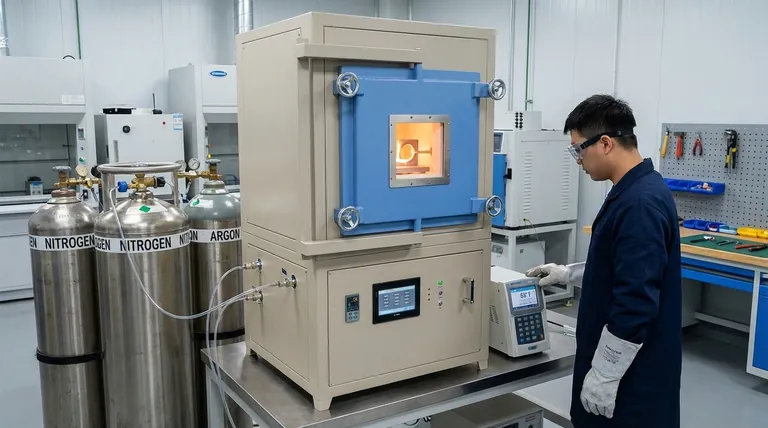
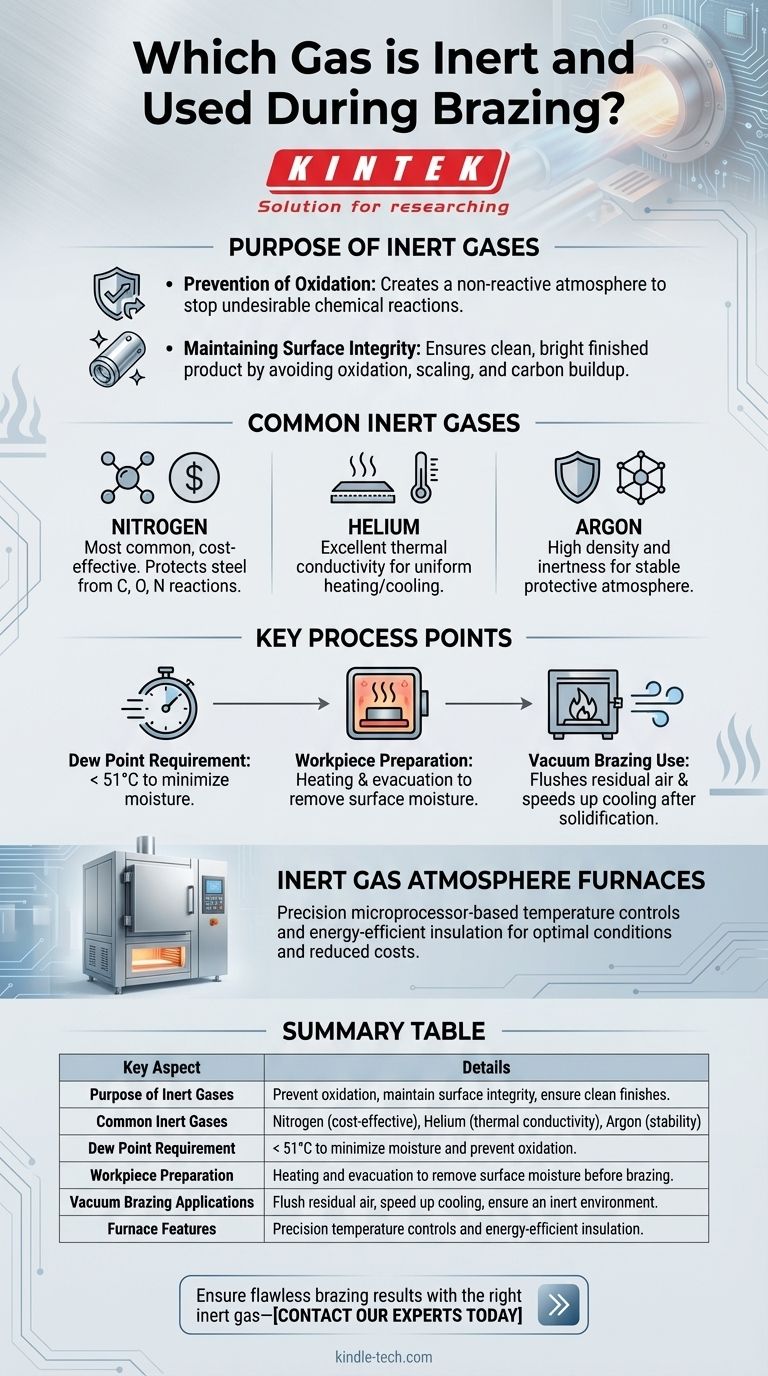
Inert gases are crucial in brazing processes to prevent oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions that could degrade the quality of the joint. Commonly used inert gases include nitrogen, helium, and argon. These gases create a protective atmosphere that ensures a clean and bright finished product by eliminating issues like oxidation, scaling, and carbon buildup. The inert gas must have a dew point of less than 51°C, and heating and evacuation are often used to remove moisture from the workpiece surface before applying the inert gas. Additionally, inert gases can assist in flushing out residual air and speeding up cooling after the brazing process.

