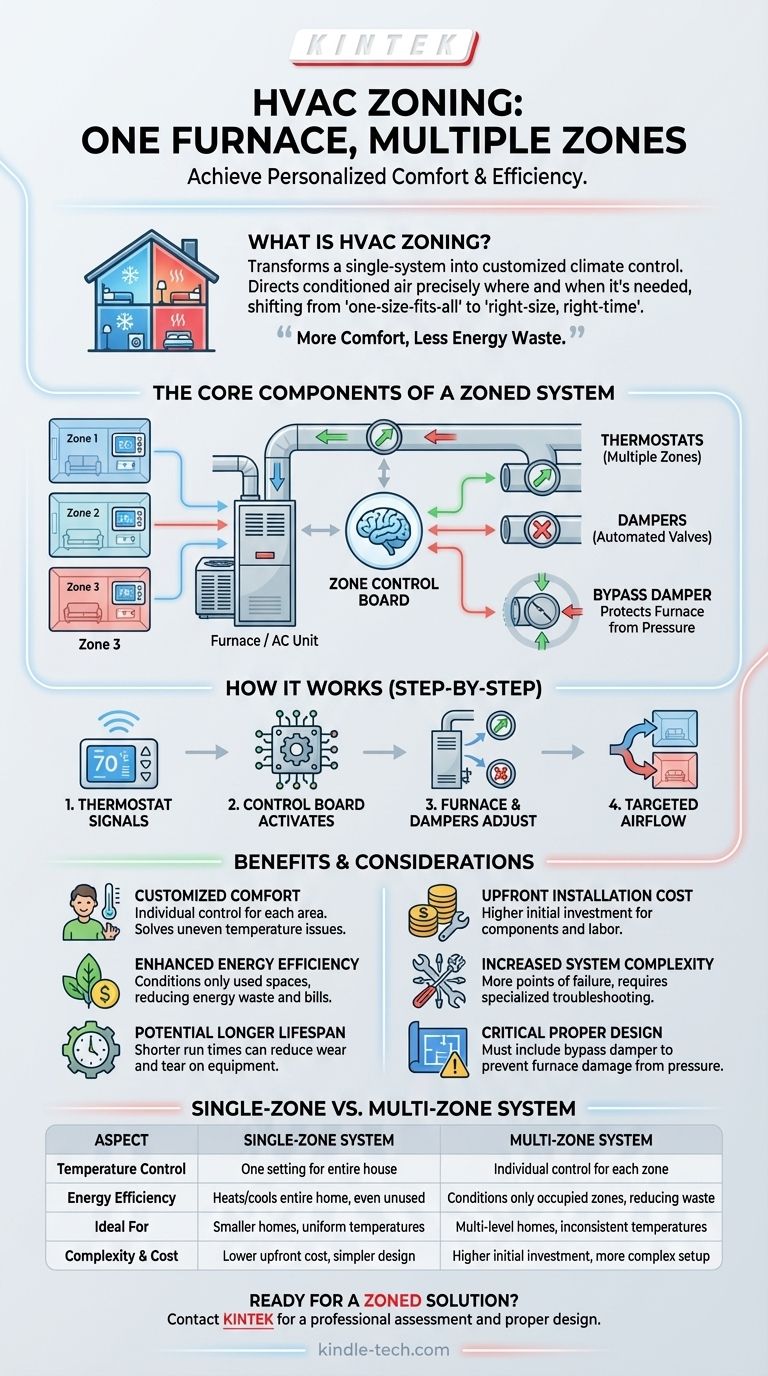
Yes, a single furnace can absolutely be configured to create multiple heating and cooling zones. This process, known as HVAC zoning, transforms a standard, single-policy system into a highly efficient and customized climate control solution. It allows you to direct conditioned air precisely where it's needed, at the time it's needed, by dividing your home's ductwork into distinct areas.
At its core, HVAC zoning is about moving from a "one-size-fits-all" approach to a "right-size, right-time" strategy. It gives you room-by-room temperature control, which directly translates to increased comfort and significant energy savings.

