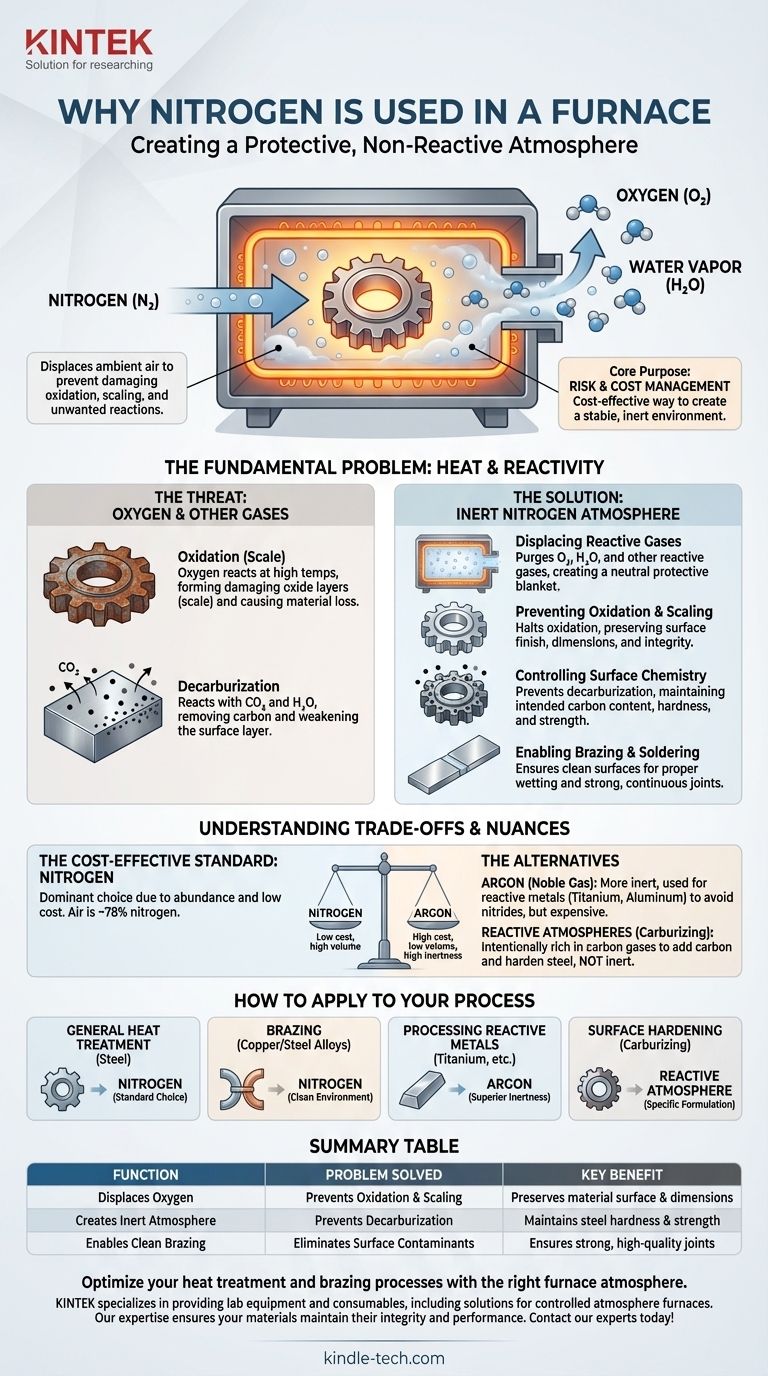
In short, nitrogen is used in a furnace to create a protective, non-reactive atmosphere. By pumping nitrogen gas into the furnace chamber, it displaces the ambient air—specifically the oxygen—which would otherwise cause damaging oxidation, scaling, and other unwanted chemical reactions on the material being heated.
The core purpose of using nitrogen is risk and cost management. It is the most cost-effective method for creating a stable, inert environment at high temperatures, preventing material degradation and ensuring the quality and integrity of the final product.

The Fundamental Problem: Heat and Reactivity
At room temperature, the air around us is relatively benign. However, introducing the intense heat of a furnace fundamentally changes its chemical behavior, turning a seemingly harmless atmosphere into a highly aggressive one.
The Primary Threat of Oxygen
The most significant issue is oxidation. Air is approximately 21% oxygen, a highly reactive element that aggressively combines with other materials, especially at high temperatures.
For metals like steel, this reaction results in the formation of an oxide layer, commonly known as scale. This scaling causes material loss, results in a poor surface finish, and can compromise the dimensional accuracy of a part.
