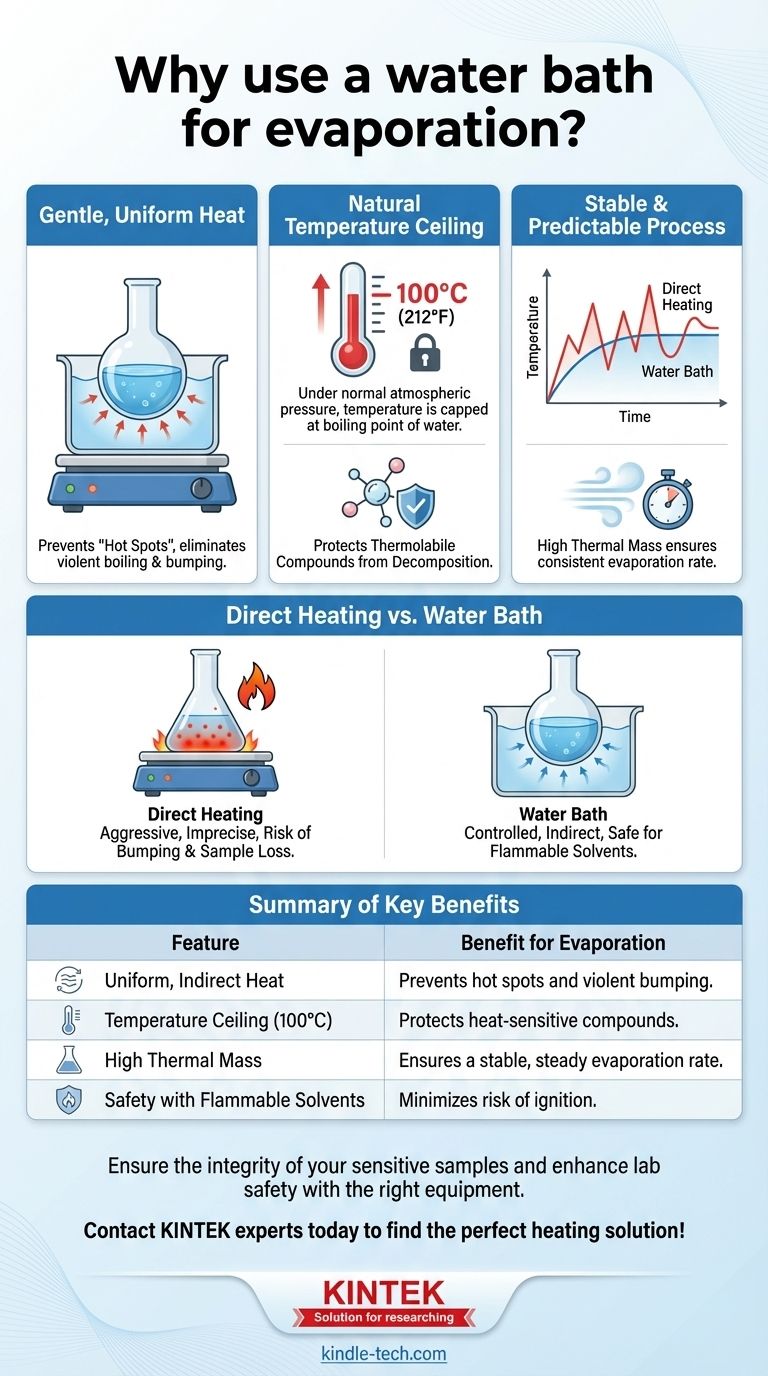
In laboratory settings, a water bath is used for evaporation to provide gentle, uniform, and precisely controlled heat. This indirect heating method is critical for preventing the decomposition of heat-sensitive substances and for safely evaporating flammable solvents. It ensures the entire surface of the container is heated evenly, eliminating dangerous "hot spots" that can cause violent boiling or charring.
The core problem with direct heating is its lack of control. A water bath solves this by acting as a thermal buffer, using water's physical properties to distribute heat evenly and create a natural temperature ceiling, ensuring a safe and predictable evaporation process.

The Challenge of Direct Heating
Directly heating a flask on a hot plate or with a flame is often too aggressive and imprecise for controlled evaporation. This approach introduces two significant risks.
