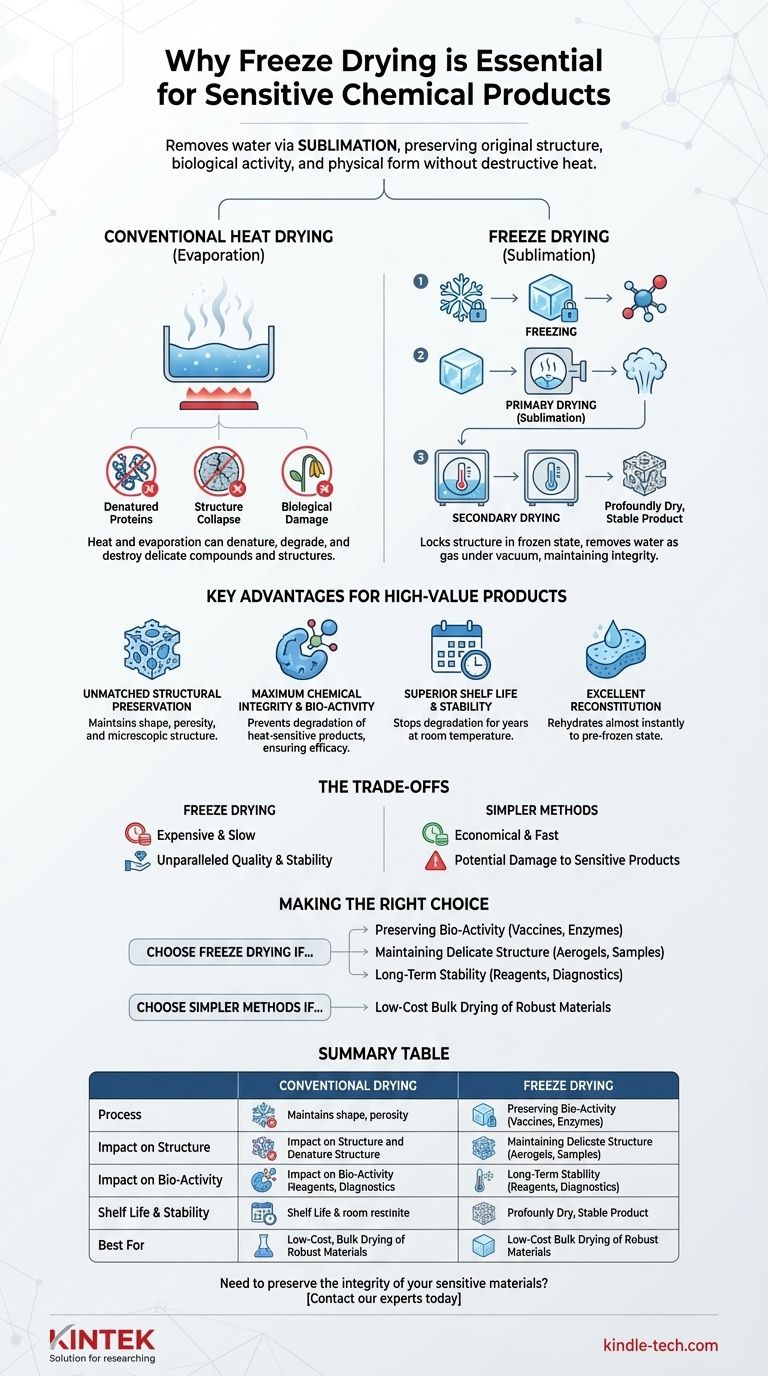
In essence, freeze drying is the premier method for preserving sensitive chemical and biological products because it removes water without using destructive heat. By turning ice directly into vapor in a process called sublimation, it maintains the product's original molecular structure, biological activity, and physical form, something that conventional drying methods cannot achieve.
The core problem with traditional drying is that heat and liquid water can irreversibly damage delicate products. Freeze drying masterfully bypasses this by locking the product's structure in a frozen state and gently removing the water as a gas, resulting in unparalleled preservation.

The Principle: Bypassing Destruction with Sublimation
To understand why freeze drying is so effective, it's useful to first consider why conventional methods often fail.
The Failure of Conventional Heat Drying
Most drying methods rely on evaporation—applying heat to turn liquid water into vapor. This process can be destructive for sensitive materials.
