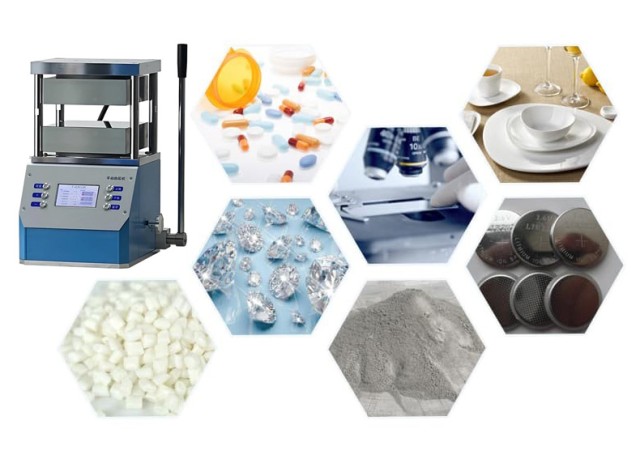
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Heated Lab Presses: A Versatile Laboratory Tool
- Types of Heated Lab Presses: Hot-Press vs. Cold-Induction
- Key Features of Heated Lab Presses: Ensuring Accuracy and Efficiency
- Applications of Heated Lab Presses: A Wide Range of Possibilities
- Safety Considerations for Heated Lab Presses: Ensuring a Secure Environment
- Maintenance and Care of Heated Lab Presses: Ensuring Longevity and Performance
- Conclusion: The Power of Heated Lab Presses in Scientific and Industrial Settings
Introduction to Heated Lab Presses: A Versatile Laboratory Tool
Heated Lab Presses stand as indispensable tools in scientific research and industrial settings, empowering laboratories to manipulate materials, prepare samples, and conduct experiments with utmost precision. Their ability to apply controlled heat and pressure enables researchers and technicians to shape materials, cure composites, and analyze substances under specific conditions. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of Heated Lab Presses, exploring their types, applications, key features, safety measures, and maintenance tips. Discover how these versatile tools contribute to advancements in various fields, ranging from polymer processing and composite manufacturing to ceramic fabrication and pharmaceutical research.
Types of Heated Lab Presses: Hot-Press vs. Cold-Induction
Hot-Press:
A hot press, also known as a heat press machine or hydraulic hot press, is a device specifically designed for pressing and bonding materials under controlled temperature and pressure. It utilizes heat transfer principles to modify the internal energy of the materials involved, as per the First Law of Thermodynamics. The heating-up speed can be adjusted according to the specific product being processed.
Function:
Hot presses play a crucial role in industries and laboratories for various applications, such as:
-
Lamination: Hot presses are widely used for laminating different materials together, creating composites or multilayer structures. The heat and pressure applied ensure a strong bond between the layers.
-
Molding: Hot presses are employed in the molding process of materials, such as plastics and ceramics. The heat and pressure help shape the material into the desired form, resulting in precise and consistent products.
-
Curing: Hot presses are utilized to cure adhesive materials, composites, and coatings. The controlled temperature and pressure promote proper curing, enhancing the material's properties and performance.
-
Compacting: Hot presses are effective in compacting powders and granular materials, reducing their porosity and increasing their density. This process is commonly used in metallurgy, ceramics, and pharmaceutical industries.
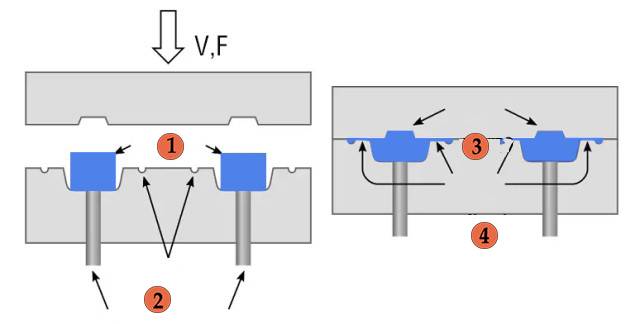
Features:
Hot presses typically offer a range of features to ensure efficient and precise operation:
-
Temperature Control: Hot presses provide precise temperature control, often achieved through the use of pulse heating technology. The temperature sampling frequency can be as low as 0.1 seconds, enabling accurate and consistent heating.
