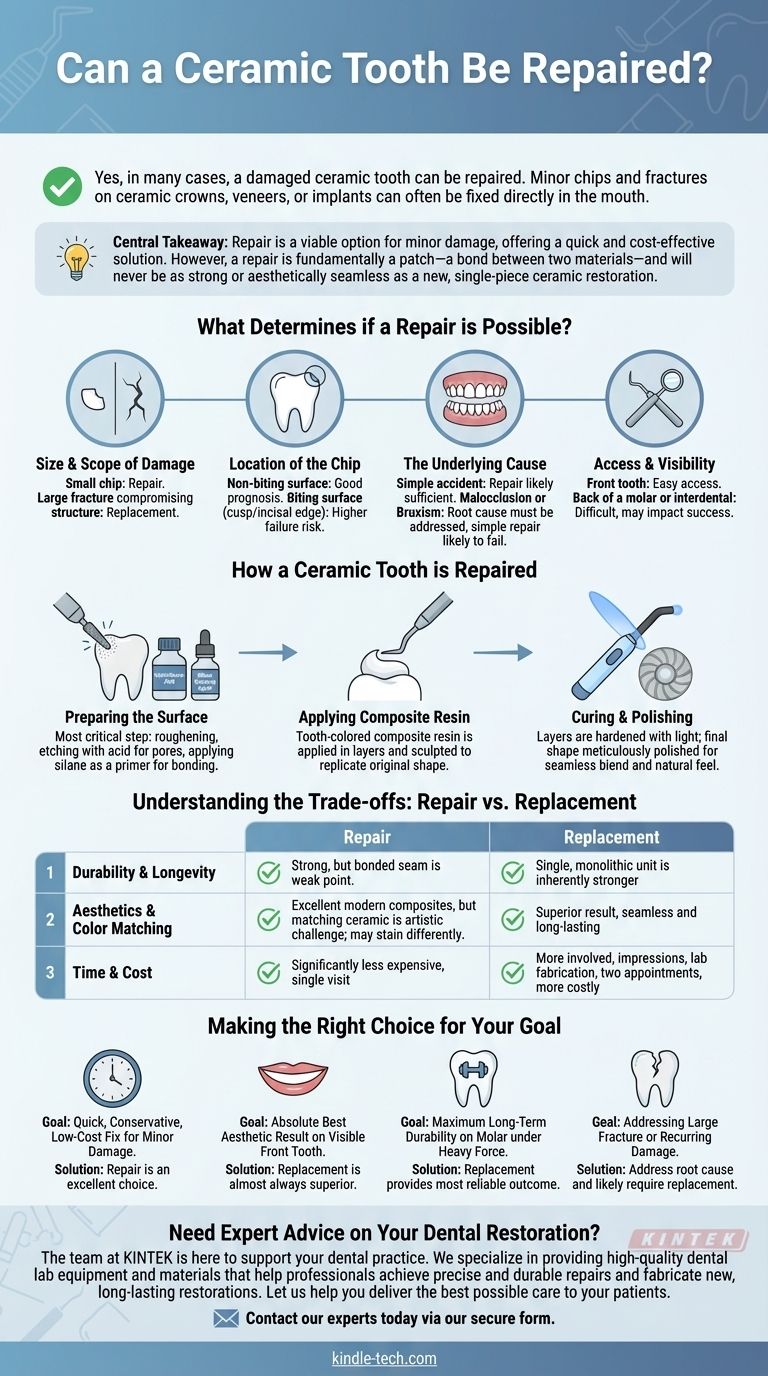
Yes, in many cases, a damaged ceramic tooth can be repaired. While a full replacement is sometimes necessary, minor chips and fractures on ceramic crowns, veneers, or implants can often be fixed directly in the mouth. The success of the repair depends heavily on the size, location, and cause of the damage, as well as the specific materials used.
The central takeaway is that repairing a ceramic tooth is a viable option for minor damage, offering a quick and cost-effective solution. However, a repair is fundamentally a patch—a bond between two different materials—which will never be as strong or aesthetically seamless as a new, single-piece ceramic restoration.
What Determines if a Repair is Possible?
Not all damage is created equal. A dentist evaluates several critical factors before recommending a repair over a full replacement. Understanding these will help you have a more informed conversation about your options.
