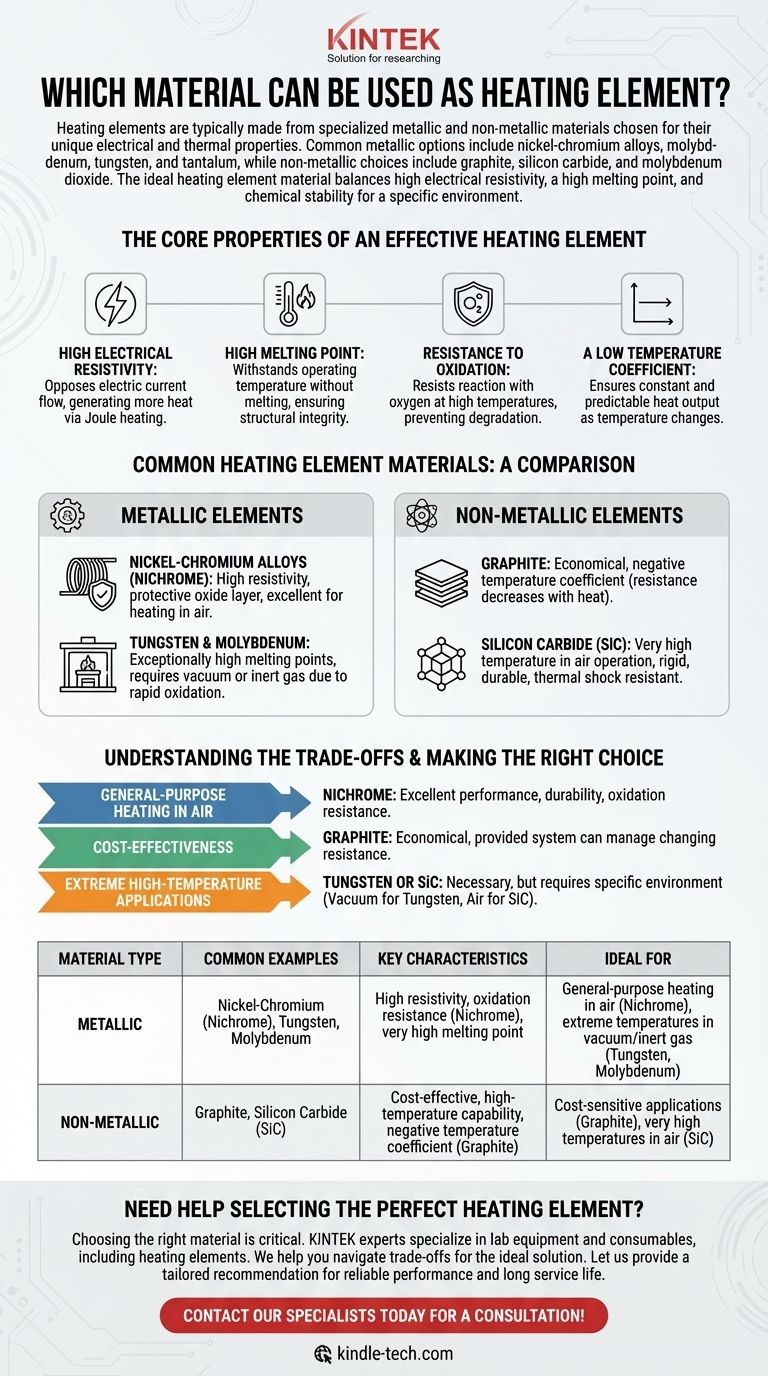
Heating elements are typically made from specialized metallic and non-metallic materials chosen for their unique electrical and thermal properties. Common metallic options include nickel-chromium alloys, molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum, while non-metallic choices include graphite, silicon carbide, and molybdenum dioxide.
The ideal heating element material is not a single "best" option. It is a material that strikes the right balance between high electrical resistivity, a high melting point, and chemical stability (like oxidation resistance) for a specific operational environment and goal.
