In the world of advanced materials, sintering is the essential manufacturing process that transforms a compacted mass of ceramic powder into a strong, dense, and highly functional solid. Without sintering, ceramics would remain brittle and porous, lacking the fundamental properties—like exceptional hardness, mechanical strength, and thermal stability—that make them indispensable in modern technology.
Sintering is far more than simple heating; it is a process of microstructural engineering. Its primary importance lies in its ability to systematically eliminate porosity, fusing individual particles into a monolithic body to unlock a ceramic's intrinsic properties and enable the creation of complex, high-performance components.
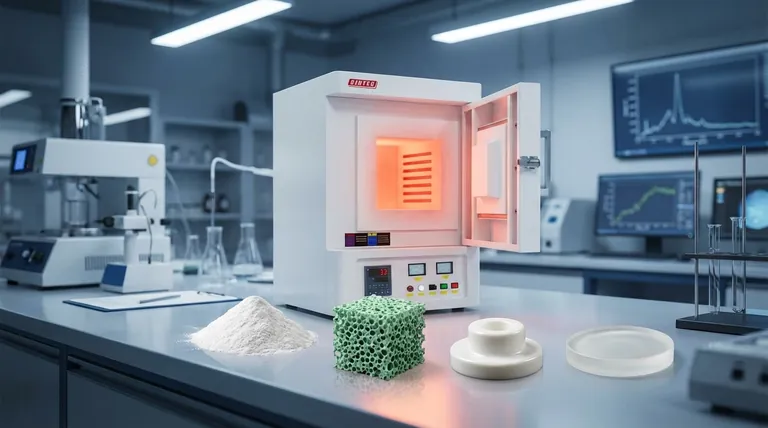

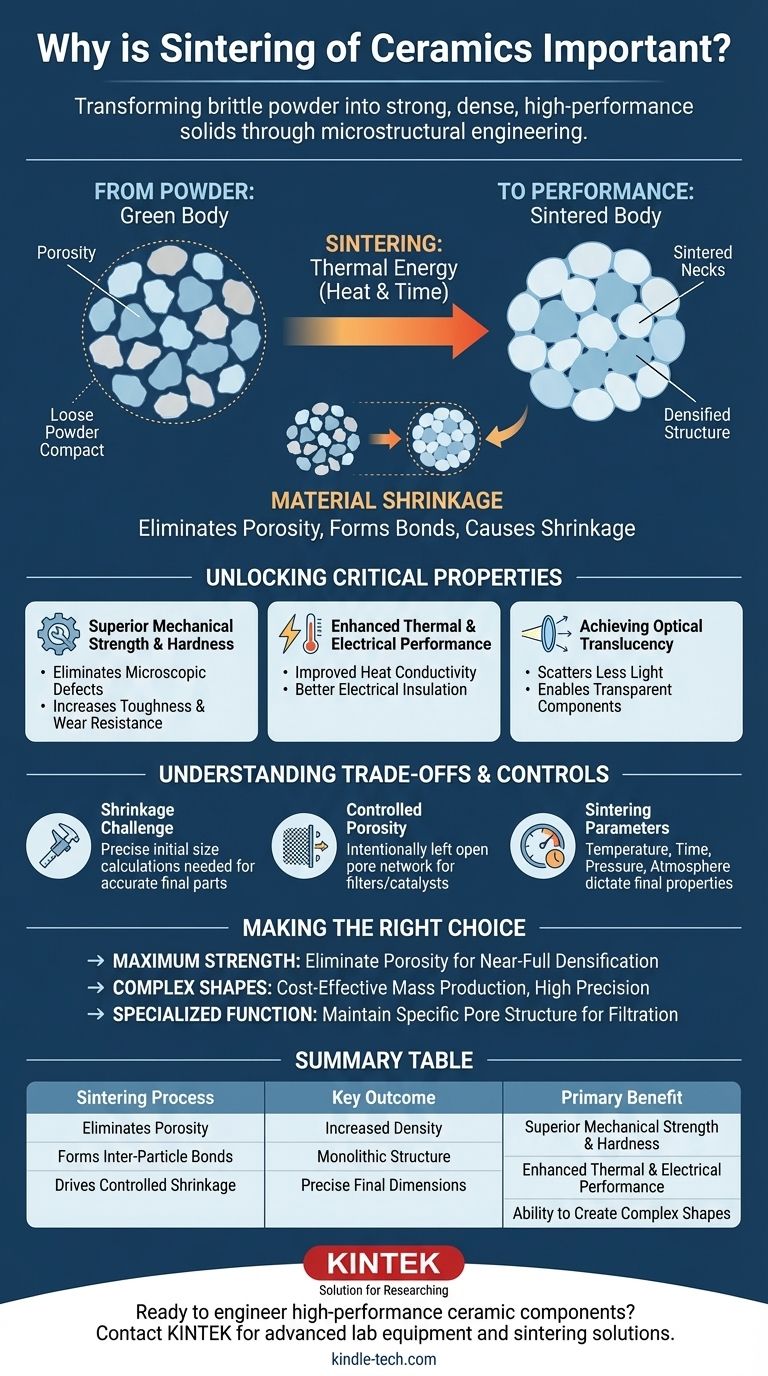
From Powder to Performance: The Core Transformation
Sintering creates a dense, solid part from a fragile powder compact. This transformation is driven by thermal energy, which initiates diffusion and bonding between particles at temperatures below the material's melting point.