-
Working Modes: Hot presses offer various working modes to accommodate different applications. These modes may include a single working platform, rotary working platform, left-right mobile platform, and more.
-
Multi-stage Temperature Rise: Hot presses allow for multi-stage temperature rise, enabling controlled heating profiles. This feature is particularly useful for materials that require specific temperature conditions during processing.
-
Real-time Temperature Curve Display: Hot presses often feature a real-time temperature curve display, allowing operators to monitor the temperature profile throughout the process. This helps ensure consistent and repeatable results.
-
Silicone Tape Indexing Mechanism: Hot presses may incorporate a silicone tape indexing mechanism, which provides accurate alignment and positioning of materials during processing.
-
CCD Vision System: Some hot presses are equipped with a CCD vision system, enabling precise alignment and quality control.
-
Program Storage and Protection: Hot presses often allow multiple programs to be pre-stored, simplifying operation and reducing setup time. Additionally, program password protection ensures unauthorized changes are prevented.
Key Features of Heated Lab Presses: Ensuring Accuracy and Efficiency
Heated lab presses are indispensable tools in various scientific and industrial applications, enabling precise temperature control and uniform pressure distribution for sample preparation, material testing, and composite bonding. These advanced devices offer a range of features that contribute to their effectiveness and accuracy:
1. Temperature Uniformity:
Precise temperature control is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable results. Heated lab presses employ advanced heating systems that utilize pulse heating technology for precise temperature regulation. This technology enables rapid temperature rise and accurate maintenance of set temperatures, with sampling frequencies as high as 0.1 seconds. The uniform distribution of heat across the platens ensures consistent sample heating and eliminates temperature variations that could compromise the integrity of the experiment.
2. Platen Size and Versatility:
Heated lab presses come in various platen sizes to accommodate different sample dimensions and applications. Larger platens allow for the simultaneous processing of multiple samples, increasing efficiency and throughput. Some models offer interchangeable platens with different surface materials, such as stainless steel, ceramic, or aluminum, to suit specific experimental requirements. Additionally, various working modes, including single working platform, rotary working platform, and left-right mobile platform, enhance the versatility of these devices.
3. Pressure Control:
Precise pressure control is essential for achieving uniform sample compaction and ensuring consistent results. Heated lab presses utilize advanced pressure control systems that enable fine-tuning of the applied pressure. The pressure can be adjusted in multiple stages to accommodate different materials and processes. This feature allows researchers to optimize pressure settings for specific applications, ensuring the desired level of compaction and bonding.
4. Computer-Controlled Operation:
Modern heated lab presses are equipped with computer-controlled interfaces that provide intuitive operation and precise control over the press parameters. These user-friendly interfaces allow researchers to program and monitor the press cycle, including temperature, pressure, and time. The ability to store multiple programs enables the efficient execution of repetitive tasks and ensures consistent results across experiments.
Applications of Heated Lab Presses: A Wide Range of Possibilities
Heated lab presses are versatile tools used in various industries for diverse applications. Their ability to apply controlled heat and pressure makes them ideal for processes such as polymer processing, composite manufacturing, ceramic fabrication, and pharmaceutical research.
Polymer Industry:
In the polymer industry, heated lab presses are employed to induce high-pressure conditions for polymerization reactions. This process transforms monomers into long-chain polymers, enabling the creation of various polymer products. By utilizing high-pressure reactors, it becomes possible to accelerate polymerization rates, control molecular weight distribution, and enhance the properties of the final polymer products.