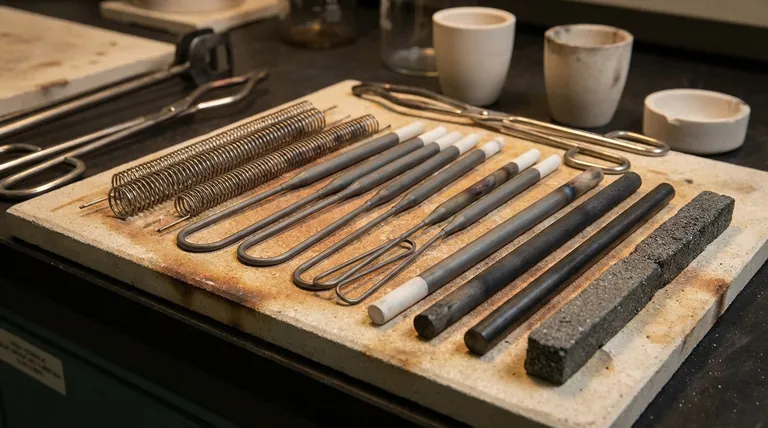

The Core Properties of an Effective Heating Element
To understand why certain materials are used, we must first look at the fundamental properties required to efficiently and reliably generate heat from electricity.
High Electrical Resistivity
A heating element works by converting electrical energy into heat through a process called Joule heating. A material with high resistivity opposes the flow of electric current more strongly, generating more heat for a given current and physical size.
High Melting Point
This is a straightforward but critical requirement. The material must be able to withstand its own operating temperature without melting or deforming, ensuring structural integrity and a long service life.
Resistance to Oxidation
At high temperatures, most materials react rapidly with oxygen in the air, a process known as oxidation. This corrosion degrades the element, causing it to thin and eventually fail. A good element must be inherently resistant to oxidation or form a protective oxide layer.
A Low Temperature Coefficient
The "temperature coefficient of resistance" describes how much a material's electrical resistance changes as its temperature changes. A low or stable coefficient is desirable because it ensures the heat output remains constant and predictable as the element heats up.
Common Heating Element Materials: A Comparison
Materials are broadly classified into two groups, each with distinct characteristics.
Metallic Elements
These are often alloys designed specifically for heating applications.
- Nickel-Chromium Alloys (Nichrome): Extremely common due to their high resistivity and ability to form a protective layer of chromium oxide, which prevents further oxidation even at high temperatures in air.
- Tungsten & Molybdenum: These refractory metals have exceptionally high melting points, making them suitable for very high-temperature applications like furnace elements. However, they oxidize rapidly and must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere.
Non-Metallic Elements
These materials offer different cost and performance profiles.
- Graphite: A less costly option than many metals, graphite is an efficient choice. Uniquely, its electrical resistance can actually decrease as it heats up, a property known as a negative temperature coefficient.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Known for its ability to operate at very high temperatures in air, SiC is rigid, durable, and resistant to thermal shock.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material involves balancing competing factors like cost, lifespan, and the environment in which the element will operate.
Cost vs. Performance
Graphite is significantly less costly than specialized metallic alloys. However, its properties, such as a changing resistance with heat, may require more complex control systems compared to a stable nickel-chromium element.
Operating Environment is Critical
The single most important factor is often the presence of oxygen. A material like tungsten is superior to nickel-chromium at extreme temperatures, but only if it is completely protected from air. For most common applications in air, nickel-chromium's self-protecting nature makes it the more practical and reliable choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific needs should guide your material selection.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in air: Nickel-chromium alloys are the industry standard for their excellent balance of performance, durability, and oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness: Non-metallic elements like graphite can provide an economical and efficient solution, provided the system can accommodate their properties.
- If your primary focus is extreme high-temperature applications: Refractory metals like tungsten or non-metallics like silicon carbide are necessary, but you must account for their specific environmental requirements (e.g., vacuum for tungsten, air for SiC).
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently select a heating element material based on its fundamental properties and suitability for your task.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic | Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome), Tungsten, Molybdenum | High resistivity, oxidation resistance (Nichrome), very high melting point | General-purpose heating in air (Nichrome), extreme temperatures in vacuum/inert gas (Tungsten, Molybdenum) |
| Non-Metallic | Graphite, Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Cost-effective, high-temperature capability, negative temperature coefficient (Graphite) | Cost-sensitive applications (Graphite), very high temperatures in air (SiC) |
Need Help Selecting the Perfect Heating Element?
Choosing the right material is critical for your lab's efficiency, safety, and budget. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including heating elements for a wide range of applications. We can help you navigate the trade-offs between cost, performance, and operating environment to find the ideal solution for your specific needs.
Let us provide you with a tailored recommendation that ensures reliable performance and long service life.
Contact our specialists today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
People Also Ask
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process














