At its core, hydrogen is used in annealing furnaces for two primary reasons: it is an exceptional reducing agent that prevents surface oxidation, and its high thermal conductivity allows for much faster heating and cooling cycles. This combination results in a cleaner final product and a more efficient thermal process.
The decision to use a hydrogen atmosphere is a critical trade-off. It offers unparalleled surface quality and process speed but introduces significant safety risks and material compatibility challenges that must be engineered and managed with precision.

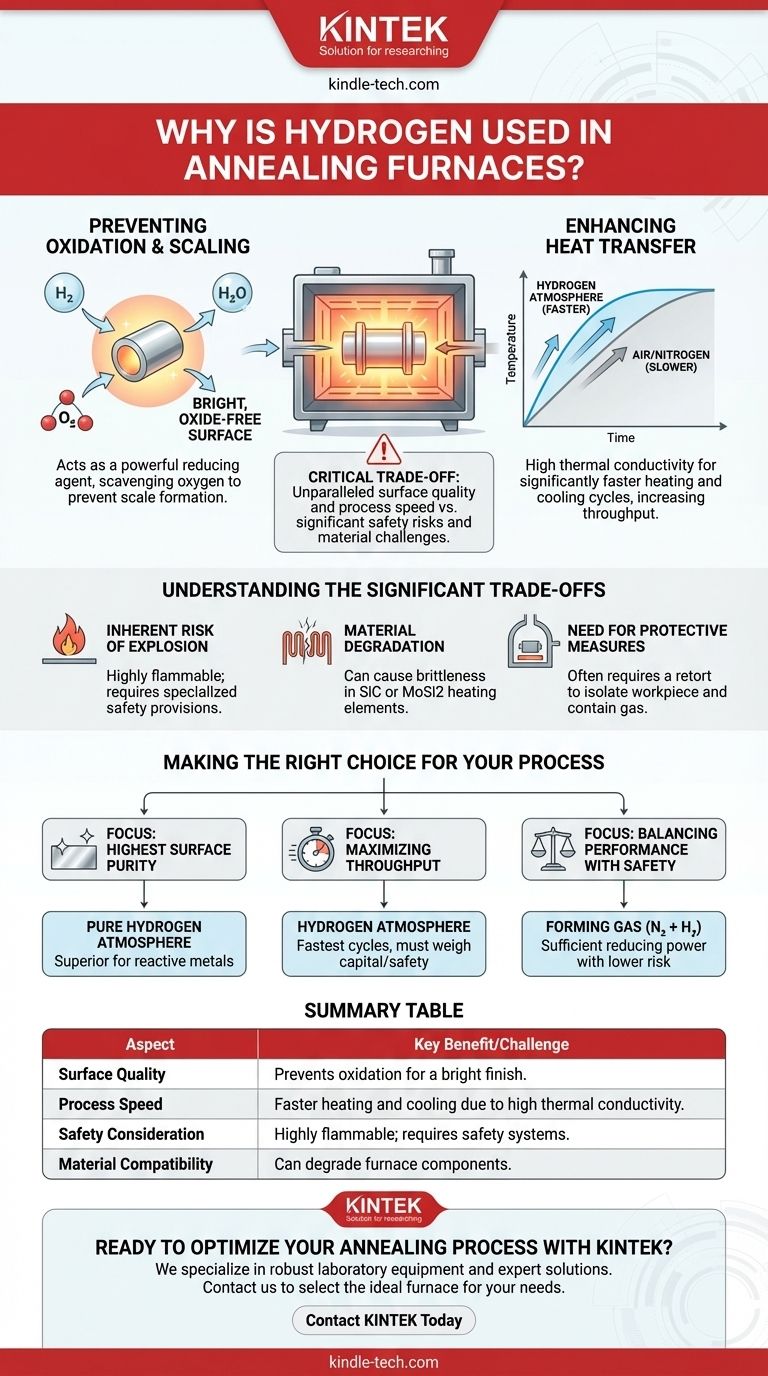
The Core Functions of Hydrogen in Annealing
To understand the use of hydrogen, we must look at its specific chemical and physical properties at high temperatures. These properties directly address common challenges in heat treatment.
