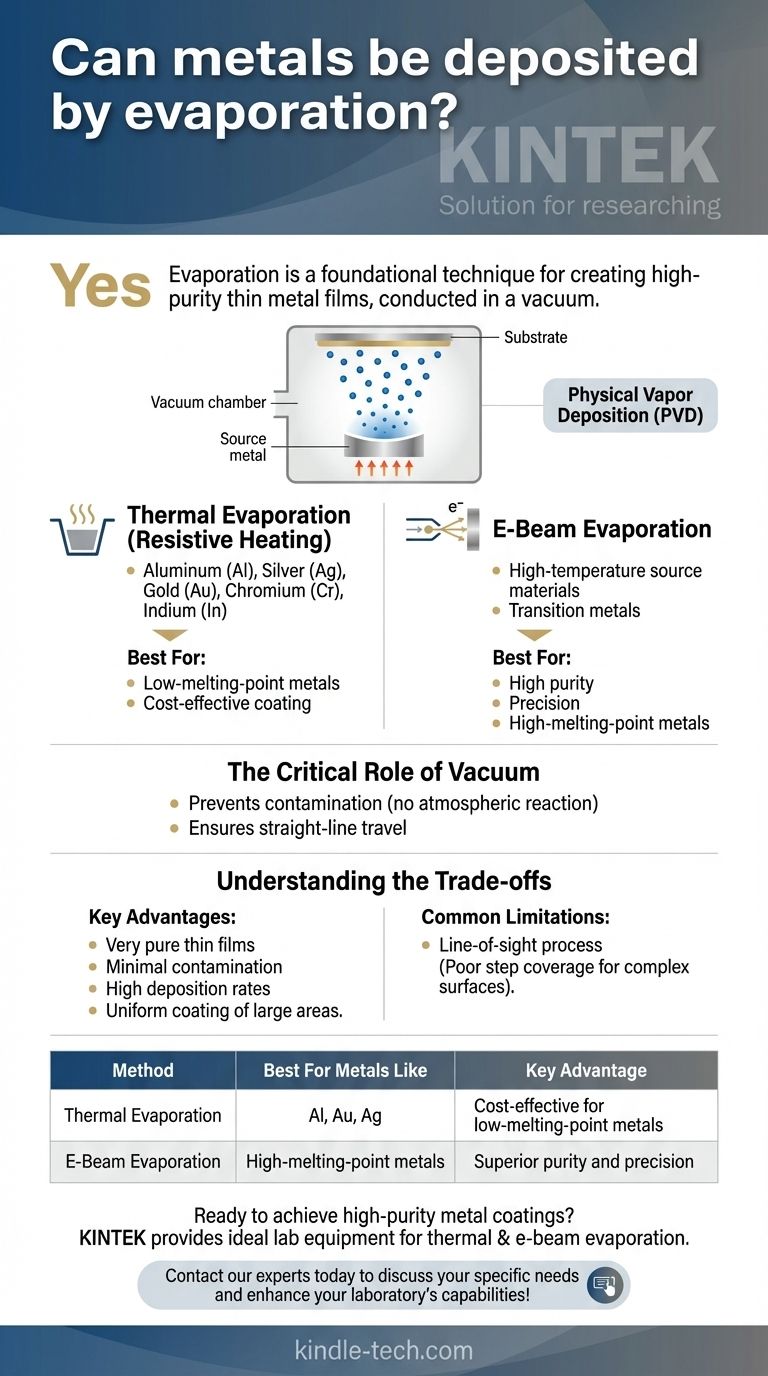
Yes, not only can metals be deposited by evaporation, but it is a foundational and widely used technique for creating high-purity thin metal films. This process, conducted in a vacuum, involves heating a metal until it vaporizes and then allowing it to condense onto a substrate. Many common metals, including Aluminum, Silver, Gold, Nickel, and Chromium, are regularly deposited using this method.
