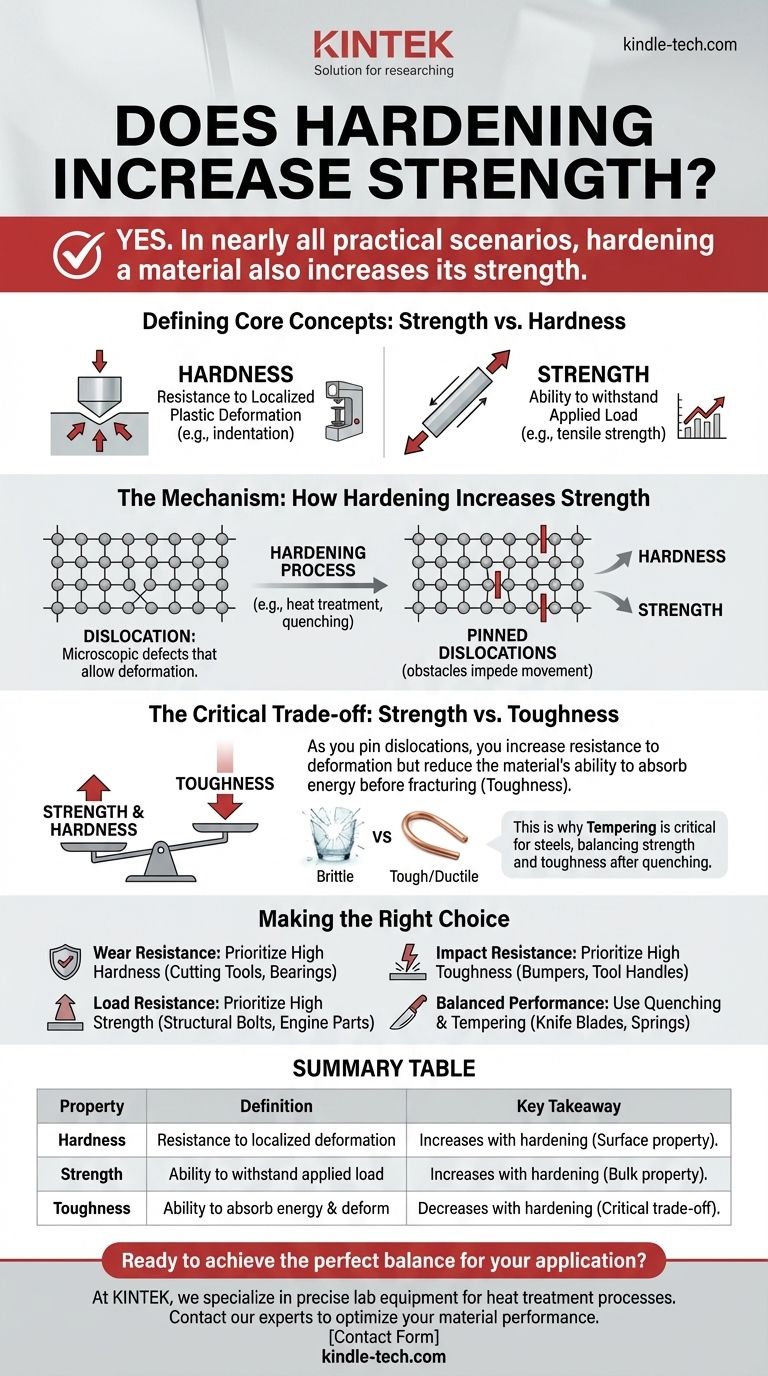
Yes, in nearly all practical scenarios, hardening a material also increases its strength. While the two properties are distinct, they are intrinsically linked at a microscopic level. Hardening processes work by impeding the internal movement that allows a material to deform, which not only makes it more resistant to surface indentation (hardness) but also increases its ability to resist being pulled apart (strength).
The fundamental takeaway is that hardness and strength are different measurements of the same underlying principle: a material's resistance to permanent deformation. Increasing this resistance makes a material both harder and stronger, but almost always at the expense of its toughness, making it more brittle.

Defining the Core Concepts: Strength vs. Hardness
To understand their relationship, we must first be precise about what each term means. They are often used interchangeably in casual conversation, but in engineering and materials science, they describe different behaviors.
What is Hardness?