Key Points Explained:
-
Purpose of Inert Gases in Brazing:
- Prevention of Oxidation: Inert gases like nitrogen, helium, and argon are used to create a non-reactive atmosphere that prevents oxidation and other undesirable chemical reactions during brazing.
- Maintaining Surface Integrity: By avoiding oxidation, these gases help maintain the integrity and appearance of the workpiece, resulting in a clean and bright finish.
-
Common Inert Gases Used in Brazing:
- Nitrogen: The most commonly used inert gas due to its availability and cost-effectiveness. It provides a protective environment where carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen do not react with steel.
- Helium: Often used for its excellent thermal conductivity, which can help in uniform heating and cooling of the workpiece.
- Argon: Used for its high density and inertness, making it ideal for creating a stable protective atmosphere.
-
Dew Point Requirement:
- Dew Point Less Than 51°C: The inert gas used must have a dew point of less than 51°C to ensure that moisture is minimized, which is crucial for preventing oxidation and other moisture-related issues.
-
Preparation of Workpiece:
- Heating and Evacuation: Before applying the inert gas, the workpiece is often heated and evacuated to remove any water molecules from the surface. This step is essential to ensure that the inert gas can effectively create a protective atmosphere.
-
Use of Inert Gas in Vacuum Brazing:
- Flushing Out Residual Air: In vacuum brazing, inert gases are used to flush out residual air from the capillary paths of the part to be brazed. This ensures that the brazing process occurs in a completely inert environment.
- Speeding Up Cooling: Inert gases can also be used to speed up the cooling process after the filler material has solidified, which can improve the efficiency of the brazing process.
-
Inert Gas Atmosphere Furnaces:
- Precision Controls: Furnaces designed for inert gas brazing often feature precision microprocessor-based temperature controls to ensure optimal conditions for the brazing process.
- Energy-Efficient Insulation: These furnaces are also designed with energy-efficient insulation to minimize heat loss and reduce operational costs.
By understanding these key points, a purchaser can make informed decisions about the type of inert gas and equipment needed for specific brazing applications, ensuring high-quality results and cost-effective operations.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose of Inert Gases | Prevent oxidation, maintain surface integrity, and ensure clean finishes. |
| Common Inert Gases | Nitrogen (cost-effective), Helium (thermal conductivity), Argon (stability). |
| Dew Point Requirement | Less than 51°C to minimize moisture and prevent oxidation. |
| Workpiece Preparation | Heating and evacuation to remove surface moisture before brazing. |
| Vacuum Brazing Applications | Flush residual air, speed up cooling, and ensure an inert environment. |
| Furnace Features | Precision temperature controls and energy-efficient insulation. |
Ensure flawless brazing results with the right inert gas—contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is the purpose of using an atmosphere-controlled heating furnace for Cu reduction? Achieve Active Catalytic States
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



















