Making things hot is easy. Any resistance coil and a power source can generate heat.
Making things hot exactly the same way twice is incredibly difficult.
In the world of material science and chemical engineering, heat is not just a utility; it is a variable. If that variable fluctuates—if the temperature at the center of your sample differs from the temperature at the edge by even a few degrees—your data is compromised. Uncertainty is the enemy of the laboratory.
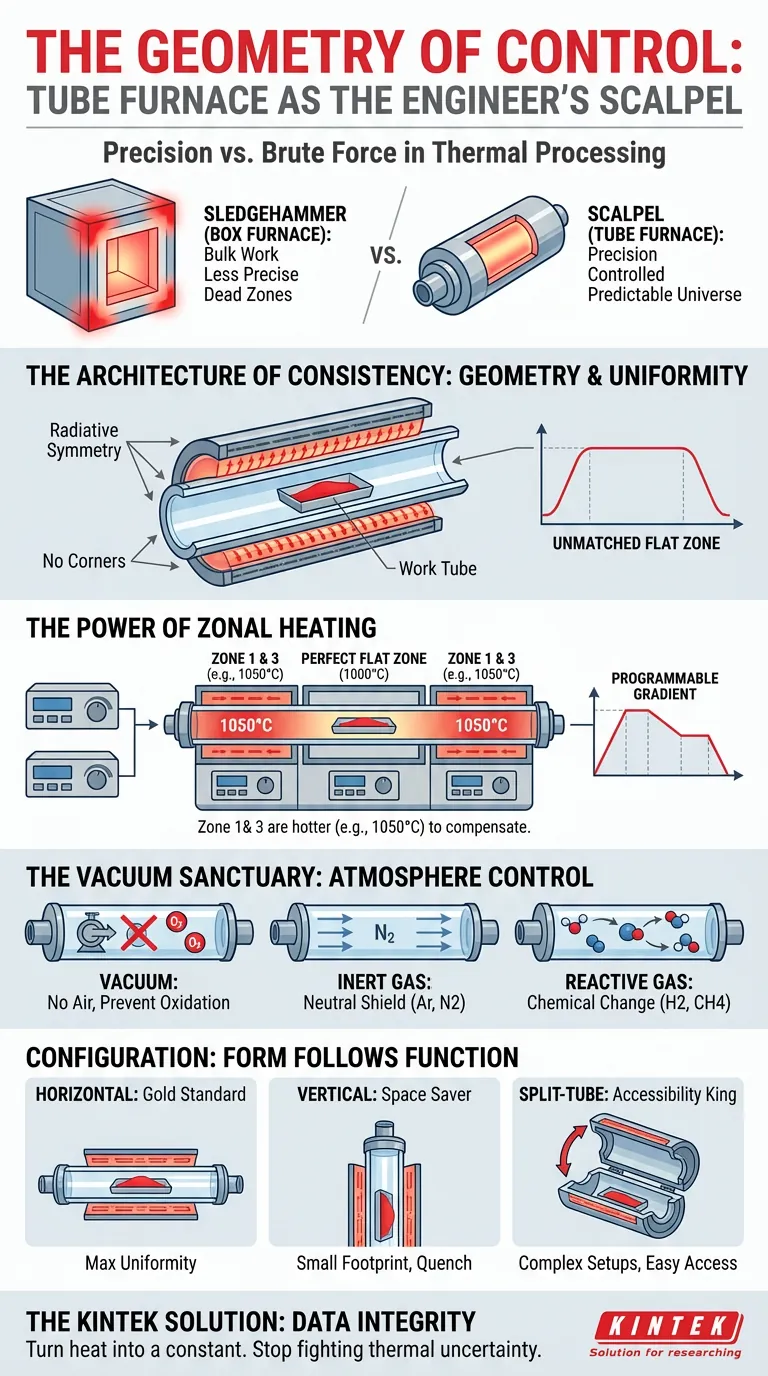
The standard box furnace is the sledgehammer of the thermal world. It is powerful, spacious, and effective for bulk work. But when precision is non-negotiable, you need a scalpel.
Enter the tube furnace. Its value isn't just that it gets hot; it is that it creates a predictable, isolated universe for your sample.
The Architecture of Consistency
The primary struggle in thermal processing is uniformity.
In a square box, corners trap heat or create cold spots (dead zones). Air currents behave chaotically.
The tube furnace solves this through geometry. By arranging heating elements around a cylindrical work tube, it creates a symmetrical thermal environment. There are no corners. Radiative heat transfer is equal from all sides.
