Introduction to Vacuum Induction Furnace
Vacuum induction furnaces play a crucial role in various industrial processes such as smelting and ceramic firing. Understanding their components and operating principles is essential for ensuring optimal performance. This article will explore the concept of vacuum induction furnaces and their significance in industrial applications. We will outline the basic functionalities of these furnaces and their critical components. By delving into this introduction, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of vacuum induction furnaces and their role in industrial processes.
Electrical Failure Troubleshooting
When dealing with electrical failures in vacuum induction furnaces, it is crucial to address temperature abnormalities and display errors promptly. Proper diagnosis and troubleshooting of these issues are essential to ensure the efficient functioning of the furnace. Here are detailed steps for diagnosing and addressing temperature-related faults, such as over-temperature alarm failures and temperature display inaccuracies, along with methods to inspect and validate the proper functioning of key components.
Diagnosing Temperature-Related Faults
Over-temperature Alarm Failures:
- Check Thermostat Parameters: Verify the normal functioning of the thermostat parameters in the working area and compare them with certified parameters of other normal thermostats.
- Inspect Solid State Relay Output: Refer to the circuit diagram to check for potential damage in the output of the solid-state relay in the corresponding working area. This can be done by measuring the output resistance using a multimeter, where normal resistance should be several megawatts or higher. If damaged, immediate replacement with a newer model of the same type is necessary.
- Examine Thermocouple Probe: Upon powering on, shake the thermocouple probe in the appropriate operating area to detect any significant jumps in the corresponding thermostat. If identified, it indicates poor contact of the thermocouple probe, necessitating replacement with a new one.

Temperature Display Inaccuracies:
- Verify Thermostat Parameters and Output Signal: Ensure that the parameters of the thermostat in the work area are normal and that there is a proper output signal.
- Check Thermocouple Condition: Inspect the condition of the thermocouples in the corresponding work area. Connect the thermocouple to the thermostat and observe the temperature display for any faults. Damaged thermocouples must be promptly replaced.
- Test Heater Operation: After switching on the power supply, initiate heating according to the circuit diagram and test the heater tube's corresponding working area for power availability. Additionally, measure the current difference between the current working areas using a suitable fixture.
Inspecting Key Components
- Thermostats: Regularly inspect and validate the functioning of thermostats to ensure accurate temperature control and regulation within the furnace.
- Solid State Relays: Pay close attention to the output of solid-state relays, checking for any signs of damage or malfunction that may impact temperature regulation.
- Thermocouples: Thoroughly examine thermocouples for wear and damage, promptly replacing any faulty components to maintain accurate temperature readings.
Testing and Replacement of Damaged Components
When detecting faulty components within the furnace's electrical system, critical steps for testing and replacement should be implemented promptly to restore optimal functionality and prevent prolonged downtime. Testing procedures should adhere to established safety protocols and industry standards to mitigate risks associated with faulty electrical components.
By following these detailed steps, technicians can effectively diagnose and address electrical failures in vacuum induction furnaces, ensuring reliable and accurate temperature control to support various industrial processes.
This section covers detailed troubleshooting steps for diagnosing and addressing electrical failures in vacuum induction furnaces, highlighting critical components such as thermostats, solid state relays, and thermocouples. The emphasis on proper maintenance and prompt replacement of damaged components underscores the importance of ensuring the efficient functioning of these furnaces.
Post-Operation Inspection and Maintenance
After the completion of a vacuum furnace cycle, it is crucial to conduct a thorough post-operation inspection to ensure the furnace's optimal performance and longevity. The following comprehensive guidelines outline essential checks and maintenance practices for vacuum induction furnaces:
Furnace Chamber Inspection
- Inspect the furnace chamber for any signs of damage, wear, or contamination and clean it as needed to maintain a pristine environment.
Component Examination and Replacement
- Thoroughly examine the heating elements, thermocouples, and sensors for any indications of damage or wear, and promptly replace any compromised components to maintain operational efficiency.
Vacuum Pump Oil Assessment
- Regularly check the vacuum pump oil for any signs of contamination or degradation, and replace it when necessary to uphold optimal functioning.
Water-Cooling System Verification
- Verify the proper functioning of the water-cooling system, ensuring there are no leaks, blockages, or pressure issues that could compromise performance.

