Science is often a battle against variables. In the laboratory, heat is one of the oldest and most volatile variables to control.
When you are equipping a lab, the decision between a muffle furnace and a tube furnace often feels like a technicality. It isn’t.
It is a fundamental choice about the philosophy of your experiment.
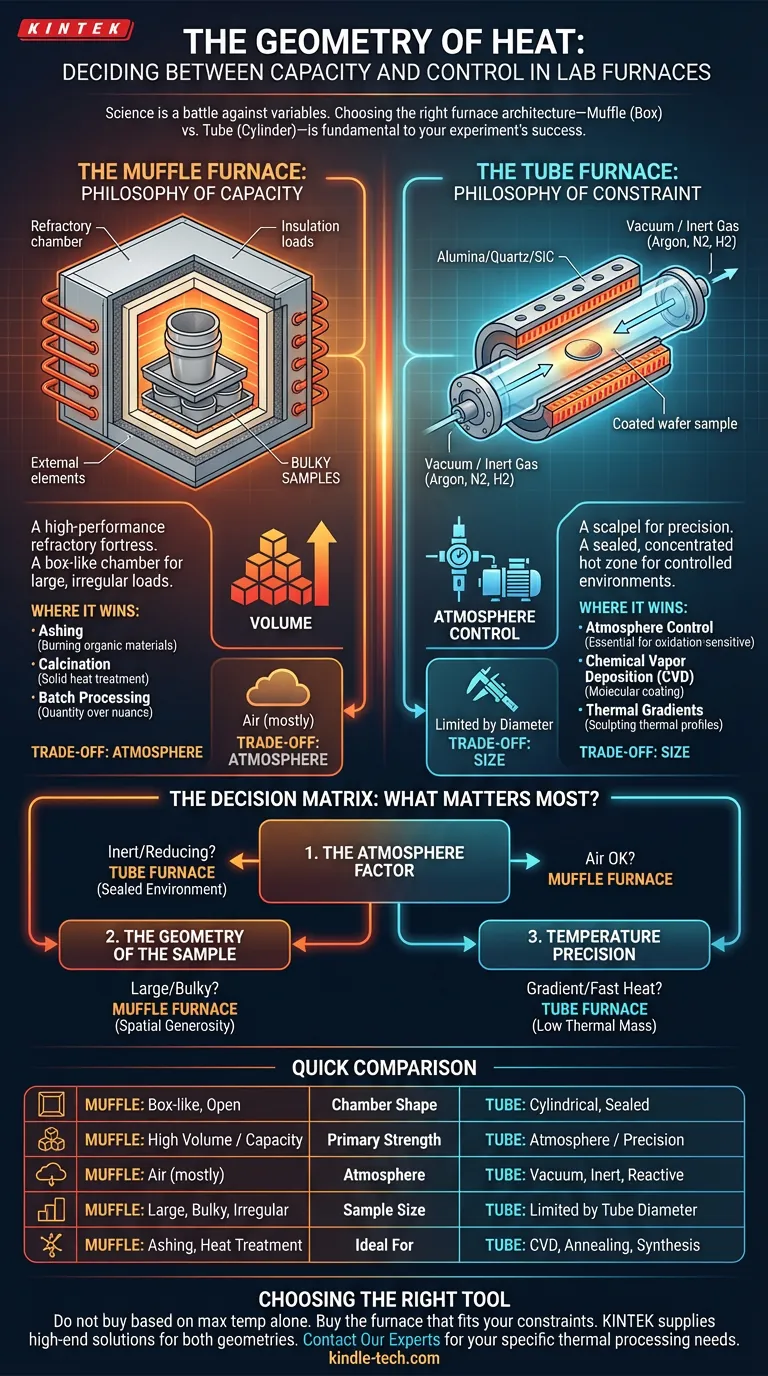
At its core, the difference comes down to geometry. One is a box; the other is a cylinder. That simple physical distinction dictates everything else: from how much you can heat, to the purity of the air surrounding your sample.
Here is how to choose the right architecture for your heat treatment.
The Muffle Furnace: The Philosophy of Capacity
Think of the muffle furnace as a high-performance, refractory fortress.
It features a box-like chamber, usually insulated with ceramic fiber. The heating elements are external to the working volume. The design is ancient, robust, and effective.
