It is a critical and common misconception that tempering increases hardness. The opposite is true: tempering is a process performed after initial hardening to decrease hardness and relieve internal stress. This reduction in hardness is a deliberate trade-off to gain a massive increase in toughness, transforming the steel from a brittle, glass-like state into a resilient, usable material.
The core purpose of heat treatment is not just to make steel hard, but to achieve a precise balance of properties. Tempering is the crucial second step that sacrifices a small amount of the extreme, unusable hardness gained from quenching in exchange for the toughness required for real-world applications.

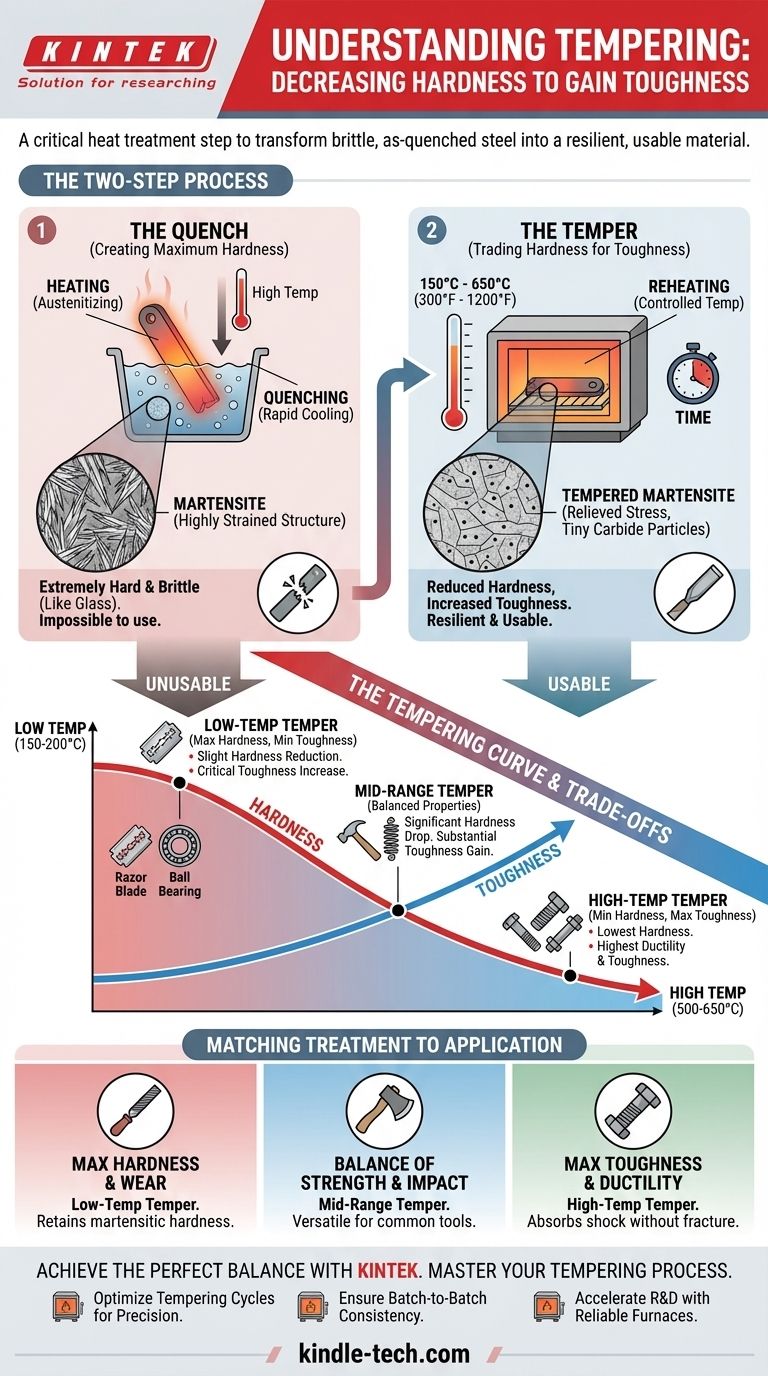
The Two-Step Process: Hardening and Tempering
To understand tempering, you must first understand the process it follows: quenching. Steel's final properties are a result of this essential two-stage treatment.
Step 1: The Quench (Creating Maximum Hardness)
The first step is to heat the steel to a high temperature (a process called austenitizing) and then cool it very rapidly, typically by plunging it into water or oil. This is called quenching.
This rapid cooling traps carbon atoms within the iron's crystal structure, forcing it into a highly strained, distorted arrangement called martensite.