Hardness is a measure of a material's resistance to localized plastic deformation, such as scratching or indentation. When you press a sharp object into a material, hardness is the property that resists the creation of a permanent dent.
It's a surface-level property, typically measured by standardized tests like the Rockwell, Brinell, or Vickers tests, which quantify the size of an indentation left by a specific force.
What is Strength?
Strength is a material's ability to withstand an applied load without failure or permanent deformation. Unlike hardness, it's a bulk property that describes how the entire component behaves.
The most common measure is tensile strength, which is the maximum stress a material can endure while being stretched or pulled before it breaks. Another critical measure is yield strength, the point at which it begins to deform permanently.
The Mechanism: How Hardening Increases Strength
The connection between hardness and strength lies in the material's microstructure. Both properties are governed by how easily microscopic defects, called dislocations, can move through the material's crystal lattice.
The Role of Dislocations
Think of a material's atomic structure as a perfectly ordered grid. A dislocation is a mistake—an extra or missing row of atoms. Permanent deformation (like bending a metal bar) occurs when these dislocations are forced to move through the grid.
Pinning the Dislocations
Hardening processes are designed to introduce microscopic obstacles that impede or "pin" dislocation movement. By making it more difficult for these defects to move, you make it more difficult for the material to deform.
This resistance to local deformation is what we measure as an increase in hardness. Because the same mechanism prevents deformation throughout the bulk of the material, its yield strength and tensile strength also increase.
The Critical Trade-off: Strength vs. Toughness
This is the most important concept for any practical application. While making a material harder and stronger is often desirable, it almost always comes with a significant and dangerous downside: a loss of toughness.
Introducing Toughness
Toughness is a material's ability to absorb energy and deform plastically before fracturing. It represents the material's resistance to breaking or shattering upon impact.
The Inverse Relationship
As you pin dislocations more effectively, you increase strength but reduce the material's ability to deform. This lack of "give" means that when the material is overloaded, it has no way to safely absorb the energy and is more likely to fail catastrophically.
A piece of chalk is very hard but has almost no toughness; it shatters easily. A copper wire is soft but very tough; it bends and stretches extensively before breaking. This inverse relationship between hardness/strength and toughness is the central challenge in materials engineering.
The Power of Tempering
This trade-off is why processes like tempering are so critical for steels. After quenching, steel is extremely hard and strong but also very brittle. Tempering is a secondary heat treatment that slightly reduces hardness and strength to regain a significant amount of toughness, creating a more reliable and useful final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this balance allows you to select or treat a material to match your specific objective. The "best" material is rarely the hardest or strongest, but the one with the right combination of properties.
- If your primary focus is wear and scratch resistance: Prioritize high hardness, accepting low toughness. This is ideal for cutting tools, ball bearings, or files.
- If your primary focus is resisting deformation under a steady load: Prioritize high tensile strength, which correlates directly with high hardness. This is crucial for structural bolts, engine components, or building cables.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance and preventing catastrophic failure: Prioritize high toughness, which means choosing a material with lower hardness and strength. This is essential for car bumpers, structural beams in earthquake zones, or tool handles.
- If you need a balanced performance: Use processes like quenching and tempering to achieve a specific point on the strength-vs-toughness curve. This is the goal for knife blades, springs, and high-performance axles.
Effective engineering is not about maximizing a single property, but about achieving the optimal balance of properties for the intended application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Definition | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Resistance to localized plastic deformation (e.g., indentation). | Increases with hardening. A surface property. |
| Strength | Ability to withstand applied load without failure (e.g., tensile strength). | Increases with hardening. A bulk property. |
| Toughness | Ability to absorb energy and deform before fracturing (impact resistance). | Decreases with hardening. This is the critical trade-off. |
Ready to achieve the perfect balance of strength and toughness for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for heat treatment processes like hardening and tempering. Whether you're developing cutting tools, structural components, or any application requiring optimized material performance, our expertise and high-quality products are here to support your R&D and quality control.
Let's discuss your material challenges and find the right solution. Contact our experts today to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of ash analysis? Dry vs. Wet Ashing Methods Explained
- How does heat affect strength materials? The Science of Thermal Degradation Explained
- Why must a muffle furnace be paired with a sealed crucible? Accurate Biomass Volatile Matter Analysis Explained
- What does a high ash content mean? A Guide to Material Quality & Contamination
- What are the different types of ashing analysis? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results



















