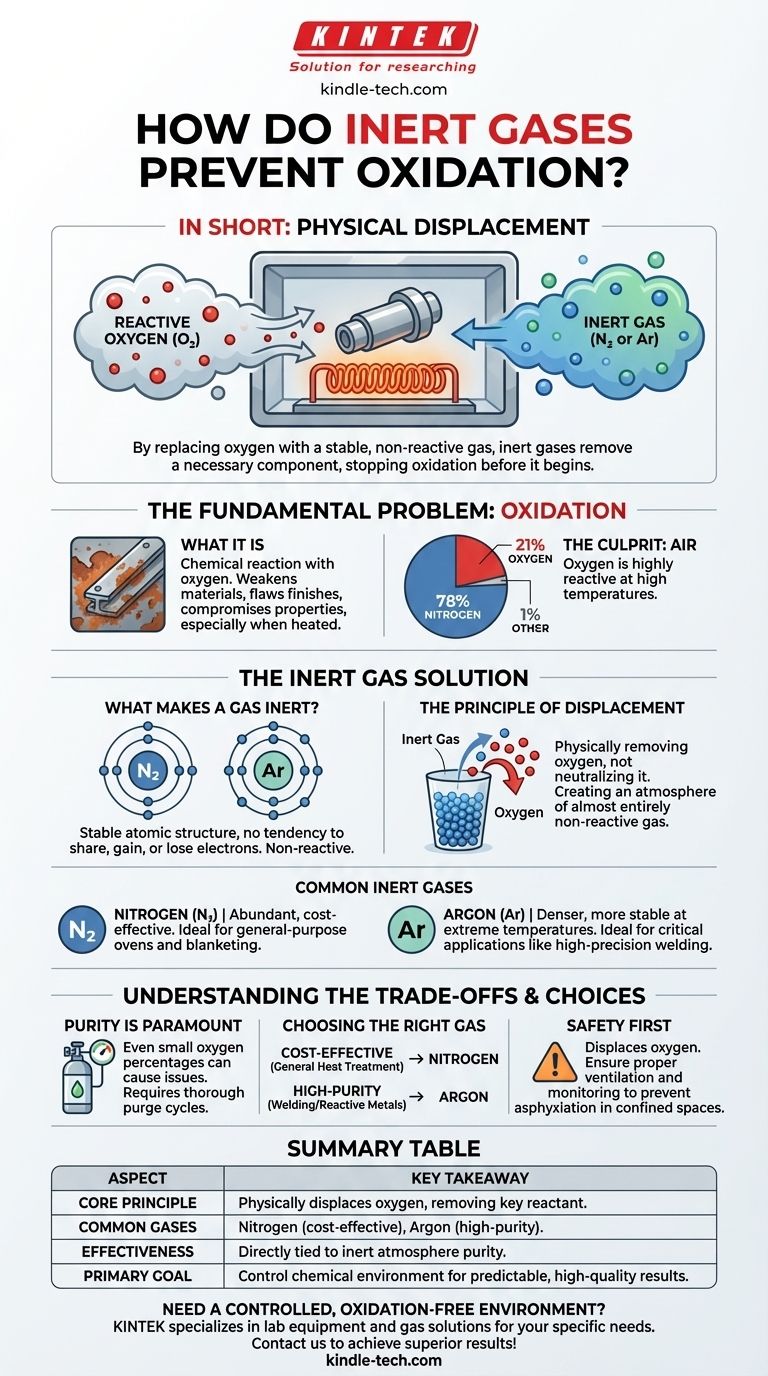
In short, inert gases prevent oxidation by physically displacing oxygen. They are pumped into a sealed environment, pushing out the reactive oxygen-rich air and replacing it with a stable, non-reactive gas that forms a protective barrier around the material.
The core principle is simple: oxidation is a chemical reaction that requires oxygen as a key ingredient. By replacing the oxygen with a gas that is chemically stable and refuses to participate in reactions, you effectively remove a necessary component, stopping oxidation before it can begin.

The Fundamental Problem: Oxidation
What is Oxidation?
Oxidation is a chemical process that occurs when a substance reacts with oxygen. This is the same reaction that causes iron to rust, a cut apple to turn brown, or a fire to burn.
In industrial settings, especially when materials are heated, this process accelerates dramatically. Unwanted oxidation can weaken materials, compromise their electrical properties, or create a flawed surface finish.
Why Air is the Culprit
The air around us is approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. While nitrogen is fairly stable, the oxygen is highly reactive and readily combines with other elements, especially at high temperatures.
Therefore, the goal in many sensitive manufacturing or scientific processes is to create an environment completely free of this reactive oxygen.
The Inert Gas Solution
What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
A gas is considered "inert" or "noble" because of its atomic structure. Gases like argon and nitrogen have a full outer shell of electrons.
This stable configuration means they have no tendency to share, gain, or lose electrons. As a result, they do not participate in chemical reactions under most conditions.
The Principle of Displacement
Using an inert gas isn't about neutralizing oxygen; it's about physically removing it. Imagine filling a cup full of water with sand—the sand displaces the water, pushing it out until the cup contains only sand.
Similarly, an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is fed into a chamber (such as an oven or a welding area), purging the oxygen and creating a new atmosphere composed almost entirely of the non-reactive gas.
Common Inert Gases
The most common inert gases used for this purpose are Nitrogen (N₂) and Argon (Ar).
Nitrogen is abundant and inexpensive, making it the go-to choice for many applications. Argon is denser than air and even more inert than nitrogen, making it ideal for critical applications like high-precision TIG welding where absolute protection is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Purity is Paramount
The effectiveness of an inert atmosphere is directly tied to its purity. Even a small percentage of remaining oxygen can be enough to cause unwanted oxidation, especially at high temperatures.
This is why processes often involve a "purge cycle" to flush the chamber thoroughly before the primary operation (like heating) begins.
Choosing the Right Gas
While both nitrogen and argon are inert, they are not interchangeable for all tasks. Nitrogen is a cost-effective workhorse for general-purpose ovens and blanketing.
Argon, being denser and more stable at extreme temperatures, provides a more robust shield. It's preferred for welding exotic metals or in advanced manufacturing where even the slightest reaction with nitrogen could be a problem.
Safety and Handling
It is critical to remember that while inert gases are non-toxic, they displace oxygen. In a confined space, a leak can create an oxygen-deficient atmosphere that poses a serious asphyxiation hazard. Proper ventilation and monitoring are essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct approach depends entirely on the sensitivity and goal of your process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective oxidation prevention for general heat treatment: Nitrogen is almost always the superior choice due to its low cost and high availability.
- If your primary focus is high-purity welding or processing reactive metals at extreme temperatures: Argon provides a more reliable and completely non-reactive shield, justifying its higher cost.
Ultimately, using an inert gas is about taking deliberate control of the chemical environment to guarantee a predictable and high-quality result.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Physically displaces oxygen, removing a key reactant needed for oxidation. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (cost-effective), Argon (high-purity for critical applications). |
| Effectiveness | Directly tied to the purity of the inert atmosphere; even small oxygen levels can cause issues. |
| Primary Goal | Control the chemical environment to prevent unwanted reactions and ensure predictable results. |
Need to create a controlled, oxidation-free environment for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment and gas solutions to meet your specific needs. Whether you require cost-effective nitrogen blanketing or high-purity argon systems for sensitive applications, our expertise ensures your materials are protected. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments



