Martensite is extremely hard because the trapped carbon atoms prevent the crystal planes from slipping past one another. However, this structure is under immense internal stress, making it incredibly brittle. An as-quenched piece of high-carbon steel can shatter like glass if dropped.
The Problem with Pure Martensite
While martensite registers exceptionally high on a hardness scale, its brittleness makes it useless for almost any practical purpose.
A tool made of pure martensite, like a knife or chisel, would be impossible to sharpen without chipping and would snap on its first use. It has hardness but no toughness—the ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing.
Step 2: The Temper (Trading Hardness for Toughness)
This is where tempering comes in. The hardened, brittle steel is carefully reheated to a temperature well below its hardening temperature (typically between 150°C and 650°C or 300°F and 1200°F).
This gentle reheating provides just enough energy for the trapped carbon atoms to move. They migrate out of the strained martensite structure and form tiny, well-distributed particles of iron carbide, most commonly cementite (Fe₃C).
This migration has two profound effects: it significantly relieves the internal stress of the martensite lattice and allows the structure to become slightly more ductile. The result is a new microstructure known as tempered martensite.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Tempering Curve
The key to tempering is that the final properties are directly controlled by the tempering temperature. A higher temperature allows more carbon to precipitate and relieves more stress, resulting in a softer but tougher final product.
Low-Temperature Tempering (~150-200°C / 300-400°F)
This process only slightly reduces hardness but provides a critical increase in toughness, relieving the most extreme stresses from the quench.
It's used for tools that require maximum hardness and wear resistance, such as razor blades, files, and ball bearings, where a slight gain in toughness is enough to prevent catastrophic failure.
Mid-Range Tempering (~300-500°C / 570-930°F)
Here, there is a more significant drop in hardness in exchange for a substantial increase in toughness and strength.
This range is ideal for tools that must withstand impact and flex, such as hammers, chisels, axe heads, and springs. The material is still very hard but now has the resilience to absorb shock.
High-Temperature Tempering (~500-650°C / 930-1200°F)
This results in the lowest hardness but the highest ductility and toughness. The steel becomes much less brittle and can endure significant impact and plastic deformation before fracturing.
This is used for applications where toughness is the most critical property, such as structural bolts, vehicle axles, and shafts that must handle high stress and fatigue.
Matching the Treatment to the Application
The decision of how to temper is always driven by the intended use of the component. You are tailoring the steel's microstructure for a specific job.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: A low-temperature temper is required to retain as much martensitic hardness as possible while only relieving the most severe internal stresses.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and impact resistance: A mid-range temper provides the versatility needed for many common tools that must be both hard and tough.
- If your primary focus is maximum toughness and ductility: A high-temperature temper is essential to create a component that can safely absorb shock and fatigue without fracturing.
Ultimately, tempering is the metallurgist's essential tool for transforming a brittle, unusable material into a precisely engineered component with a predictable and reliable balance of properties.
Summary Table:
| Tempering Temperature | Primary Effect on Hardness | Primary Effect on Toughness | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (150-200°C / 300-400°F) | Slight Reduction | Slight Increase | Razor blades, files, ball bearings |
| Mid (300-500°C / 570-930°F) | Moderate Reduction | Significant Increase | Hammers, chisels, axe heads, springs |
| High (500-650°C / 930-1200°F) | Significant Reduction | Maximum Increase | Structural bolts, vehicle axles, shafts |
Achieve the Perfect Balance of Hardness and Toughness with KINTEK
Mastering the tempering process is key to creating durable, high-performance steel components. Whether you're developing cutting tools, impact-resistant parts, or structural elements, precise heat treatment is non-negotiable.
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that empower your research and quality control. Our reliable furnaces and temperature control systems are engineered to deliver the consistent, repeatable results you need to perfect your heat treatment protocols.
Let us help you transform your materials:
- Optimize Your Tempering Cycles with precise temperature control.
- Ensure Batch-to-Batch Consistency for reliable product quality.
- Accelerate Your R&D with robust and easy-to-use laboratory furnaces.
Ready to engineer superior materials? Contact our thermal processing experts today to find the ideal solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is ash analysis? A Complete Guide to Understanding Inorganic Material Composition
- What is the muffle furnace method? A Guide to Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature calcination furnace play in converting composite fibers? Achieve Pure TiO2 & ZnO.
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a drying oven? Choose the Right Thermal Tool
- What is a muffle vs tube furnace? Choose the Right High-Temp Tool for Your Lab
- What PPE is required for a muffle furnace? Essential Gear for High-Temperature Safety
- What is ash content in coal? The Key to Fuel Quality, Efficiency, and Cost
- What is the use of muffle oven in laboratory? For Clean, High-Temperature Material Processing



















