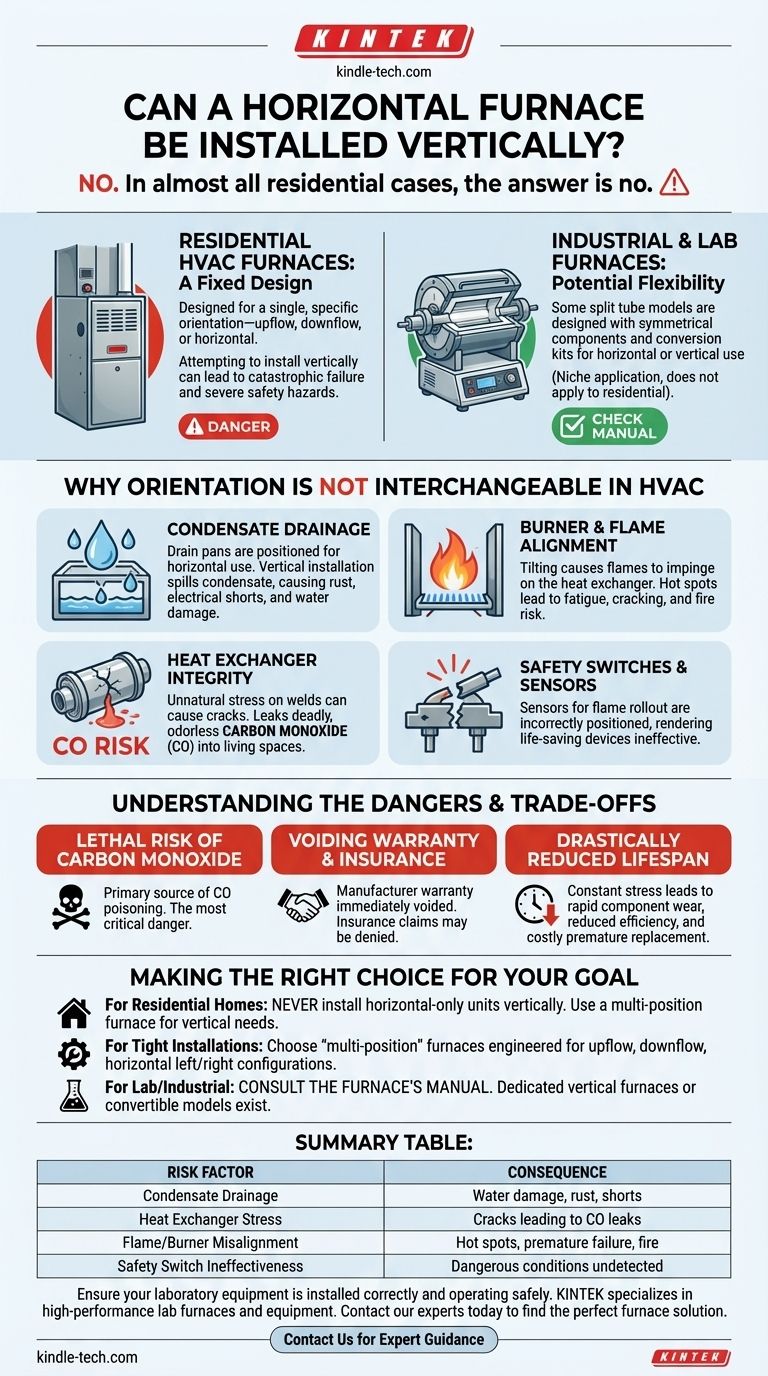
In almost all residential cases, the answer is no. A furnace specifically designated as "horizontal" is engineered exclusively for that orientation, and installing it vertically can lead to catastrophic failure and severe safety hazards. The only exception to this rule applies to specific "multi-position" or convertible furnaces, which are explicitly designed and certified by the manufacturer for installation in various orientations.
A furnace's orientation is not a suggestion; it's a fundamental aspect of its engineering. Attempting to install a standard horizontal furnace vertically can lead to component failure, water damage, and severe safety hazards like fire or carbon monoxide leaks.
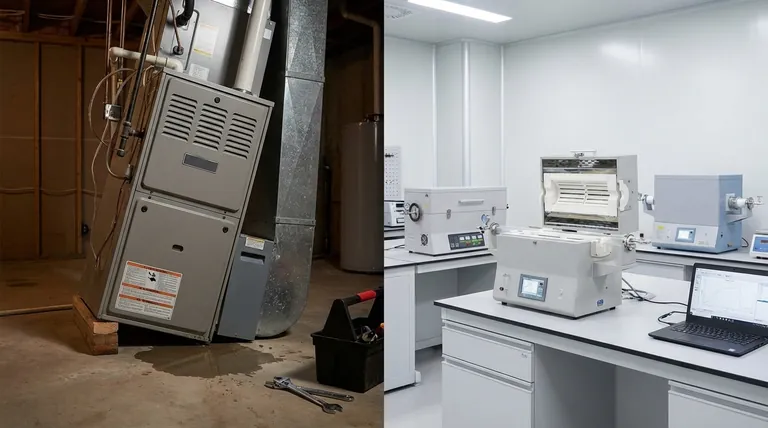

The Critical Distinction: HVAC vs. Industrial Furnaces
The term "furnace" can refer to different types of equipment. Understanding the context is essential before determining if an orientation change is possible.
