In short, yes, but not always. Specific heat treatments like hardening and age hardening are designed to significantly increase a metal's tensile strength. However, other processes like annealing are intentionally used to do the opposite—they decrease tensile strength to increase softness and ductility. The outcome depends entirely on the specific process, the material, and the intended goal.
The purpose of heat treatment is not simply to increase strength, but to precisely control a material's internal structure. This control allows you to achieve a desired balance of mechanical properties, often trading strength for toughness, to meet the demands of a specific application.

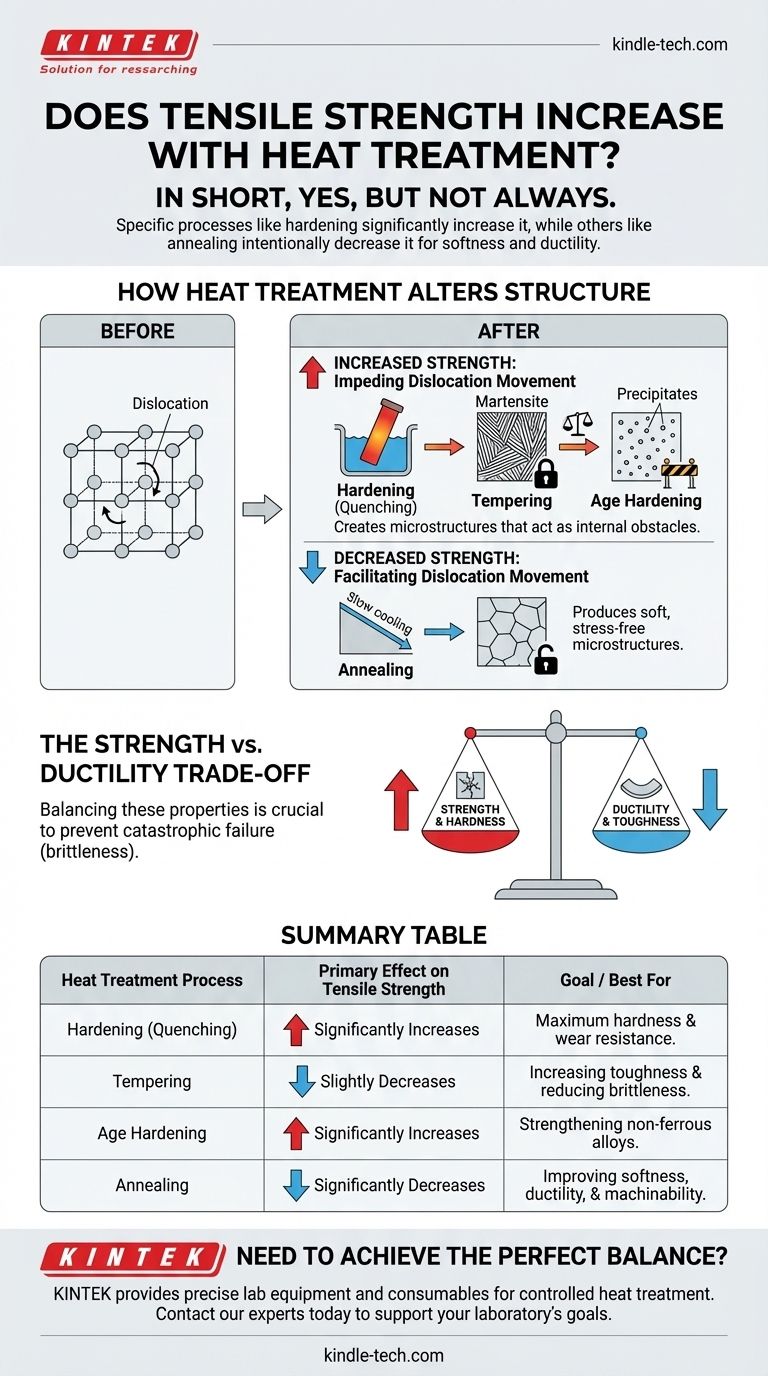
How Heat Treatment Alters a Metal's Core Structure
To understand how heat treatment affects strength, you must first understand that a material's properties are dictated by its internal crystal structure, or microstructure. Heat treatment is the process of manipulating that structure.
The Goal: Manipulating the Microstructure
Metals are composed of microscopic crystals called grains. The size, shape, and composition of these grains determine properties like strength, hardness, and ductility. Heat treatment uses controlled heating and cooling cycles to change this internal architecture.
The Mechanism: Dislocation Movement
Tensile strength is fundamentally a measure of how much stress a material can withstand before it deforms or breaks. At a microscopic level, this deformation happens when defects in the crystal lattice, called dislocations, move.