Material Science and Technology:
Heated lab presses play a crucial role in material science and nanotechnology, facilitating the production of advanced materials and nanoparticles. These high-pressure reactors enable the synthesis of unique materials with specific properties, such as enhanced strength, improved catalytic activity, and optimized electrical conductivity.
Pharmaceutical Industry:
In the pharmaceutical industry, heated lab presses are used for various applications, including tablet manufacturing, encapsulation, and drug synthesis. The precise control of temperature and pressure allows for the formation of uniform tablets with consistent active ingredient distribution. Additionally, heated lab presses facilitate the encapsulation of drugs into specific carriers, enhancing drug delivery and bioavailability.

Other Applications:
Heated lab presses also find applications in various other industries, including:
-
Laminating: Bonding multiple layers of materials together under heat and pressure, creating composite structures with enhanced strength and durability.
-
Rubber and Plastic Molding: Shaping rubber and plastic materials into specific forms using heated molds and pressure. This process is commonly used in the manufacturing of automotive parts, electrical components, and household items.
-
R&D Work and Testing: Heated lab presses are valuable tools in research and development laboratories, enabling scientists and engineers to investigate material properties, optimize processing parameters, and evaluate product performance.
-
Short Runs and Limited Production: Heated lab presses are suitable for small-scale production runs or limited manufacturing, allowing for the rapid prototyping of new products or the production of specialized components.
-
Cell Manufacturing and Lean Manufacturing: Heated lab presses play a role in cell manufacturing and lean manufacturing processes, facilitating the efficient production of high-quality products with minimal waste.
The versatility and wide-ranging applications of heated lab presses make them indispensable tools in various industries, contributing to advancements in material science, pharmaceutical research, and manufacturing processes.

Safety Considerations for Heated Lab Presses: Ensuring a Secure Environment
Heated Lab Presses are indispensable tools in various laboratory settings, enabling researchers to perform experiments involving high temperatures and pressures. However, these powerful devices also pose potential hazards if not handled properly. This section highlights the safety precautions that must be taken when operating Heated Lab Presses to ensure a secure environment for laboratory personnel and prevent accidents.
Potential Hazards:
-
High Pressure: Lab presses generate immense clamping pressure during operation, which can cause severe injuries if fingers or hands are caught between the platens.
-
High Temperature: Heated Lab Presses can reach extremely high temperatures, posing a burn hazard to users if proper protective measures are not taken.
-
Flying Debris: In the event of press failure or improper material handling, there is a risk of flying debris being ejected from the press, potentially causing injury to nearby individuals.
Guidelines for Safe Operation:
-
Protective Gear: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when operating a Heated Lab Press. This includes lab coats, safety glasses, gloves rated for high temperatures, and closed-toe shoes.
-
Training: Before operating a Heated Lab Press, all users must receive thorough training on its safe operation, including proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and maintenance protocols.
-
Safe Material Handling: Carefully select materials that are compatible with the temperature and pressure ranges of the press. Ensure that materials are properly secured and positioned within the press to prevent slippage or ejection.
-
Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect the press for any signs of wear, damage, or malfunction. Conduct routine maintenance and calibration as recommended by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance and safety.
-
Emergency Procedures: Develop and familiarize yourself with emergency procedures in case of accidents or press failure. This includes knowing how to shut down the press, activate safety features, and respond to potential hazards such as fires or chemical spills.
-
Safe Work Environment: Ensure that the lab press is operated in a well-ventilated area to prevent the accumulation of hazardous fumes or vapors. Keep the work area clean and free of clutter to minimize the risk of accidents.
-
Follow Manufacturer's Guidelines: Always adhere to the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for operating the Heated Lab Press. This includes following recommended temperature and pressure limits, using appropriate accessories, and conducting regular maintenance as specified.
By implementing these safety measures and fostering a culture of safety awareness in the laboratory, institutions can minimize the risks associated with Heated Lab Presses and create a secure environment for conducting experiments involving high temperatures and pressures.