Preventing Oxidation and Scaling
During annealing, the heated metal surface is highly reactive with any oxygen present. This reaction forms an undesirable layer of oxides, often called scale.
Hydrogen acts as a powerful reducing agent. It proactively scavenges and reacts with residual oxygen in the furnace, forming water vapor (H₂O) and preventing the oxygen from bonding with the metal's surface.
This results in a bright, clean, and oxide-free surface straight out of the furnace, often eliminating the need for subsequent costly and time-consuming cleaning processes like acid pickling or abrasive blasting.
Enhancing Heat Transfer
Hydrogen gas has a very high thermal conductivity, far greater than air or nitrogen.
This physical property means it transfers heat to and from the part much more effectively. The practical benefits are significantly faster heating and cooling rates.
Faster cycle times increase the overall throughput and efficiency of the manufacturing operation.
Understanding the Significant Trade-offs
While the benefits are clear, hydrogen is a demanding and hazardous process gas that requires specialized equipment and strict safety protocols.
The Inherent Risk of Explosion
Hydrogen is highly flammable and can form an explosive mixture with air.
Furnaces using hydrogen atmospheres must be equipped with comprehensive safety provisions, such as purging cycles, gas monitoring systems, and explosion-proof construction, to mitigate this risk.
Material Degradation and Brittleness
At high temperatures, hydrogen can react negatively with certain materials used to build the furnace itself.
Heating elements made from materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) can become brittle and have a shortened lifespan when exposed to a hydrogen-rich atmosphere.
The Need for Protective Measures
To manage these challenges, high-temperature hydrogen furnaces often use an inner sealed chamber called a retort.
The retort contains the hydrogen atmosphere and the workpiece, effectively isolating it from the furnace's primary heating elements and insulation. This protects the furnace components from chemical attack and contains the hazardous gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right atmosphere depends entirely on the material being processed, the required surface finish, and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible surface purity: A pure hydrogen atmosphere is often the superior choice for highly reactive metals like stainless steels or for parts requiring a perfectly bright finish.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Hydrogen's excellent thermal conductivity enables the fastest possible heating and cooling cycles, but this must be weighed against the high capital and safety overhead.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance with safety: A "forming gas," a non-flammable mixture of nitrogen and a small percentage of hydrogen, often provides sufficient reducing power with a much lower safety risk.
Ultimately, leveraging a hydrogen atmosphere is a calculated engineering decision that balances the pursuit of perfect surface quality against the management of operational risk.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Benefit/Challenge |
|---|---|
| Surface Quality | Prevents oxidation, resulting in a bright, oxide-free finish. |
| Process Speed | High thermal conductivity allows for faster heating and cooling cycles. |
| Safety Consideration | Highly flammable; requires specialized safety systems and equipment. |
| Material Compatibility | Can degrade certain furnace components like silicon carbide heating elements. |
Ready to optimize your annealing process with the right atmosphere?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and expert solutions for demanding thermal processing applications. Whether you're working with reactive metals requiring a pristine hydrogen atmosphere or need a safer alternative like forming gas, our team can help you select the ideal furnace configuration to balance performance, safety, and efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss your specific annealing needs and discover how KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment can enhance your results and productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions
- Why is a hydrogen atmosphere furnace necessary for W-Cu composite? Unlock Superior Infiltration and Density
- What is the use of hydrogen in furnace? A Key to Oxygen-Free High-Temperature Processing
- Why is an industrial furnace with hydrogen atmosphere control necessary for the pre-sintering of Fe-Cr-Al materials?
- What are hydrogen furnaces used for? Achieve Purity and Speed in High-Temperature Processing



