Record Keeping for Maintenance
It is essential to maintain a daily log of pertinent information to ensure the overall health of the vacuum furnace. This includes recording normal maintenance practices for mechanical components, such as lubrication, cleaning, and proof of operation. Furthermore, substantial care must be taken to maintain a leak-free vacuum environment as the successful operation of vacuum furnaces is highly dependent on this factor.
Critical Areas in Vacuum Furnace Preventive Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance is vital for ensuring a safe operational environment and the longevity of equipment. Key areas that require proper and periodic maintenance include the furnace chamber, leak prevention, hot-zone functionality and integrity, bake-out and leak-rate checking, power supply, vacuum pumps, water and gas lines, and accurate maintenance records. Adhering to these general guidelines in each of these critical areas significantly minimizes potential problems in the future.
Daily Maintenance Checklist for Vacuum Furnaces
1. Pre-Operation Inspection
Before initiating the vacuum furnace, the following checks must be performed:
- Inspect the furnace chamber for debris, dirt, or obstructions, and clean the chamber thoroughly to ensure the absence of foreign material.
- Check the vacuum pump oil level, ensuring it is within the recommended range, and top off or replace the oil as needed.
- Inspect the electrical connections and wiring for signs of wear, damage, or loose connections, and promptly repair or replace any compromised components.
- Thoroughly examine the heating elements, thermocouples, and sensors for any signs of damage or wear, promptly replacing any compromised components.
- Verify the proper functioning of the water-cooling system, ensuring no leaks, blockages, or pressure issues are present.
Following these comprehensive post-operation inspection and maintenance practices is paramount for ensuring the sustained functionality and performance of vacuum induction furnaces. Regular cleaning, component replacement, and system integrity verification are integral components of maintaining an efficient and reliable vacuum furnace.
Operation Monitoring and Corrective Actions
During the operation of vacuum induction furnaces, it is crucial to monitor several parameters to ensure smooth and efficient functioning. These parameters include vacuum level, temperature, pressure, and furnace door seal integrity. Deviations from specified operating
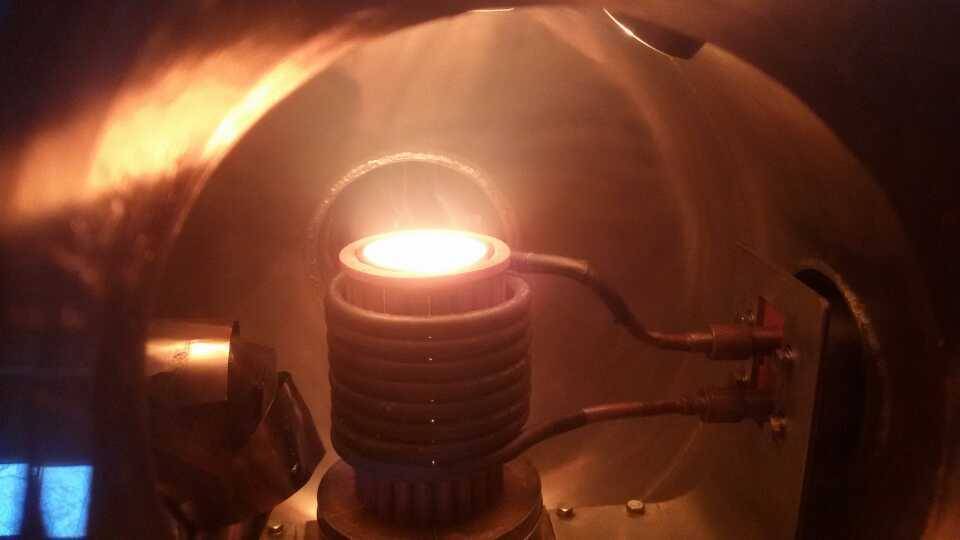

Record Keeping Practices
Maintaining comprehensive records for vacuum induction furnace operations is crucial for facilitating proactive maintenance and performance analysis. A structured framework for daily log maintenance is essential to encompass key information such as furnace status, vacuum level, temperature readings, and any notable observations. This is the foundation for effective maintenance and operation of the vacuum furnace.
-
Furnace Operating Parameters: It is important to maintain a daily log of furnace operating parameters, including temperature, pressure, and vacuum level readings. This enables a clear understanding of the furnace's performance and any deviations from normal operating ranges.
-
Maintenance Activities: Any maintenance performed, including component replacements, cleaning, or repairs, should be diligently recorded. This log of maintenance activities provides a comprehensive history of the furnace's upkeep and aids in identifying patterns or recurring issues.
-
Issue Encounters and Corrective Actions: Recording any issues encountered during operation and the corresponding corrective actions taken is essential. This log of troubleshooting and problem resolution contributes to building a knowledge base for handling similar situations in the future.
By adhering to this structured framework for record-keeping, maintenance teams can effectively track the performance of the vacuum furnace, identify potential areas for improvement, and ensure the longevity of the equipment.
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
Related Articles
- Mastering Vacuum Furnace Brazing: Techniques, Applications, and Advantages
- Why Your Brazed Joints Fail: The Truth About Furnace Temperature and How to Master It
- Why Your Brazed Joints Are Inconsistent—And the Fix Isn't in the Furnace
- The Engineering of Nothingness: Why Vacuum Furnaces Define Material Integrity
- The Art of the Void: When Precision Matters More Than Power