The primary advantage here is volume.
Because the chamber is a square or rectangular void, it is forgiving. You can load bulky samples. You can stack crucibles. You can process trays of powder.
Where it wins:
- Ashing: Burning off organic materials requires space and airflow.
- Calcination: Heat treatment of solid chemical compounds.
- Batch Processing: When quantity matters more than atmospheric nuance.
The trade-off? The atmosphere. A muffle furnace is generally designed to heat samples in air. While some models allow for basic gas venting, they are not sealed systems. You are heating the sample and the room air trapped inside.
The Tube Furnace: The Philosophy of Constraint
If the muffle furnace is a blunt instrument, the tube furnace is a scalpel.
The design is built around a narrow cylinder—typically made of alumina, quartz, or silicon carbide. Heating elements surround this tube, creating a concentrated, uniform hot zone.
The physical constraint is the point.
Because the heating chamber is a tube, the ends can be sealed. This changes the game entirely. Once sealed, you can evacuate the air to create a vacuum. Or, you can flow specific gases—Argon, Nitrogen, Hydrogen—through the tube.
Where it wins:
- Atmosphere Control: Essential for processes that oxidize instantly in air.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Coating materials at the molecular level.
- Thermal Gradients: Multi-zone tube furnaces can hold different temperatures at different points along the tube, allowing you to "sculpt" the thermal profile.
The trade-off? Size. You are limited by the diameter of the tube, often just 1 to 6 inches. If your sample doesn't fit in the cylinder, the experiment is over before it begins.
The Decision Matrix: What Matters Most?
In engineering, there are no perfect solutions, only trade-offs.
When our clients at KINTEK ask which unit they need, we look at the failure points of their intended experiments. We ask what creates the bottleneck.
Here is the breakdown of the trade-offs:
1. The Atmosphere Factor
This is the decisive factor. If your material requires an inert atmosphere or a reducing environment (like Hydrogen), a muffle furnace will likely fail you. It cannot maintain the purity required.
You need the sealed environment of a tube furnace.
2. The Geometry of the Sample
If you are testing large mechanical components or processing liters of material at once, a tube furnace is physically incapable of doing the job.
You need the spatial generosity of a muffle furnace.
3. Temperature Precision
Tube furnaces generally have a smaller thermal mass. They heat up faster. They cool down faster.
More importantly, multi-zone tube furnaces allow for gradient control. This is critical for crystal growth, where one end of the sample must be hotter than the other. A muffle furnace is designed to be one uniform temperature throughout.
Quick Comparison
For the engineer who prefers data over narrative, here is the functional split:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Shape | Box-like, open | Cylindrical, sealed |
| Primary Strength | High volume / Capacity | Atmosphere / Precision |
| Atmosphere | Air (mostly) | Vacuum, Inert, Reactive |
| Sample Size | Large, bulky, irregular | Limited by tube diameter |
| Ideal For | Ashing, Heat Treatment | CVD, Annealing, Synthesis |
Choosing the Right Tool
Do not buy a furnace based on maximum temperature alone. Both types can reach 1700°C.
Buy the furnace that fits your constraints.
- Choose the Muffle Furnace for robustness, ease of loading, and processing bulky batches in air.
- Choose the Tube Furnace for precision, atmospheric purity, and complex thermal profiling.
At KINTEK, we understand that equipment is just a means to an end. The goal is the successful experiment. We supply high-end solutions for both geometries, ensuring that whether you need capacity or control, the heat is applied exactly where you need it.
Unsure if your sample will fit or if your atmosphere requires a vacuum seal?
Contact Our Experts to discuss your specific thermal processing needs, and let us help you engineer the perfect setup.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
Related Articles
- Muffle vs. Tube Furnace: How One Choice Prevents Costly Research Failures
- Why Your Furnace Experiments Fail: The Hidden Mismatch in Your Lab
- Comprehensive Guide to Muffle Furnaces: Types, Uses, and Maintenance
- Box Furnace vs. Muffle Furnace: Are You Using the Wrong Tool for the Job?
- Why Your High-Temperature Experiments Fail: The Furnace Flaw Most Labs Overlook




















