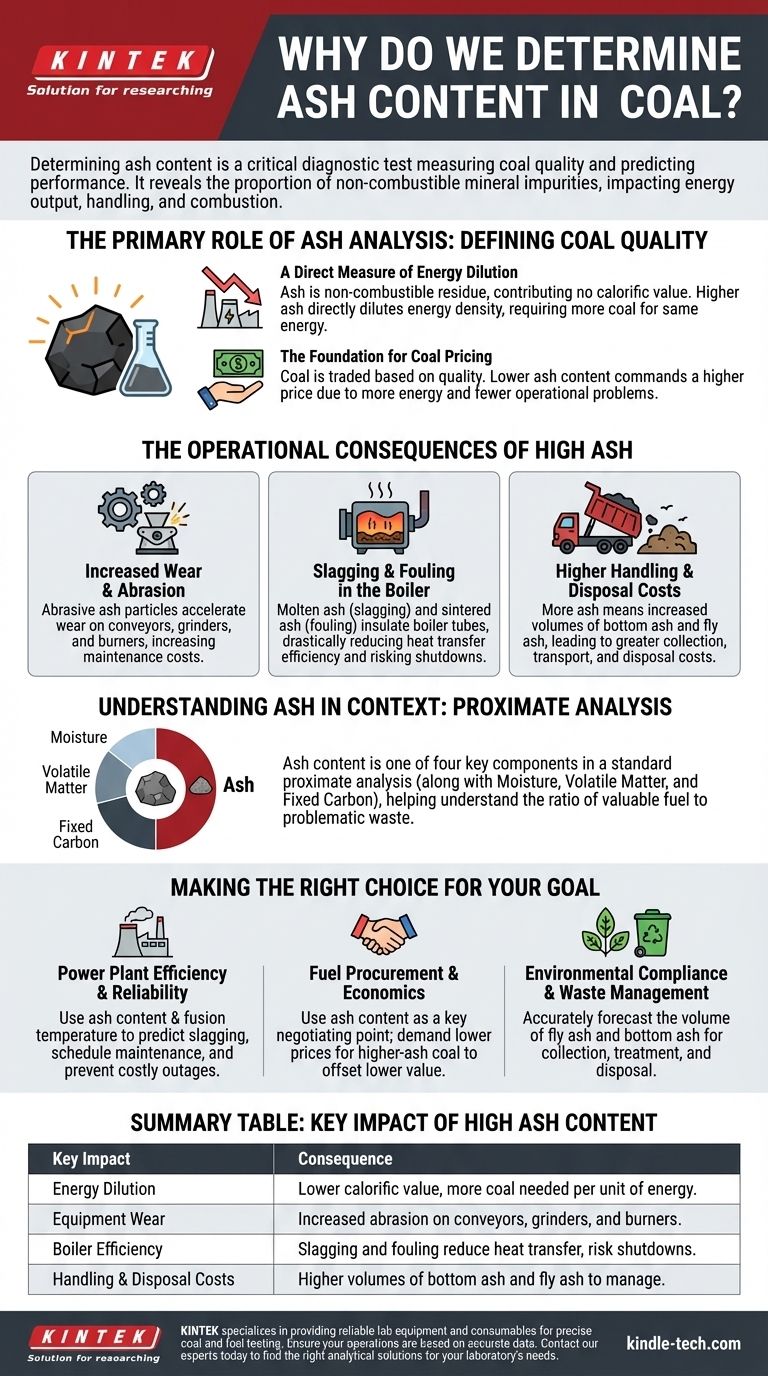
Determining the ash content of coal is a critical diagnostic test that directly measures its quality and predicts its performance. This single value reveals the proportion of non-combustible mineral impurities within the coal, fundamentally impacting its energy output, handling costs, and effect on combustion equipment. It is one of the most important parameters in assessing the economic and operational value of a coal supply.
Ash content is not merely a measure of purity; it is a predictive tool for operational efficiency and financial risk. A higher ash percentage directly translates to lower energy yield per ton, increased equipment wear, and greater waste disposal costs, making its determination essential for forecasting the true cost of using a specific coal.

The Primary Role of Ash Analysis: Defining Coal Quality
Ash content is the residue left after the complete combustion of coal. It is a direct measurement of the inert mineral matter—such as clay, feldspar, quartz, and pyrite—present in the fuel.