To increase strength, you must impede or block the movement of these dislocations. Heat treatment achieves this by creating specific microstructures that act as internal obstacles.
The Role of Temperature and Cooling Rate
The two primary levers in heat treatment are temperature and cooling rate. Heating a metal rearranges its atomic structure, and the speed at which it is cooled locks in a particular phase or structure, each with distinct properties.
Processes That Increase Tensile Strength
Certain heat treatments are specifically designed to create microstructures that are highly resistant to dislocation movement, resulting in a dramatic increase in strength and hardness.
Hardening (Quenching)
This is the most well-known strengthening process, used primarily on medium-to-high carbon steels. The steel is heated to a high temperature to form a structure called austenite, then rapidly cooled (quenched) in a medium like water, oil, or air.
This rapid cooling traps carbon atoms within the iron crystal lattice, creating a new, highly strained, and very hard microstructure called martensite. Martensite is exceptionally effective at blocking dislocation movement, leading to a massive increase in tensile strength.
Tempering: The Crucial Follow-Up
A part that has only been quenched is extremely strong but also very brittle, making it unsuitable for most applications. Tempering is a secondary heat treatment where the hardened part is reheated to a lower temperature.
This process relieves internal stresses and slightly softens the martensite, significantly increasing the material's toughness (resistance to fracture). While tempering reduces the peak tensile strength slightly, the final component is still vastly stronger than its original state but now has the ductility needed to be useful.
Age Hardening (Precipitation Hardening)
This is the primary strengthening method for many non-ferrous alloys, including aluminum, titanium, and nickel-based alloys. The process involves heating the material to dissolve alloying elements, quenching it to trap them in a supersaturated solution, and then "aging" it at a lower temperature.
During aging, very fine particles of a second phase precipitate out of the solution. These tiny, dispersed particles act as powerful obstacles to dislocation movement, dramatically increasing the alloy's tensile strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Strength vs. Ductility Dilemma
No material property exists in isolation. When you change one, you almost always affect others. The most critical trade-off in heat treatment is between strength and toughness.
The Inverse Relationship
As a general rule, as you increase a metal's tensile strength and hardness, you decrease its ductility and toughness. A very strong material is often brittle, while a very ductile (soft) material typically has low strength.
Why Brittleness is a Critical Failure Mode
A brittle material will fracture suddenly under load with little to no warning or plastic deformation. For applications involving impact, vibration, or potential overload, this is a catastrophic failure mode. The goal of many heat treatment plans is to find the optimal balance point on the strength-toughness curve.
Processes That Decrease Strength to Gain Ductility
Sometimes, the goal is to make a material softer. Annealing, which involves heating a metal and then cooling it very slowly, is used for this purpose. It produces a soft, stress-free microstructure that has low tensile strength but high ductility, making the material easy to machine, form, or weld.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct heat treatment is the one that produces the ideal balance of properties for your component's function.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: A hardening (quench) process followed by a low-temperature temper is the solution.
- If your primary focus is toughness and impact resistance: A hardening process followed by a higher-temperature temper is required to sacrifice some hardness for crucial ductility.
- If your primary focus is machinability or formability: Annealing is the correct choice to soften the material before subsequent manufacturing operations.
- If your primary focus is a uniform, stress-relieved structure: Normalizing provides a consistent and reliable baseline for many components, with properties between an annealed and a hardened state.
By understanding the purpose behind each treatment, you can select the precise process to engineer the exact material performance you need.
Summary Table:
| Heat Treatment Process | Primary Effect on Tensile Strength | Goal / Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening (Quenching) | Significantly Increases | Maximum hardness and wear resistance. |
| Tempering | Slightly Decreases (after hardening) | Increasing toughness and reducing brittleness. |
| Age Hardening | Significantly Increases | Strengthening non-ferrous alloys (e.g., aluminum, titanium). |
| Annealing | Significantly Decreases | Improving softness, ductility, and machinability. |
Need to achieve the perfect balance of strength, hardness, and toughness for your components? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for controlled heat treatment processes. Our solutions help you manipulate material microstructures to meet demanding application requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's material testing and development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tube Racks
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the steps in sieving method? A Guide to Accurate Particle Size Separation
- What type of materials can be separated using the method of sieving? A Guide to Efficient Particle Size Separation
- How do you use a sieve shaker? Master Particle Size Analysis for Quality Control
- How long do I run my sieve shaker for? Find Your Material's Optimal Sieving Time
- What are the advantages of the sieve method? Achieve Fast, Reliable Particle Size Analysis



