Maintenance and Care of Heated Lab Presses: Ensuring Longevity and Performance
Providing essential maintenance tips to prolong the lifespan and ensure optimal performance of Heated Lab Presses. Cover routine inspections, cleaning procedures, and lubrication guidelines.

Routine Inspections
-
Check for Leaks: Regularly inspect the press for any leaks in hoses, seals, or fittings. Leaks can lead to loss of hydraulic fluid, reduced pressure, and potential safety hazards.
-
Inspect Seals and Gaskets: Examine seals and gaskets for signs of wear, cracks, or damage. Worn or damaged seals can cause leaks and affect the press's performance.
-
Check for Cracks: Inspect the press frame, platens, and other components for cracks or structural damage. Cracks can compromise the press's integrity and safety.
-
Monitor Vibration: Pay attention to any unusual vibrations or noises during press operation. Excessive vibration can indicate loose components, misalignment, or other issues that need attention.
Cleaning Procedures
-
Keep it Clean: Regularly clean the press's exterior surfaces to remove dirt, dust, and debris. Use a mild detergent and water solution, avoiding harsh chemicals that can damage the finish.
-
Clean Platens: Clean the platens thoroughly before and after each use. Remove any residue, contaminants, or lubricants from the platens to ensure proper heat transfer and sample integrity.
-
Inspect Hydraulic System: Periodically inspect the hydraulic system for contamination, discoloration, or signs of deterioration. Change hydraulic oil according to the manufacturer's recommendations or when necessary.
-
Lubricate Moving Parts: Lubricate moving parts, such as bearings, linkages, and slides, according to the manufacturer's instructions. Proper lubrication reduces friction, wear, and tear, extending the press's lifespan.
Lubrication Guidelines
-
Use the Right Lubricant: Select the appropriate lubricant based on the manufacturer's recommendations and the specific application. Different types of lubricants may be required for different components.
-
Lubricate Regularly: Follow the manufacturer's recommended lubrication schedule. Regular lubrication helps prevent wear and tear, reduces friction, and extends the life of moving parts.
-
Avoid Over-Lubrication: Over-lubrication can attract dirt and contaminants, leading to premature wear and potential safety hazards. Apply lubricant sparingly and only when necessary.
-
Monitor Lubricant Condition: Regularly check the condition of the lubricant. If it appears discolored, contaminated, or has lost its viscosity, it should be replaced.
By following these maintenance and care guidelines, you can help ensure the longevity, reliability, and optimal performance of your Heated Lab Press. Regular inspections, cleaning, and lubrication will minimize downtime, prevent costly repairs, and extend the lifespan of your valuable laboratory equipment.
Conclusion: The Power of Heated Lab Presses in Scientific and Industrial Settings
Heated Lab Presses stand as indispensable tools in scientific research and industrial applications, empowering laboratories with their versatility and precision. Their ability to shape materials, prepare samples, and conduct experiments with controlled temperature and pressure makes them essential for diverse fields. The two main types, Hot-Press and Cold-Induction, offer distinct advantages depending on the application. Key features like temperature uniformity, platen size, and computer-controlled operation ensure accuracy and efficiency. Their wide range of applications spans polymer processing, composite manufacturing, ceramic fabrication, and pharmaceutical research. Safety considerations, including proper protective gear and training, are crucial for safe operation. Regular maintenance and care, such as routine inspections and lubrication, extend the lifespan and maintain optimal performance. Heated Lab Presses continue to revolutionize scientific and industrial processes, driving advancements and product development with their versatility and reliability.
Related Products
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
Related Articles
- Optimizing Laboratory Analysis with Split Automatic Heated Lab Pellet Press
- How Much Pressure Do You Need in a Heated Lab Press
- Automatic Hydraulic Press: The Ultimate Guide for Efficient Sample Preparation and Industrial Processes
- Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press: An Efficient Tool for Spectral Analyses Preparation
- Automatic flat plate heat press operating steps



