A Direct Measure of Energy Dilution
The primary value of coal comes from its combustible components. Ash does not burn and therefore contributes no calorific (heat) value.
A higher ash content means there is less combustible material per ton of coal. This directly dilutes the energy density of the fuel, meaning you must burn more coal to produce the same amount of energy.
The Foundation for Coal Pricing
Coal is traded based on its quality specifications, and ash content is a primary factor. Buyers are purchasing energy, not rock.
A contract for coal will almost always specify an acceptable range for ash content. Coal with a lower ash content commands a higher price because it offers more energy and creates fewer operational problems.
The Operational Consequences of High Ash
Beyond simple energy dilution, high ash content creates significant and costly problems for any facility burning coal, particularly power plants. These consequences are often the deeper reason for conducting the analysis.
Increased Wear and Abrasion
Ash particles are hard, abrasive minerals. As coal is transported, crushed, and pulverized, these particles act like sandpaper on the equipment.
This leads to accelerated wear and tear on conveyors, grinders, and burners, increasing maintenance costs and the frequency of equipment failure.
Slagging and Fouling in the Boiler
This is one of the most severe consequences. At high temperatures inside a boiler, certain mineral components of the ash can soften and melt.
Slagging occurs when this molten ash sticks to boiler walls and heat-transfer surfaces in the hottest parts of the furnace. It forms a hard, glass-like coating that is extremely difficult to remove.
Fouling is similar but occurs in the cooler, downstream sections of the boiler, where ash particles sinter together. Both slagging and fouling insulate the boiler tubes, drastically reducing heat transfer efficiency and potentially forcing a complete plant shutdown for cleaning.
Higher Handling and Disposal Costs
Every ton of ash that enters the plant with the coal must be removed and managed. This waste material is known as bottom ash (which collects at the bottom of the boiler) and fly ash (which is captured from exhaust gases).
Higher ash content directly increases the volume of this waste, leading to greater costs for collection, transportation, and disposal in ash ponds or landfills.
Understanding Ash in Context: Proximate Analysis
Determining ash content is rarely done in isolation. It is one of the four key components of a proximate analysis, the standard method for characterizing solid fuels.
The Four Key Components
A proximate analysis reports the percentage of four distinct components in a coal sample:
- Moisture: Water present in the coal, which adds weight but no energy value.
- Volatile Matter: Components that are driven off as gas when heated. They ignite easily and contribute to initial combustion.
- Fixed Carbon: The solid combustible residue left after volatile matter is removed. It provides the bulk of the sustained energy release.
- Ash: The non-combustible mineral residue.
How the Components Work Together
These four components always add up to 100%. The energy-producing elements are the volatile matter and fixed carbon.
The non-energy-producing elements—the diluents—are moisture and ash. Knowing the ash percentage helps you understand the relative proportion of valuable fuel versus problematic waste in your supply.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The significance of ash content varies based on your specific operational role and goals. Understanding this data allows for proactive decision-making.
- If your primary focus is power plant efficiency and reliability: Use ash content and ash fusion temperature data to predict slagging potential and schedule soot blowing or maintenance to prevent costly unplanned outages.
- If your primary focus is fuel procurement and economics: Use ash content as a key negotiating point, demanding lower prices for higher-ash coal to offset its lower energy value and higher operational costs.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and waste management: Use ash data to accurately forecast the volume of fly ash and bottom ash that will require collection, treatment, and disposal.
Ultimately, measuring coal ash transforms an unknown variable into a manageable risk, empowering you to optimize performance and protect your bottom line.
Summary Table:
| Key Impact of High Ash Content | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Energy Dilution | Lower calorific value, more coal needed per unit of energy |
| Equipment Wear | Increased abrasion on conveyors, grinders, and burners |
| Boiler Efficiency | Slagging and fouling reduce heat transfer, risk shutdowns |
| Handling & Disposal Costs | Higher volumes of bottom ash and fly ash to manage |
Accurate ash content analysis is the first step to optimizing your fuel efficiency and protecting your equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for precise coal and fuel testing. Ensure your operations are based on accurate data—contact our experts today to find the right analytical solutions for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace test? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- What is the structure of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components and Design
- What are the safety precautions for muffle furnace? A Complete Guide to Safe High-Temperature Operation
- What is the principle of muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Precise High-Temperature Heating
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an incubator? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab



















