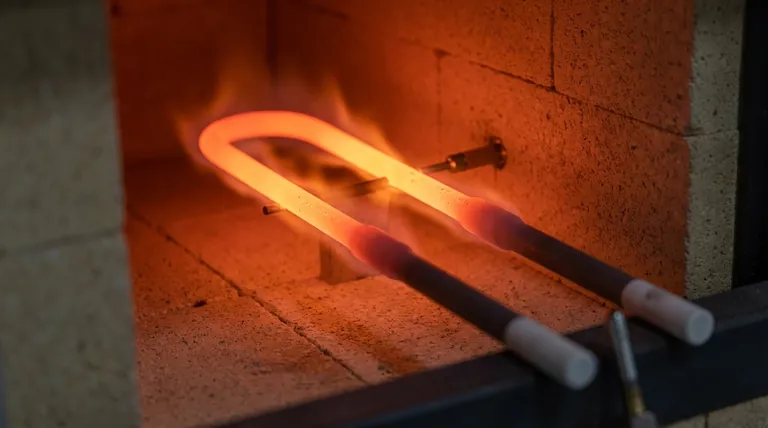
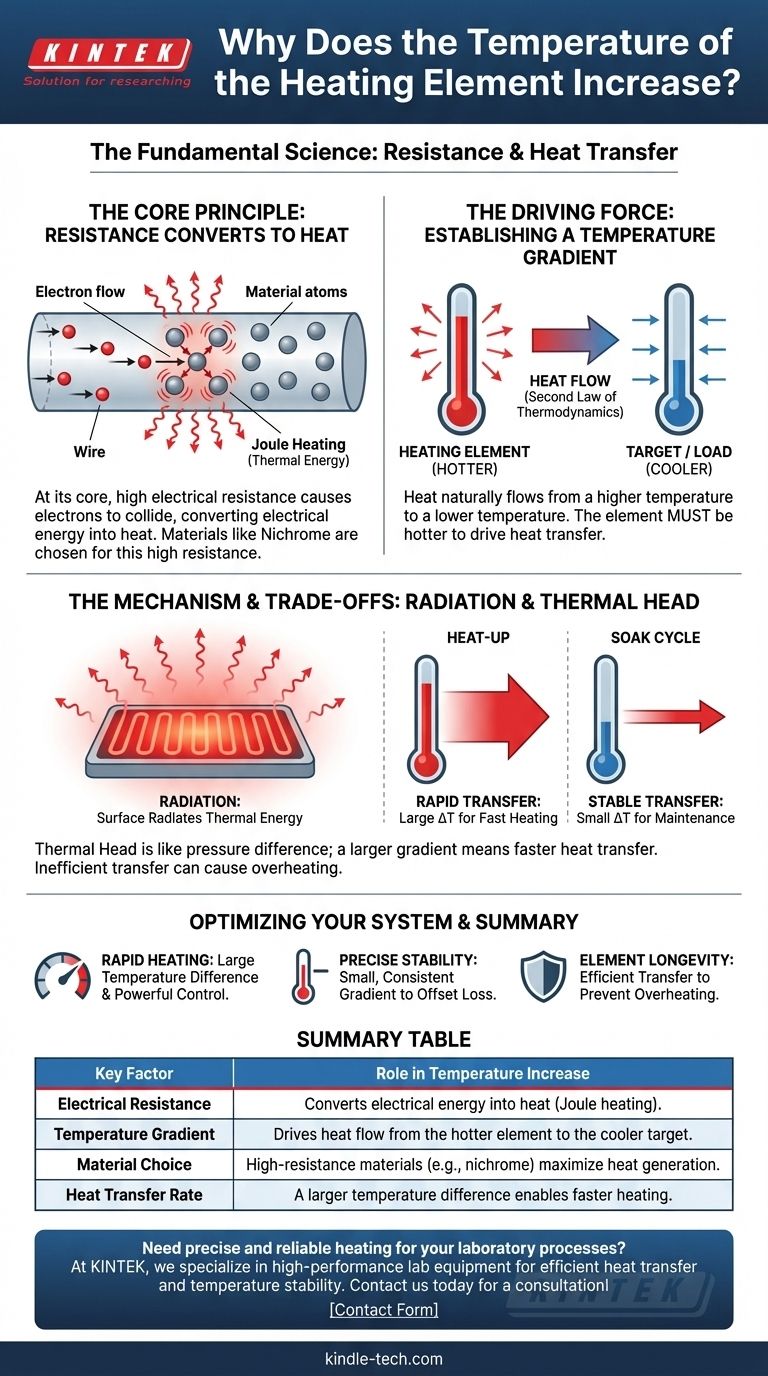
At its core, a heating element's temperature increases because it is designed to resist the flow of electricity. This resistance converts electrical energy directly into thermal energy, and to transfer this heat effectively to a cooler environment, the element must become significantly hotter than its surroundings.