Evaporation is a core vacuum deposition process for applying thin metal films to a surface. The choice between its two primary methods—thermal evaporation and e-beam evaporation—is determined by the metal's melting point and the required purity and precision of the final coating.
The Fundamentals of Metal Evaporation
To understand how metals are deposited via evaporation, it’s essential to grasp the core principle of the process. It is a form of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
The Basic Principle
The source metal is placed inside a high-vacuum chamber and heated until its atoms transform into a vapor. These gaseous metal atoms then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler target surface, known as the substrate, forming a thin, uniform film.
The Critical Role of Vacuum
The entire process must occur in a vacuum for two key reasons. First, it prevents the vaporized metal atoms from reacting with oxygen, nitrogen, or other atmospheric gases, which would contaminate the film. Second, the vacuum ensures the metal atoms can travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate without colliding with other particles.
Key Evaporation Methods for Metals
While the principle is simple, the method of heating the metal source material is a critical distinction. The two dominant techniques have different capabilities and are suited for different types of metals.
Thermal Evaporation (Resistive Heating)
In this method, the source metal is placed in a small crucible or "boat" made of a refractory material like tungsten. A high electrical current is passed through this boat, causing it to heat up rapidly and, in turn, heat the source metal to its evaporation point.
This technique is excellent for metals with relatively low melting points. It is widely used for materials such as Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag), Gold (Au), Chromium (Cr), and Indium (In).
Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
For metals with very high melting temperatures, resistive heating is often insufficient. E-beam evaporation uses a high-energy beam of electrons, guided by magnetic fields, to directly strike and heat the source metal in a crucible.
This method can generate intense, localized heat, making it highly effective for depositing high-temperature source materials. E-beam evaporation is preferred when creating extremely pure and precise metal coatings or when working with transition metals and their oxides.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technical process, metal evaporation has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Key Advantages
The primary benefit of evaporation is its ability to produce very pure thin films. Because the process is relatively simple and driven by heat, it introduces minimal contamination compared to other methods. It can also achieve high deposition rates and is an excellent method for coating large areas uniformly.
Common Limitations
The most significant limitation of evaporation is that it is a line-of-sight process. The vaporized metal atoms travel in a straight line, which means they may not effectively coat complex, three-dimensional surfaces with undercuts or trenches. This is known as poor step coverage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct method depends entirely on the material you are working with and the desired characteristics of the final film.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coating with common metals (like Aluminum or Silver): Thermal evaporation is often the most direct and efficient method.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-melting-point metals or achieving maximum film purity: E-beam evaporation provides the necessary energy and control for a superior result.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex surface with varied topography: You must consider the line-of-sight limitations and may need to investigate alternative deposition techniques like sputtering.
By understanding these core principles, you can select the ideal evaporation technique to achieve a precise and pure metallic thin film for your project.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For Metals Like | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation | Aluminum, Gold, Silver | Cost-effective for low-melting-point metals |
| E-Beam Evaporation | High-melting-point metals | Superior purity and precision |
Ready to achieve high-purity metal coatings for your project?
KINTEK specializes in providing the ideal lab equipment for both thermal and e-beam evaporation processes. Whether you are working with common metals like aluminum and gold or require the precision of high-temperature deposition, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for superior thin film results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific metal deposition needs and enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the flash evaporation method for thin film deposition? Achieve Precise Stoichiometry in Your Films
- What are the advantages of e-beam evaporation over thermal evaporation? Achieve Higher Purity and Versatility
- What is the method of evaporation deposition? A Guide to Creating Ultra-Thin Films
- What are the applications of thin film in electronics? Building the Foundation of Modern Devices
- What is the temperature of thermal evaporation deposition? It's Material-Dependent, Not a Fixed Number
- What is thermal vapor deposition? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Coating
- What is the evaporation theory of thin films? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the temperature of e-beam evaporation? Mastering the Two-Zone Thermal Process for Precision Films



