Residential HVAC Furnaces: A Fixed Design
For most homeowners and technicians, a furnace is the central heating component of an HVAC system. These units are almost always designed for a single, specific orientation—upflow, downflow, or horizontal. This is not an arbitrary limitation.
Industrial & Laboratory Furnaces: Potential Flexibility
In scientific or industrial settings, "tube furnaces" are used for high-temperature material processing. Some of these, particularly "split tube" models, are designed with symmetrical components that allow for either horizontal or vertical use, often with specific conversion kits. This is a niche application and does not apply to residential heating equipment.
Why Orientation Is Not Interchangeable in HVAC
Installing a horizontal-only HVAC furnace vertically compromises several critical systems that rely on gravity and a specific internal layout.
Condensate Drainage
Modern high-efficiency furnaces extract so much heat from the exhaust gas that moisture condenses. This water must drain properly from a collection pan via a drain line. A horizontal furnace's drain pan is positioned to catch this water only when the unit is on its side.
If installed vertically, the pan will be in the wrong place. Condensate will spill over and collect inside the furnace cabinet, leading to rusted components, electrical shorts, and eventually, water damage to your home.
Burner and Flame Alignment
Gas burners are precisely aligned to ensure the flame heats the heat exchanger correctly. Tilting the assembly can cause the flame to "impinge" or directly touch the metal walls of the heat exchanger.
This creates a hot spot that can cause the metal to fatigue, crack, and fail prematurely.
Heat Exchanger Integrity
The heat exchanger is the barrier between the toxic combustion gases and the breathable air being circulated through your home. A cracked heat exchanger is the most dangerous failure a furnace can have, as it can leak deadly, odorless carbon monoxide (CO) into your living space.
Improper orientation puts unnatural stress on the heat exchanger's welds and surfaces, dramatically increasing the risk of a crack.
Safety Switches and Sensors
Furnaces are equipped with numerous safety switches, such as rollout sensors that detect if flames are escaping the combustion chamber. These sensors are positioned based on the expected behavior of heat and flame in the correct orientation.
Changing the orientation can render these life-saving devices ineffective, allowing a dangerous condition to go undetected.
Understanding the Dangers and Trade-offs
Ignoring the manufacturer's specifications is not a shortcut; it is a serious gamble with equipment, property, and personal safety.
The Lethal Risk of Carbon Monoxide
This is the most critical point. An improperly installed furnace with a compromised heat exchanger is a primary source of carbon monoxide poisoning in homes. The risk is simply too high to ignore.
Voiding Your Warranty and Insurance
A manufacturer's warranty is immediately voided if the equipment is not installed according to the instructions in the installation manual. Furthermore, in the event of a fire or other damage, your homeowner's insurance may deny the claim if it's found that the furnace was installed improperly.
Drastically Reduced Lifespan and Efficiency
Even if the unit functions initially, it will be operating under constant stress. Components will wear out rapidly, and its efficiency will be compromised, leading to higher energy bills and the need for a premature and costly replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Always refer to the furnace's data plate and the official installation manual. These documents are the ultimate source of truth for your specific model.
- If your primary focus is installing a furnace in a home: Never install a horizontal-only unit vertically. If your space requires a vertical setup (like in a basement or closet), you must purchase a furnace specifically designed for vertical or "multi-position" installation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing a tight installation space: Look for multi-position furnaces. These are engineered with features like adaptable drain pans and symmetrical components that allow for safe installation in upflow, downflow, horizontal left, or horizontal right configurations.
- If you are working in a lab or industrial setting: Consult the furnace's manual. Some specialized "split tube" furnaces are designed for both orientations, but dedicated vertical furnaces exist for processes that specifically require them.
Ultimately, the furnace's installation manual is the definitive guide to ensuring a safe, efficient, and reliable system.
Summary Table:
| Risk Factor | Consequence of Incorrect Installation |
|---|---|
| Condensate Drainage | Water damage, rust, electrical shorts |
| Heat Exchanger Stress | Cracks leading to carbon monoxide leaks |
| Flame/Burner Misalignment | Hot spots, premature failure, fire risk |
| Safety Switch Ineffectiveness | Dangerous conditions go undetected |
Ensure your laboratory equipment is installed correctly and operating safely. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment, providing expert guidance for safe installation and optimal operation. Don't risk equipment failure or safety hazards—contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?



















