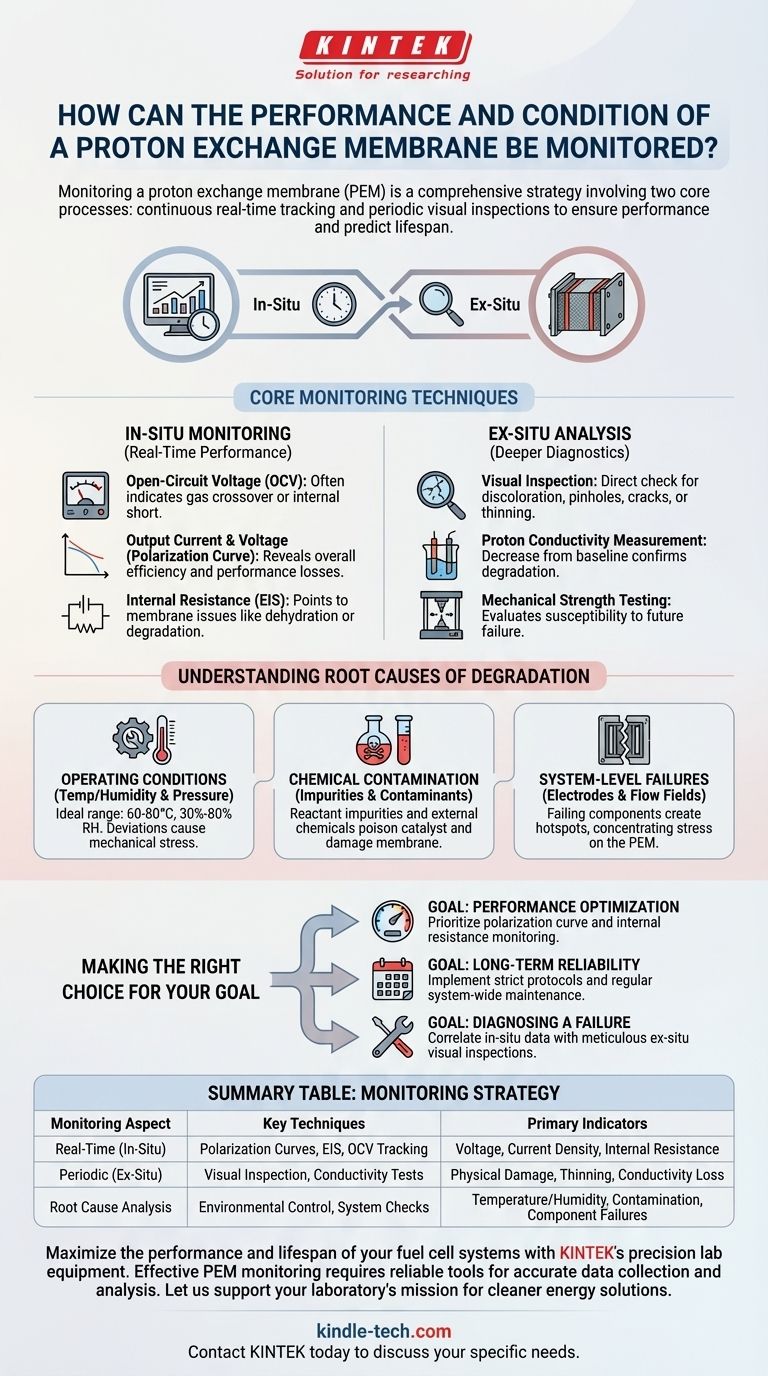
In essence, monitoring a proton exchange membrane (PEM) is a two-part process. You must continuously track key electrochemical indicators like voltage and internal resistance during operation, while also conducting periodic visual inspections for physical damage, such as cracks or discoloration, when the system is disassembled.
Monitoring a PEM is not a single task, but a comprehensive strategy. True reliability comes from understanding that real-time electrical data reveals a PEM's current performance, while its physical condition and operating environment dictate its future lifespan.

Core Monitoring Techniques
Effective monitoring combines real-time (in-situ) data with periodic offline (ex-situ) analysis to provide a complete picture of the membrane's health.
In-Situ Monitoring: Assessing Real-Time Performance
These checks are performed while the electrochemical cell is operational and provide immediate feedback on its efficiency.
- Open-Circuit Voltage (OCV): A lower-than-expected OCV is often the first sign of a problem, typically indicating gas crossover or an internal short circuit within the cell.
- Output Current and Voltage: Plotting voltage against current density (a polarization curve) is the most comprehensive in-situ test. It reveals the overall efficiency and can help diagnose specific performance losses.