Size and Scope of the Damage
A small chip on the edge of a crown is a prime candidate for repair. Conversely, a large fracture that compromises the structural integrity of the tooth or extends below the gumline almost always requires a replacement.
Location of the Chip
Location is a key predictor of success. A chip on a smooth, non-biting surface is relatively easy to repair and has a good prognosis. Damage on a biting surface, such as the cusp of a molar or the incisal edge of a front tooth, is under constant pressure and is far more likely to fail.
The Underlying Cause
It's crucial to understand why the ceramic failed. If it was a simple accident, a repair might be sufficient. However, if the damage was caused by an underlying bite issue (malocclusion) or teeth grinding (bruxism), a simple repair will likely fail again until the root cause is addressed.
Access and Visibility
The dentist must have excellent access and visibility to the damaged area to perform a successful repair. A chip on the front of a tooth is easily accessible, while damage between teeth or on the back of a molar can be extremely difficult to isolate and bond to properly.
How a Ceramic Tooth is Repaired
Repairing ceramic is a highly technical process that involves creating a strong chemical bond between the existing ceramic and a new composite resin material.
Preparing the Surface
This is the most critical step. The dentist will slightly roughen the chipped ceramic surface. They will then apply a special etchant, often hydrofluoric acid, to create microscopic pores, followed by a silane coupling agent. This two-step process acts like a powerful primer, creating the ideal surface for the new material to grip.
Applying Composite Resin
Once the surface is prepared, the dentist will apply a tooth-colored composite resin—the same material used for modern fillings—in layers. They will carefully sculpt this material to replicate the original shape of the tooth.
Curing and Polishing
Each layer of resin is hardened using a special curing light. After the final shape is achieved, the dentist will meticulously polish the repaired area to blend it seamlessly with the surrounding ceramic and ensure a smooth, natural feel.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Repair vs. Replacement
Choosing to repair or replace involves a balance of durability, aesthetics, and cost. There is no single "best" answer for everyone.
Durability and Longevity
A repair's weak point is the bonded seam between the old ceramic and the new composite. While strong, this bond is more susceptible to chipping or breaking than a solid piece of ceramic. A brand-new crown is a single, monolithic unit, making it inherently stronger and more durable for the long term.
Aesthetics and Color Matching
Modern composites are excellent, but matching the unique translucency and light-reflecting properties of ceramic is a significant artistic challenge. Over time, the composite resin may also stain at a different rate than the ceramic, making the repair more noticeable. For a front tooth where aesthetics are paramount, a replacement often yields a superior result.
Time and Cost
Repair is the clear winner here. It is significantly less expensive and can typically be completed in a single office visit. A replacement is a more involved process that requires impressions, lab fabrication, and at least two appointments, making it more costly and time-consuming.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on a clear discussion with your dentist about your specific situation and priorities.
- If your primary focus is a quick, conservative, and low-cost fix for minor damage: A repair is an excellent and appropriate solution.
- If your primary focus is the absolute best aesthetic result on a visible front tooth: Replacement is almost always the superior choice for a seamless, long-lasting look.
- If your primary focus is maximum long-term durability, especially on a molar under heavy biting force: Replacement provides the most reliable and robust outcome.
- If your primary focus is addressing a large fracture or recurring damage: You must address the root cause and will likely require a replacement.
Consulting with your dentist allows you to align the right clinical solution with your personal priorities for longevity, aesthetics, and cost.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Favorable for Repair | Usually Requires Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Damage Size | Minor chip | Large fracture compromising structure |
| Location | Non-biting surface | Biting surface (cusp, incisal edge) |
| Underlying Cause | Simple accident | Malocclusion or bruxism |
| Goal | Quick, low-cost fix | Maximum durability or aesthetics |
Need Expert Advice on Your Dental Restoration?
If you're dealing with a chipped or cracked ceramic crown, veneer, or implant, the team at KINTEK is here to support your dental practice. We specialize in providing high-quality dental lab equipment and materials that help professionals achieve precise and durable repairs and fabricate new, long-lasting restorations.
Let us help you deliver the best possible care to your patients.
Contact our experts today via our secure form to discuss how our solutions can enhance your practice's capabilities and outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics



