How a Single Furnace Manages Multiple Zones
A standard HVAC system is designed to heat or cool an entire house to a single temperature set by one thermostat. Zoning retrofits this system with a set of components that work together to provide granular control.
The Core Components of a Zoned System
A zone control board acts as the central brain. It receives signals from thermostats in each zone and coordinates the furnace and dampers to meet the demand.
Thermostats are installed in each designated zone. When a zone's thermostat calls for heating or cooling, it sends a signal to the control board.
Dampers are the critical mechanical components. These are essentially automated valves installed inside your ductwork. The control board instructs these dampers to open or close, directing the flow of conditioned air only to the zones that need it.
The Step-by-Step Process
Imagine your upstairs is too hot in the summer. A thermostat in that zone detects the temperature is above your set point and signals the control board.
The board then activates your air conditioner and simultaneously sends a signal for the dampers leading to the cooler, downstairs zones to close.
The full output of your AC unit is now directed exclusively to the upstairs zone until the thermostat is satisfied. The process reverses for heating in the winter.
The Primary Benefits of a Zoned System
Understanding the advantages helps clarify why this upgrade is so effective for many homes.
Customized Comfort
The most immediate benefit is solving common problems like a second floor that's always hotter than the first, or a basement that remains frigid. Each area can maintain its own ideal temperature.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
By not heating or cooling unused areas—like guest rooms or formal dining rooms—you eliminate significant energy waste. You're only paying to condition the spaces you are actively using.
Potential for a Longer System Lifespan
Because a zoned system can satisfy the needs of individual areas more quickly, the entire system may run for shorter periods. This can reduce overall wear and tear on the furnace and air conditioner components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a zoned system is not a universal solution. Objectivity requires acknowledging its potential downsides.
Upfront Installation Cost
Retrofitting an existing HVAC system for zoning involves significant labor and specialized components. The cost is higher than that of a standard, single-zone setup.
Increased System Complexity
Adding a control board, multiple thermostats, and mechanical dampers introduces more points of potential failure. While reliable, the system requires more sophisticated troubleshooting if a problem arises.
The Critical Need for Proper Design
Simply adding dampers can be dangerous for your furnace. Restricting airflow increases static pressure inside the ductwork, which can strain the furnace blower motor and damage the heat exchanger.
A properly designed system must account for this. Often, this requires installing a bypass damper that reroutes excess air back to the system, protecting the equipment from pressure-related damage. This is not a DIY project and requires a qualified HVAC professional.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide if zoning is the correct path, evaluate your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is solving uneven temperatures: A zoned system is the most direct and effective solution for homes with multi-level or inconsistent heating and cooling issues.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency: Zoning provides significant savings, especially in larger homes or homes where room usage varies drastically throughout the day.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial cost and complexity: A traditional single-zone system remains the most straightforward and affordable option for smaller homes or those with uniform heating and cooling needs.
Ultimately, zoning empowers you to take precise control over your home's climate, ensuring comfort and efficiency are managed on your terms.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Single-Zone System | Multi-Zone System |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | One setting for entire house | Individual control for each zone |
| Energy Efficiency | Heats/cools entire home, even unused rooms | Conditions only occupied zones, reducing waste |
| Ideal For | Smaller homes with uniform temperatures | Multi-level homes, inconsistent temperatures |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower upfront cost, simpler design | Higher initial investment, more complex setup |
Ready to solve uneven temperatures and reduce your energy bills?
A properly designed zoned HVAC system from KINTEK can transform your home's comfort and efficiency. Our expertise in climate control solutions ensures your system is configured correctly, with critical components like bypass dampers to protect your furnace.
We specialize in helping homeowners like you achieve:
- Personalized Comfort: Say goodbye to hot upstairs and cold basements.
- Significant Energy Savings: Pay only to condition the spaces you use.
- Long-Term System Health: Proper design reduces strain on your equipment.
Contact us today for a professional assessment and discover the perfect zoned solution for your home!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas



