Eliminating Porosity
The starting point for a ceramic component is often a "green body," which is a compacted collection of powders with significant empty space, or porosity, between the particles. Sintering uses high heat to cause the atoms to migrate, filling these voids and drastically increasing the material's density.
Forming Inter-Particle Bonds
As the temperature rises, the individual ceramic particles begin to fuse at their points of contact. These connections, known as "sintered necks," grow over time, gradually replacing the empty spaces and creating a strong, interconnected network.
The Result of Material Shrinkage
The direct consequence of eliminating pores is that the entire component shrinks in size. This consolidation of the powdery structure is the defining physical change that turns a fragile shape into a robust, solid object.
Unlocking Critical Engineering Properties
The reduction of porosity directly translates into a dramatic improvement in the material's performance characteristics. This is the central reason why sintering is so crucial.
Superior Mechanical Strength and Hardness
Pores act as microscopic defects where cracks can easily initiate under stress. By eliminating these voids, sintering significantly increases a ceramic's strength, toughness, and hardness, making materials suitable for demanding applications like cutting tools and wear-resistant components.
Enhanced Thermal and Electrical Performance
A dense, non-porous structure is far more effective at conducting heat. Sintering improves a material's thermal conductivity and stability. This process is also fundamental to creating high-performance electrical insulators and other electronic components.
Achieving Optical Translucency
For certain advanced ceramics, achieving transparency is a key goal. Pores scatter light, making a material opaque. By sintering a ceramic to full density, it is possible to create translucent or transparent components used in applications like high-pressure lamps or armor.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Controls
While powerful, sintering is a precise process that requires careful management to achieve the desired outcome. The process is not without its challenges and requires a deep understanding of material science.
The Challenge of Shrinkage
Because the part shrinks during sintering, its initial "green body" dimensions must be carefully calculated to achieve the correct final size. Predicting and controlling this shrinkage is critical for producing accurate and repeatable parts.
Controlled Porosity for Special Applications
While maximum density is often the goal, some applications require a specific level of porosity. For components like filters or catalysts, sintering is controlled to create sufficient particle bonding for strength while intentionally leaving an open, interconnected pore network.
The Impact of Sintering Parameters
The final properties of the ceramic are dictated by the sintering parameters. Factors like temperature, time, pressure, and atmospheric conditions are meticulously controlled to manage grain growth and achieve the desired microstructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying sintering effectively means aligning the process with the final application's requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability: The goal is to achieve near-full densification by optimizing sintering parameters to eliminate virtually all porosity.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes at scale: Sintering offers a cost-effective path to mass-producing intricate parts with high precision, bypassing difficult and expensive machining operations.
- If your primary focus is a specialized function like filtration: The process must be controlled to maintain a specific, interconnected pore structure while still providing the necessary structural integrity.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about controlling the microstructure to precisely engineer the final properties of a ceramic component.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Process | Key Outcome | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Eliminates Porosity | Increased Density | Superior Mechanical Strength & Hardness |
| Forms Inter-Particle Bonds | Monolithic Structure | Enhanced Thermal & Electrical Performance |
| Drives Controlled Shrinkage | Precise Final Dimensions | Ability to Create Complex Shapes |
Ready to engineer high-performance ceramic components? The precise control of the sintering process is key to achieving the exact material properties your application demands. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for perfecting ceramic sintering. Whether your goal is maximum density, controlled porosity, or complex shape formation, our solutions support your R&D and production needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you unlock the full potential of your ceramic materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- Why is it called a muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Heating
- What is a muffle furnace used to estimate? A Key Tool for Precise Ash Determination
- What is the operation temperature of the muffle furnace? A Guide to Internal and Ambient Ranges
- What is the importance of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precision Heating



















