Yes, stainless steel can be effectively soldered and brazed, but it demands a different approach than conventional steels. The process is not inherently difficult, but it is unforgiving of improper preparation. Success hinges entirely on overcoming the unique chemical properties that make stainless steel "stainless" in the first place.
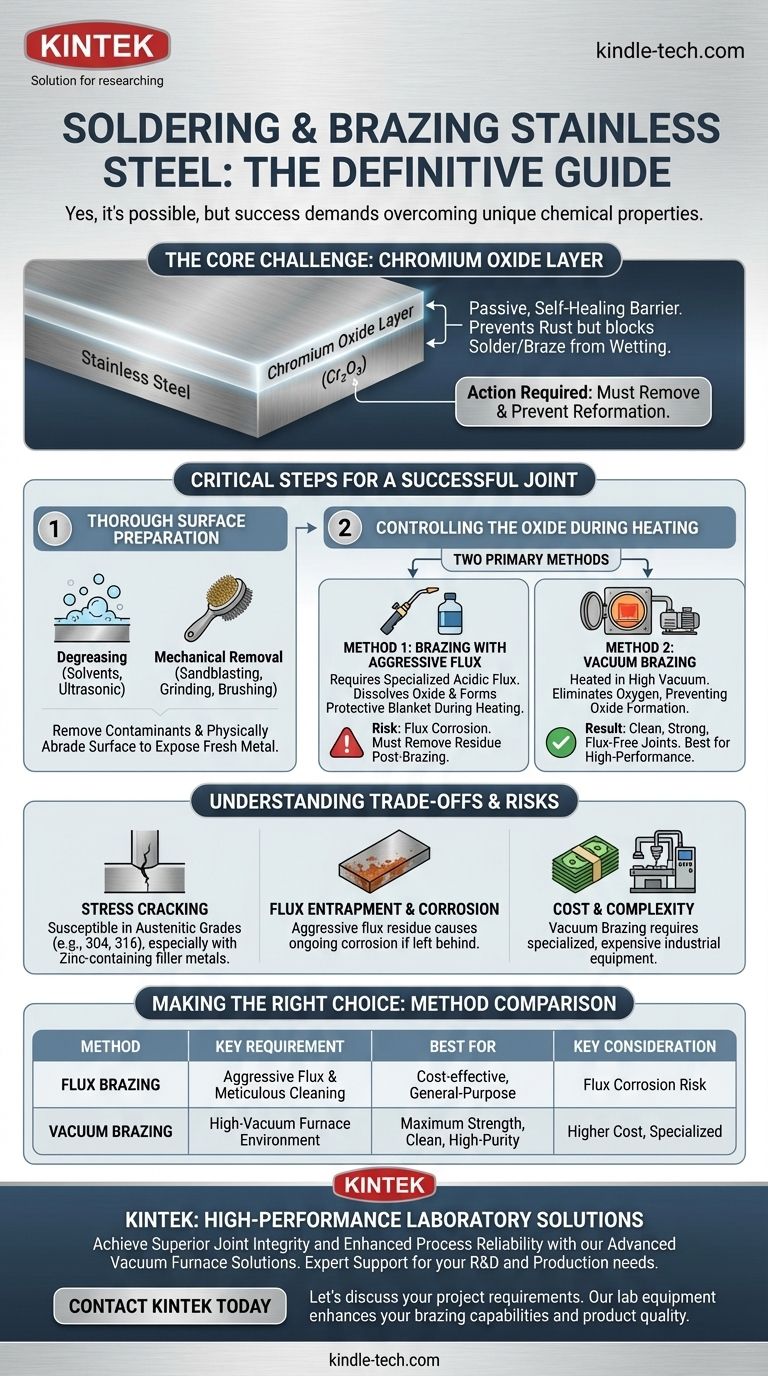
The core challenge in joining stainless steel is its passive, self-healing layer of chromium oxide. This invisible layer, which prevents rust, also acts as a barrier that prevents solder or braze filler metal from wetting and adhering to the surface. Therefore, the entire joining process is designed to remove this oxide layer and prevent it from reforming.

The Core Challenge: Stainless Steel's Protective Oxide Layer
The very reason you choose stainless steel—its corrosion resistance—is the primary obstacle you must overcome when joining it.
What is the Oxide Layer?
Stainless steel contains chromium, which reacts with oxygen in the air to form a thin, dense, and transparent layer of chromium oxide. This passive layer is incredibly stable and instantly reforms if scratched or removed.