Hot Spots and Uneven Heating
A hot plate's surface does not heat perfectly evenly. This creates localized hot spots on the bottom of the flask.
These hot spots can superheat the liquid in one area, causing it to boil violently and suddenly. This phenomenon, known as bumping, can lead to loss of the sample and is a safety hazard.
Thermal Decomposition
Many chemical compounds are thermolabile, meaning they break down or decompose when exposed to high temperatures.
Direct contact with a hot spot can easily exceed the decomposition temperature of the substance you are trying to isolate, destroying your product.
How a Water Bath Provides Superior Control
A water bath elegantly solves the problems of direct heating by acting as a medium for heat transfer. It leverages the unique properties of water to create a stable and safe heating environment.
Uniform, Indirect Heating
By immersing the evaporation flask in heated water, you ensure that heat is transferred gently and uniformly to the entire submerged surface of the flask.
Think of it like a bain-marie or double boiler used in cooking to melt chocolate or make custards. The water envelops the flask, providing a cushion of heat rather than a direct, concentrated point of contact.
A Natural Temperature Ceiling
Perhaps the most important feature is that, under normal atmospheric pressure, a water bath cannot exceed 100°C (212°F).
This creates a natural, foolproof temperature limit. No matter how high you set the hot plate, the flask's contents will never be exposed to a temperature above the boiling point of water, protecting sensitive compounds.
High Thermal Mass and Stability
Water has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it can absorb a lot of heat energy without its own temperature rising rapidly.
This property gives the bath a high thermal mass, making it a very stable heat source that is not prone to sudden temperature fluctuations. This ensures the evaporation rate remains steady and controllable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, a water bath is not the solution for every situation. Understanding its limitations is key to proper lab procedure.
When a Water Bath is Essential
A water bath is the standard and safest choice when working with thermolabile compounds or volatile, flammable solvents (like ethanol or ether). The indirect heat keeps ignition sources away from flammable vapors.
When Another Method is Required
The 100°C temperature limit is also its main limitation. If you need to evaporate a solvent with a higher boiling point, such as dimethylformamide (DMF) or water itself, a water bath is ineffective.
In these cases, an oil bath or a sand bath must be used to achieve the necessary higher temperatures.
A Slower Process
The trade-off for safety and control is speed. Heating a substance via a water bath is inherently slower than applying direct heat. However, for most chemical procedures, this is a worthwhile compromise for reproducibility and sample integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating method is fundamental to a successful outcome. Your choice depends entirely on the properties of the substances you are working with.
- If your primary focus is protecting a heat-sensitive compound: A water bath is non-negotiable. Its gentle, uniform heat prevents decomposition.
- If your primary focus is safety with flammable solvents: A water bath provides a much safer, indirect heat source that minimizes the risk of fire.
- If you must evaporate a solvent with a boiling point above 100°C: A water bath will not work; you must use an alternative like an oil or sand bath.
- If speed is your only priority and your compound is thermally robust: Direct heating may be an option, but it requires constant supervision to manage the risk of bumping.
Ultimately, using a water bath is a foundational technique for achieving safe, controlled, and reproducible results in the laboratory.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Evaporation |
|---|---|
| Uniform, Indirect Heat | Prevents hot spots and violent bumping by evenly heating the container. |
| Temperature Ceiling (100°C) | Protects thermolabile compounds by providing a natural, safe temperature limit. |
| High Thermal Mass | Ensures a stable, steady evaporation rate without sudden temperature fluctuations. |
| Safety with Flammable Solvents | Indirect heating minimizes the risk of igniting volatile solvent vapors. |
Ensure the integrity of your sensitive samples and enhance lab safety with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory water baths and evaporation systems designed for precise temperature control and uniform heating. Whether you are working with heat-sensitive compounds or flammable solvents, our solutions help you achieve reproducible results safely. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 5L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is the delta 20 rule? A Guide to Diagnosing and Perfecting Your Espresso
- What is the cooling system of an induction furnace? Essential for Safe, Reliable Melting
- How can hydraulic fluid temperature be reduced? Fix the Root Cause of Overheating
- How do you cool an induction coil? Master the Key to System Reliability and Performance
- What are the safety precautions for a water bath? Essential Guidelines for Lab Safety and Efficiency



















