Yes, you can carburize stainless steel, but it requires a specialized process. Unlike standard carbon steels, the protective chromium oxide layer on stainless steel prevents carbon absorption in a normal atmosphere. The solution is high-temperature vacuum carburizing, which overcomes this barrier to create an exceptionally hard, wear-resistant surface on the component.
The core challenge with carburizing stainless steel is its natural, passive chromium oxide layer. By using a high-temperature vacuum environment, this protective layer is bypassed, allowing carbon to diffuse into the surface and create a hard case while preserving the tough, corrosion-resistant core.

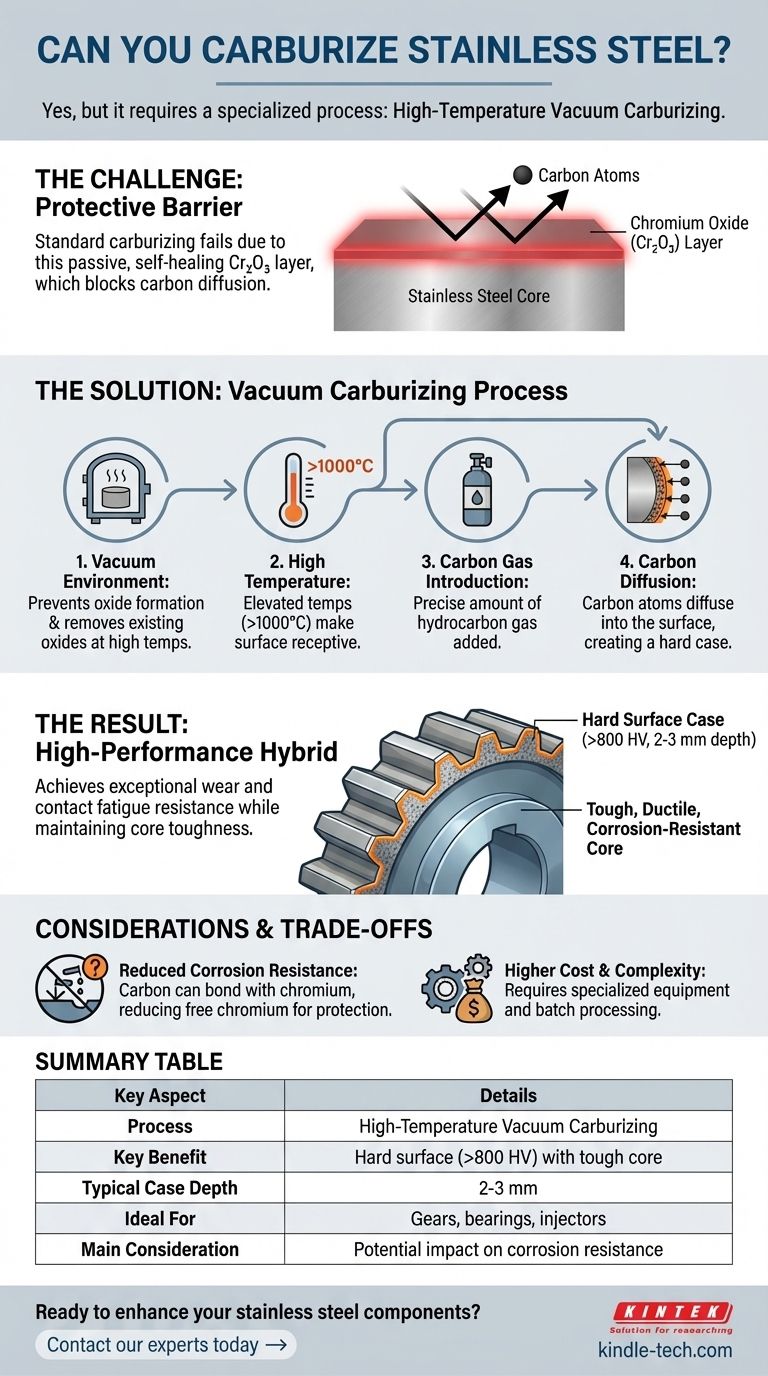
The Challenge: Stainless Steel's Protective Layer
Why Standard Carburizing Fails
Stainless steel’s defining feature is its corrosion resistance, which comes from a thin, invisible, and self-healing layer of chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃) on its surface.
This passive layer is a formidable barrier. In a traditional gas carburizing atmosphere, it effectively blocks carbon atoms from diffusing into the steel, rendering the process ineffective.
How Vacuum Carburizing Solves the Problem
Vacuum carburizing is a modern heat treatment that makes it possible to harden the surface of stainless steel effectively. It operates on a few key principles.
Bypassing the Oxide Barrier
By processing the components in a high-purity vacuum, the formation of the chromium oxide layer is prevented. At the very high temperatures used in this process, any existing oxides become unstable and are removed from the surface.
This creates a chemically "clean" surface that is receptive to carbon.
High-Temperature Carbon Diffusion
With the barrier gone, the process can proceed. The temperature is raised significantly, often above 1,000°C (1,832°F), and a precise amount of a hydrocarbon gas (like acetylene or methane) is introduced.
At these elevated temperatures, the carbon atoms from the gas readily diffuse into the steel's surface, creating a high-carbon "case."
The Result: A High-Performance Hybrid
The final outcome is a component with dual properties. The surface can achieve a hardness exceeding 800 HV, with a case depth reaching 2-3 mm, providing exceptional wear and contact fatigue resistance.
Beneath this extremely hard case, the core of the stainless steel remains tough, ductile, and retains its fundamental corrosion resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum carburizing stainless steel is not without its considerations. An objective analysis requires understanding the potential downsides.
Potential Impact on Corrosion Resistance
The primary trade-off involves corrosion resistance. As carbon is added to the surface, it can bond with chromium to form chromium carbides.
This "ties up" chromium, meaning there is less free chromium available in the surrounding metal matrix to maintain the passive protective layer. In highly corrosive environments, this can lead to localized corrosion (sensitization), so a careful evaluation of the end-use environment is critical.
Process Complexity and Cost
Vacuum carburizing is an advanced, batch-based process that requires specialized equipment. It is inherently more complex and costly than conventional atmospheric heat treatments for standard steels.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting this process depends entirely on your engineering goal. It is a powerful tool for solving specific material challenges where standard stainless steel falls short.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear and fatigue resistance: Vacuum carburizing is an excellent choice for components like gears, bearings, or injectors, creating a surface that can outperform many through-hardened tool steels.
- If your primary focus is balancing wear with corrosion resistance: This process is ideal, but you must validate the performance in your specific service environment to ensure the post-treatment corrosion resistance is sufficient.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose hardening on a budget: Other materials or surface treatments may be more economical. This process is best reserved for high-performance applications where its benefits justify the cost.
By understanding the principles of vacuum processing, you can successfully transform stainless steel into a high-performance material tailored for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | High-Temperature Vacuum Carburizing |
| Key Benefit | Hard surface (>800 HV) with a tough, corrosion-resistant core |
| Typical Case Depth | 2-3 mm |
| Ideal For | Gears, bearings, injectors requiring extreme wear resistance |
| Main Consideration | Potential impact on corrosion resistance in the case layer |
Ready to enhance your stainless steel components?
KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions for demanding laboratory and industrial applications. Our expertise in vacuum carburizing can help you achieve the perfect balance of surface hardness and core properties for your high-performance parts.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your materials for superior wear and fatigue resistance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components



