The Secondary Threat of Other Gases
Oxygen isn't the only problem. Other components in the air, like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water vapor (H₂O), can also cause undesirable reactions.
A key example is decarburization in steel. At high temperatures, the carbon near the surface of a steel part can react with these gases and be drawn out, leaving the surface layer softer and weaker than the core.
Nitrogen as the Solution: Creating an Inert Atmosphere
The solution to this heat-induced reactivity is to replace the air with a gas that will not react with the material being processed. This is known as creating an inert atmosphere.
Displacing Reactive Gases
Nitrogen gas (N₂) is pumped into the sealed furnace chamber, purging the oxygen, water vapor, and other reactive gases. Because nitrogen is relatively non-reactive under most heat treatment conditions, it acts as a neutral protective blanket.
Preventing Oxidation and Scaling
With oxygen removed from the environment, the oxidation process is halted. This ensures the material's surface remains clean, bright, and free from scale, preserving both its dimensions and its integrity.
Controlling Surface Chemistry
By providing a truly neutral environment, a pure nitrogen atmosphere also prevents secondary reactions like decarburization. This guarantees that the carbon content—and therefore the hardness and strength—of a steel part's surface remains exactly as intended.
Enabling Brazing and Soldering
Processes like furnace brazing require exceptionally clean surfaces for the filler metal to properly wet and bond the parent materials. A nitrogen atmosphere prevents oxides from forming during heating, creating the ideal conditions for a strong, continuous joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While nitrogen is the industry workhorse, it is not a universally perfect solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Cost-Effectiveness of Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the dominant choice for one simple reason: cost. The air we breathe is ~78% nitrogen, making it abundant and cheap to separate and purify compared to truly inert noble gases.
When Nitrogen Isn't "Inert" Enough
At very high temperatures, nitrogen can become reactive with certain metals. For example, it will react with titanium, aluminum, and magnesium to form nitrides on the surface. While this effect is sometimes desired in a process called nitriding, it is often an unwanted form of contamination.
The Alternative: Noble Gases
For applications involving highly reactive metals or where absolute inertness is non-negotiable, a noble gas like argon (Ar) is used. Argon is significantly more inert than nitrogen and will not react even at extreme temperatures, but it is also much more expensive.
The Alternative: Reactive Atmospheres
Sometimes, the goal is not to prevent reactions but to control them. In processes like carburizing, the furnace atmosphere is intentionally rich in carbon-donating gases (like carbon monoxide or methane) to add carbon to the surface of steel, making it harder. This stands in direct contrast to the protective goal of a nitrogen atmosphere.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing the correct furnace atmosphere depends entirely on the material, the process, and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment of steel: Nitrogen is the industry-standard, cost-effective choice for preventing oxidation and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is brazing copper or steel alloys: Nitrogen provides the clean, oxide-free environment necessary for a successful joint.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals like titanium: Argon is the superior choice to avoid the formation of unwanted nitrides.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening through chemical changes: You will need a specifically formulated reactive atmosphere, not an inert one.
Ultimately, selecting the right atmosphere is a critical process parameter that directly controls the quality, integrity, and performance of your heat-treated components.
Summary Table:
| Function | Problem Solved | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Displaces Oxygen | Prevents Oxidation & Scaling | Preserves material surface and dimensions |
| Creates Inert Atmosphere | Prevents Decarburization | Maintains steel hardness and strength |
| Enables Clean Brazing | Eliminates Surface Contaminants | Ensures strong, high-quality joints |
Optimize your heat treatment and brazing processes with the right furnace atmosphere. KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for controlled atmosphere furnaces. Our expertise ensures your materials maintain their integrity and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a controlled nitrogen atmosphere in Si3N4 + SiC? Ensure Superior Ceramic Stability
- Why does furnace use nitrogen? Prevent Oxidation for Flawless High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature hydrogen atmosphere furnace play in the heat treatment of tungsten plates?
- What role does an atmosphere furnace utilizing hydrogen gas play in Cu-Cr-Nb alloy powder pretreatment? (Key Insights)
- Why use a precision atmospheric control furnace for annealing HEAs? Unlock Pure Material Stability Data
- What is the main hazard associated with the use of inert gases? The Silent Danger of Oxygen Displacement
- What is hydrogen annealing? The Complete Guide to Bright Annealing
- How do atmosphere or vacuum furnaces protect sulfide electrolytes? Key Insights for Safe & High-Performance Synthesis



