Why It Prevents Brazing and Soldering
For a strong joint to form, the molten filler metal must "wet" the surface of the base metal, meaning it must flow and spread evenly. The chromium oxide layer acts like a non-stick coating, preventing the filler metal from making direct contact with the steel beneath it.
The Critical Steps for a Successful Joint
A successful stainless steel joint is achieved before the heat is even applied. The preparation phase is non-negotiable and must be performed meticulously.
Step 1: Thorough Surface Preparation
First, the surface must be free of all contaminants like oil, grease, and dirt. This is often done through degreasing with solvents like acetone or alcohol. Ultrasonic cleaning can significantly improve this step.
After degreasing, the oxide layer itself must be mechanically removed. Methods like sandblasting, grinding, or brushing with a stainless steel brush physically abrade the surface and expose the fresh metal underneath.
Step 2: Controlling the Oxide During Heating
Once the surface is clean, you must have a strategy to manage the oxide layer during the heating process. As the metal gets hot, the oxide layer will try to reform rapidly. There are two primary strategies to combat this.
Two Primary Methods for Joining Stainless Steel
Your choice of method depends on your equipment, budget, and the quality requirements of the final joint.
Method 1: Brazing with Aggressive Flux
For standard atmosphere brazing, a specialized flux is required. Unlike mild fluxes used for copper, fluxes for stainless steel are highly acidic and chemically aggressive.
During heating, the flux melts and dissolves the existing oxide layer. It then forms a protective liquid blanket over the joint area, preventing oxygen from reaching the steel and allowing the oxide to reform.
Method 2: Vacuum Brazing
Vacuum brazing is a superior method for high-performance applications. The parts are assembled and placed inside a furnace, which is then pumped down to a high vacuum.
By removing the oxygen from the environment, the oxide layer cannot form during heating. This allows the filler metal to wet the surface perfectly, resulting in exceptionally clean, strong, and aesthetically pleasing joints without any corrosive flux residue.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Joining stainless steel is not without potential pitfalls. Awareness of these issues is key to avoiding costly failures.
The Risk of Stress Cracking
Certain types of stainless steel, particularly the common austenitic grades (e.g., 304, 316), can be susceptible to stress cracking during brazing. This is especially true when using filler metals containing zinc, such as some copper-zinc alloys.
Flux Entrapment and Corrosion
If you are using the flux method, it is absolutely critical that all flux residue is removed after brazing. The aggressive chemicals that make the flux effective will continue to corrode the stainless steel if left on the joint.
Cost and Complexity of Vacuum Brazing
While vacuum brazing produces superior results, it requires specialized and expensive equipment. It is not a process that can be easily performed in a small workshop and is typically reserved for industrial or high-value production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct method comes down to balancing performance requirements with available resources.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and a clean finish: Vacuum brazing is the definitive choice for creating void-free, high-purity joints without the risk of flux corrosion.
- If your primary focus is accessibility and cost-effectiveness for general-purpose joints: Brazing with a properly selected aggressive flux and a meticulous post-cleaning procedure is a reliable and proven method.
- If you are working with austenitic stainless steel: Pay close attention to your filler metal selection to avoid alloys known to cause stress cracking, and always minimize stress on the joint during the heating and cooling cycle.
By understanding and controlling the oxide layer, you can reliably create strong, durable joints in stainless steel.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Requirement | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flux Brazing | Aggressive, specialized flux & meticulous cleaning | Cost-effective, general-purpose joints | Risk of flux corrosion if not fully removed |
| Vacuum Brazing | High-vacuum furnace environment | Maximum strength, clean, high-purity joints | Higher cost, requires specialized equipment |
Need a High-Performance Brazing Solution for Your Lab?
Joining stainless steel components requires precision and the right equipment to ensure strong, contamination-free bonds. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including vacuum furnace solutions ideal for high-integrity brazing applications.
We help you achieve:
- Superior Joint Integrity: Our vacuum furnaces prevent oxide formation, resulting in exceptionally strong, clean joints without corrosive flux residue.
- Enhanced Process Reliability: Achieve consistent, repeatable results for your critical R&D or production needs.
- Expert Support: Our team understands the challenges of joining materials like stainless steel and can help you select the right solution.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact KINTEK today to learn how our lab equipment can enhance your brazing capabilities and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What are the advantages of brazing compared to welding? Achieve Clean, Low-Distortion Metal Joining
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries



