The heat can denature proteins, degrade complex chemical compounds, and destroy biological activity. Furthermore, as water leaves, surface tension can cause delicate structures to shrink, crack, or collapse, permanently altering the product.
The Freeze-Drying Process: From Solid to Gas
Freeze drying, or lyophilization, avoids these issues by leveraging a physical phenomenon called sublimation.
The process involves three main stages:
- Freezing: The product is rapidly frozen, locking its molecular structure and components in place.
- Primary Drying (Sublimation): The frozen product is placed under a deep vacuum. This allows the ice to turn directly into water vapor without ever melting into a liquid.
- Secondary Drying: A slight temperature increase removes any remaining, unfrozen water molecules, resulting in a profoundly dry and stable final product.
Key Advantages for High-Value Products
This unique process delivers several critical advantages, especially for advanced materials, pharmaceuticals, and biologicals.
Unmatched Structural Preservation
Because the product is frozen solid during water removal, its original shape, porosity, and microscopic structure are maintained.
For materials like graphene aerogels or tissue engineering scaffolds, this is essential. Freeze drying creates a qualified precursor with a highly porous structure that would simply collapse if dried using conventional heat.
Maximum Chemical Integrity and Bio-Activity
The low-temperature process is incredibly gentle. It prevents the degradation of heat-sensitive products.
This is critical for pharmaceuticals, enzymes, vaccines, and probiotics, where biological activity is the entire point of the product. Freeze drying ensures their efficacy is preserved, which heat-based methods would destroy.
Superior Shelf Life and Stability
Removing water to such a low level—often below 1%—effectively halts biological and chemical degradation.
The absence of water inhibits the growth of bacteria, molds, and other microorganisms. This allows products to be stored for years at room temperature without refrigeration, dramatically reducing shipping and storage costs.
Excellent Reconstitution
The preserved porous structure acts like a sponge. When water or another solvent is added, the freeze-dried product rehydrates or dissolves almost instantly, returning to a state that is nearly identical to its pre-frozen condition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its benefits, freeze drying is not a universal solution. Its advantages come with clear trade-offs.
The Factor of Cost and Time
Freeze-drying equipment—requiring robust refrigeration and vacuum systems—is expensive. The process is also significantly slower and more energy-intensive than conventional heat drying, with cycles often lasting for days.
When Simpler Methods Suffice
For robust, non-sensitive bulk materials where precise structure and full bio-activity are not critical, simpler methods are far more economical. Oven drying or spray drying are perfectly suitable for materials that can withstand heat without significant degradation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
The decision to use freeze drying must be based on the specific requirements of your product and its end-use.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological activity: Freeze drying is the gold standard for products like vaccines, enzymes, or microbial cultures.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a delicate physical structure: Freeze drying is essential for creating materials like aerogels, scientific samples for microscopy, or pharmaceutical cakes.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability without refrigeration: Freeze drying provides an unmatched shelf life for reagents, reference standards, and field-deployed diagnostics.
- If your primary focus is low-cost bulk drying of a robust material: A simpler, heat-based drying method will be far more economical and efficient.
By understanding its principles, you can leverage freeze drying not just as a preservation method, but as a critical tool for creating higher-quality, more stable, and more effective products.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Conventional Drying | Freeze Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heat-based evaporation | Sublimation under vacuum |
| Impact on Structure | Can cause shrinkage/collapse | Maintains original porous structure |
| Impact on Bio-Activity | High risk of degradation | Preserves activity of enzymes, vaccines |
| Shelf Life & Stability | Limited, may require refrigeration | Years at room temperature |
| Best For | Robust, non-sensitive materials | Sensitive pharmaceuticals, biologicals, advanced materials |
Need to preserve the integrity of your sensitive materials? KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory freeze dryers and expert support for pharmaceuticals, biological samples, and advanced materials. Our solutions ensure your products maintain their structure, activity, and stability. Contact our experts today to find the perfect freeze-drying system for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Why is freeze drying considered more effective than ordinary drying? Preserve Structure, Nutrients & Flavor
- What are the main steps involved in the freeze-drying process? A Guide to the 3 Key Stages
- What is the purpose of laboratory freeze drying? Preserve Sensitive Drugs & Biologics for Stability
- What types of liquid samples can be processed using a laboratory freeze dryer? Preserve Your Sensitive Materials
- What role do laboratory freeze dryers play in the food industry? Unlock Superior Food Preservation



