This creates an unmatched flat zone—a specific length within the tube where the temperature is constant.
The Power of Zonal Heating
Modern engineering takes this a step further with multi-zone heating.
Imagine dividing the tube into three or five distinct sections, each with its own controller. You can program the ends to run hotter to compensate for heat loss, extending the length of your perfect flat zone.
Or, you can do something more romantic: you can create a deliberate gradient. You can force a material to melt at one end and recrystallize at the other. This level of control allows you to "paint" with temperature.
The Vacuum Sanctuary
The second struggle in the lab is contamination.
Oxygen is chemically aggressive. At high temperatures, it ruins samples, oxidizes metals, and skews results.
A box furnace is difficult to seal perfectly. A tube furnace, by design, is a pressure vessel.
Because the work tube is physically distinct from the heating elements, you can hermetically seal the ends. This turns the tube into a sanctuary.
- Vacuum: Remove the air entirely to prevent oxidation.
- Inert Gas: Flood the tube with Argon or Nitrogen to create a neutral shield.
- Reactive Gas: Introduce Hydrogen or Methane to induce specific chemical changes.
You are not just controlling the temperature; you are controlling the atmosphere.
Configuration: Form Follows Function
The "tube furnace" is a category, not a single device. The orientation you choose dictates what you can achieve.
1. Horizontal: The Gold Standard
This is the default for a reason. Gravity works with you to keep the sample centered in the hot zone.
- Best for: Maximum thermal uniformity.
- Use case: Thermally sensitive parts and long-duration synthesis.
2. Vertical: The Space Saver
Floorspace in a lab is expensive real estate. A vertical furnace minimizes the footprint.
- Best for: Compact labs and batch processing.
- Use case: Top-loading samples or quench testing (dropping a sample directly from the hot zone into a cooling medium).
3. Split-Tube: The Accessibility King
Standard tubes require you to slide the sample in from the end. But what if your reaction vessel has complex plumbing, large flanges, or wires attached? You can't thread it through.
- Best for: Complex setups.
- Use case: The furnace body is hinged. It opens like a clam shell, allowing you to place the reactor directly inside.
The Operational Reality
There is no free lunch in engineering. The precision of a tube furnace comes with trade-offs that must be managed.
Throughput is lower. You are usually placing samples in small "boats" and pushing them into the center with a rod. It is a manual, deliberate process. It is perfect for R&D, but harder to scale for mass production.
Tubes are consumables. Whether quartz, alumina, or silicon carbide, the tube faces the harshest conditions. It undergoes thermal shock and chemical attack. It will eventually fail, and it must be replaced.
Maintenance is mandatory. To maintain that perfect uniformity, insulation must be checked, and elements must be calibrated.
Summary: The Right Tool for the Job
If you are just burning off binder from a ceramic block, use a box furnace. But if you are growing crystals, sintering advanced ceramics, or testing thermocouples, the physics of the tube furnace are superior.
| Feature | The Engineering Benefit | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Design | Eliminates corner "dead zones" for radiative symmetry. | High-precision material synthesis. |
| Sealed Work Tube | Isolates sample from heating elements and outside air. | Vacuum or inert gas processing. |
| Multi-Zone Control | Extends the "flat zone" or creates programmable gradients. | Thermal CVD or gradient testing. |
| Split Configuration | Allows access to the heated length without threading. | Complex reactors with fixed plumbing. |
The KINTEK Solution
At KINTEK, we understand that you aren't just buying a heater; you are buying data integrity.
Whether you need the absolute precision of a horizontal multi-zone unit, the footprint efficiency of a vertical model, or the flexibility of a split-tube design, our equipment is built to turn the variable of heat into a constant.
We also supply the critical consumables—the boats, the tubes, and the fittings—that keep your process running.
Stop fighting with thermal uncertainty.
Contact Our Experts to discuss your specific temperature profiles and atmospheric requirements. Let’s build a reproducible environment for your best work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
Related Articles
- The Geometry of Heat: Engineering the Perfect Thermal Environment
- The Silent Partner in Pyrolysis: Engineering the Perfect Thermal Boundary
- Advantages of Using CVD Tube Furnace for Coating
- Gravity, Geometry, and Heat: The Engineering Behind Tube Furnace Orientation
- The Glass Ceiling: Navigating the True Thermal Limits of Quartz Tube Furnaces




