- Internal Resistance: An increase in internal resistance, often measured via Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS), points directly to issues with the membrane itself, such as dehydration or chemical degradation, which impede proton conductivity.
Ex-Situ Analysis: Deeper Diagnostic Checks
These evaluations are performed when the cell is disassembled and allow for a direct assessment of the membrane's physical and chemical state.
- Visual Inspection: This is the most straightforward check. Look for discoloration, pinholes, cracks, or signs of thinning, which indicate mechanical or chemical stress.
- Proton Conductivity Measurement: For advanced diagnostics, the membrane can be removed and its proton conductivity measured directly. A decrease from its baseline value is a definitive sign of degradation.
- Mechanical Strength Testing: Evaluating the membrane's tensile strength and elasticity can quantify physical aging and its susceptibility to future mechanical failure.
Understanding the Root Causes of Degradation
Monitoring is most effective when you know what you are looking for. Degradation is rarely caused by a single factor, but rather a combination of mechanical, chemical, and operational stresses.
The Impact of Operating Conditions
The operational environment is the most significant factor in a PEM's lifespan. The membrane is designed for a specific window of operation.
- Temperature and Humidity: The typical operating range is 60-80°C with 30%-80% relative humidity. Operating outside this range compromises proton conductivity and can cause mechanical stress due to swelling or drying.
- Pressure Differentials: Significant pressure differences across the membrane during operation can induce mechanical fatigue, leading to cracks or pinholes over time.
The Risk of Chemical Contamination
The PEM is a highly selective polymer, and its performance is sensitive to impurities.
- Reactant Impurities: Impurities in the fuel (hydrogen) or oxidant (air) streams can poison the catalyst layers, which in turn can initiate degradation of the membrane itself.
- External Contaminants: Contact with organic solvents or strong oxidizing agents during handling or storage can cause irreversible damage to the polymer structure.
The Danger of System-Level Failures
A PEM does not operate in isolation. The health of adjacent components is critical to the membrane's survival.
- Electrodes and Flow Fields: A failing electrode or a blocked flow field plate can create localized hotspots or pressure points. These effects concentrate stress on small areas of the membrane, leading to premature and catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your monitoring strategy should align directly with your primary objective, whether it is maximizing immediate power output or ensuring decades of reliable service.
- If your primary focus is real-time performance optimization: Prioritize continuous monitoring of the polarization curve and internal resistance to make immediate adjustments to operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is ensuring long-term system reliability: Implement strict startup/shutdown protocols to minimize mechanical shock and conduct regular maintenance on all system components, not just the membrane.
- If your primary focus is diagnosing a known failure: Correlate in-situ electrical data (like a sudden drop in OCV) with a meticulous ex-situ visual inspection to pinpoint the exact location and nature of the damage.
Ultimately, proactive management and a deep understanding of the operating environment are the keys to extending the life and performance of any proton exchange membrane.
Summary Table:
| Monitoring Aspect | Key Techniques | Primary Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time (In-Situ) | Polarization Curves, EIS, OCV Tracking | Voltage, Current Density, Internal Resistance |
| Periodic (Ex-Situ) | Visual Inspection, Conductivity Tests | Physical Damage, Thinning, Conductivity Loss |
| Root Cause Analysis | Environmental Control, System Checks | Temperature/Humidity, Contamination, Component Failures |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your fuel cell systems with KINTEK's precision lab equipment.
Effective PEM monitoring requires reliable tools for accurate data collection and analysis. KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables essential for fuel cell research, development, and maintenance. Our products help you precisely control operating conditions, conduct rigorous testing, and diagnose issues early.
Let us support your laboratory's mission for cleaner energy solutions.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your PEM monitoring strategy and ensure long-term system reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Proton Exchange Membrane for Batteries Lab Applications
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Custom Ion Conductivity Test Fixtures for Fuel Cell Research
- Polyethylene Separator for Lithium Battery
- Anion Exchange Membrane for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What operating conditions must be controlled when using a proton exchange membrane? Master Temperature, Humidity, and Pressure
- What initial steps are required before using a new proton exchange membrane? Ensure Peak Performance and Longevity
- What is a proton exchange membrane? The Selective Heart of Hydrogen Energy Systems
- What should be done if a proton exchange membrane is found to be contaminated or damaged? Restore Performance or Replace for Safety
- What is the function of perfluorinated sulfonic acid proton exchange membranes in the preparation of biomimetic sensors?



