The essential principle is that heat only flows from a hotter object to a colder one. A heating element must therefore achieve a higher temperature than its target to create the necessary "thermal pressure" to drive heat transfer.

The Fundamental Principle: Converting Electricity to Heat
The operation of a heating element is governed by a basic law of physics. It is not simply a byproduct but the explicit goal of its design.
Electrical Resistance as the Engine of Heat
When an electric current passes through a material, the electrons collide with the atoms of that material. In a high-resistance material, these collisions are frequent and energetic, causing the atoms to vibrate intensely.
This vibration is thermal energy, or heat. This phenomenon is known as Joule heating.
The Importance of Material Choice
Heating elements are made from materials like nichrome (a nickel-chromium alloy) specifically because they have high electrical resistance. This property ensures they efficiently convert electrical energy into heat rather than letting the current pass through with minimal effect.
Why the Element Must Be Hotter Than Its Target
Generating heat is only the first step. The ultimate goal is to move that heat to a desired location, such as the air in a room, the water in a tank, or the load inside a furnace.
Establishing a Temperature Gradient
Heat transfer is governed by the second law of thermodynamics, which dictates that thermal energy naturally flows from an area of higher temperature to one of lower temperature.
Without a temperature difference, known as a temperature gradient, heat transfer will not occur. The element must be hotter to "push" thermal energy into the cooler object or space.
The Mechanism of Heat Transfer
As noted in industrial furnace applications, this heat is often transferred via radiation. The surface of the heating element radiates thermal energy outward in all directions.
A hotter surface radiates energy at a much higher rate. To heat a furnace to a specific temperature, the element must be even hotter to radiate enough energy to raise and maintain that temperature.
The Concept of "Thermal Head"
Think of the temperature difference like water pressure. A small pressure difference allows a slow trickle of water, while a large pressure difference creates a powerful flow.
Similarly, a large temperature difference between the element and its target (the "load") results in a rapid transfer of heat. This is why the element temperature can be several hundred degrees higher than the furnace during the initial heat-up phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The temperature difference is not static; it is a dynamic variable that changes based on the operational requirements of the system.
Heat-Up vs. Soak Cycles
During a rapid heat-up cycle, a very large temperature difference is required to pump a massive amount of thermal energy into the system quickly.
During a soak or holding cycle, the goal is simply to maintain a stable temperature. The element only needs to be slightly hotter than the target to radiate enough energy to compensate for heat lost to the outside environment.
The Risk of Inefficient Transfer
A critical factor is the ability of the surrounding environment to absorb the heat. If heat is not transferred away from the element effectively, its own temperature will continue to rise.
This can lead to overheating and premature failure of the element. Proper system design ensures there is always a "load" to absorb the radiated energy.
How This Applies to Your System
Understanding this principle allows for better design, operation, and troubleshooting of any heating system. Consider your primary objective to determine the ideal behavior.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating: You must allow for a large temperature difference between the element and the target, which requires a powerful control system.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature stability: Your system must be designed to maintain a small, consistent temperature gradient just sufficient to offset ambient heat loss.
- If your primary focus is element longevity: You must guarantee efficient and continuous heat transfer away from the element to prevent it from exceeding its maximum design temperature.
Ultimately, controlling a heating process is a matter of precisely managing the flow of energy by controlling the temperature difference between the source and its target.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Temperature Increase |
|---|---|
| Electrical Resistance | Converts electrical energy into heat (Joule heating). |
| Temperature Gradient | Drives heat flow from the hotter element to the cooler target. |
| Material Choice | High-resistance materials (e.g., nichrome) maximize heat generation. |
| Heat Transfer Rate | A larger temperature difference enables faster heating. |
Need precise and reliable heating for your laboratory processes? Understanding the principles of heat transfer is the first step to optimizing your system. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces with precisely controlled heating elements. Our solutions ensure efficient heat transfer, temperature stability, and long element life for your specific applications. Let our experts help you achieve superior results—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten filament? Key Limitations in Lighting Technology
- How do coaxial heating coils in a TDS system determine hydrogen trap activation energy? Precise Thermal Control Guide
- Which element is best for heating? Match the Right Material to Your Application for Optimal Performance
- What is the electrical resistivity of molybdenum disilicide? Unlocking its High-Temperature Heating Power
- Which is better nichrome or tungsten? Choose the Right Heating Element for Your Application
- Why are K-type thermocouples shielded with niobium alloy tubes used? Ensure Accurate Microwave Pyrolysis Control
- How are heating elements made? The Science of Self-Regulating PTC Ceramic Heaters
- What is special about tungsten? The Ultimate Metal for Extreme Heat & Wear Resistance










