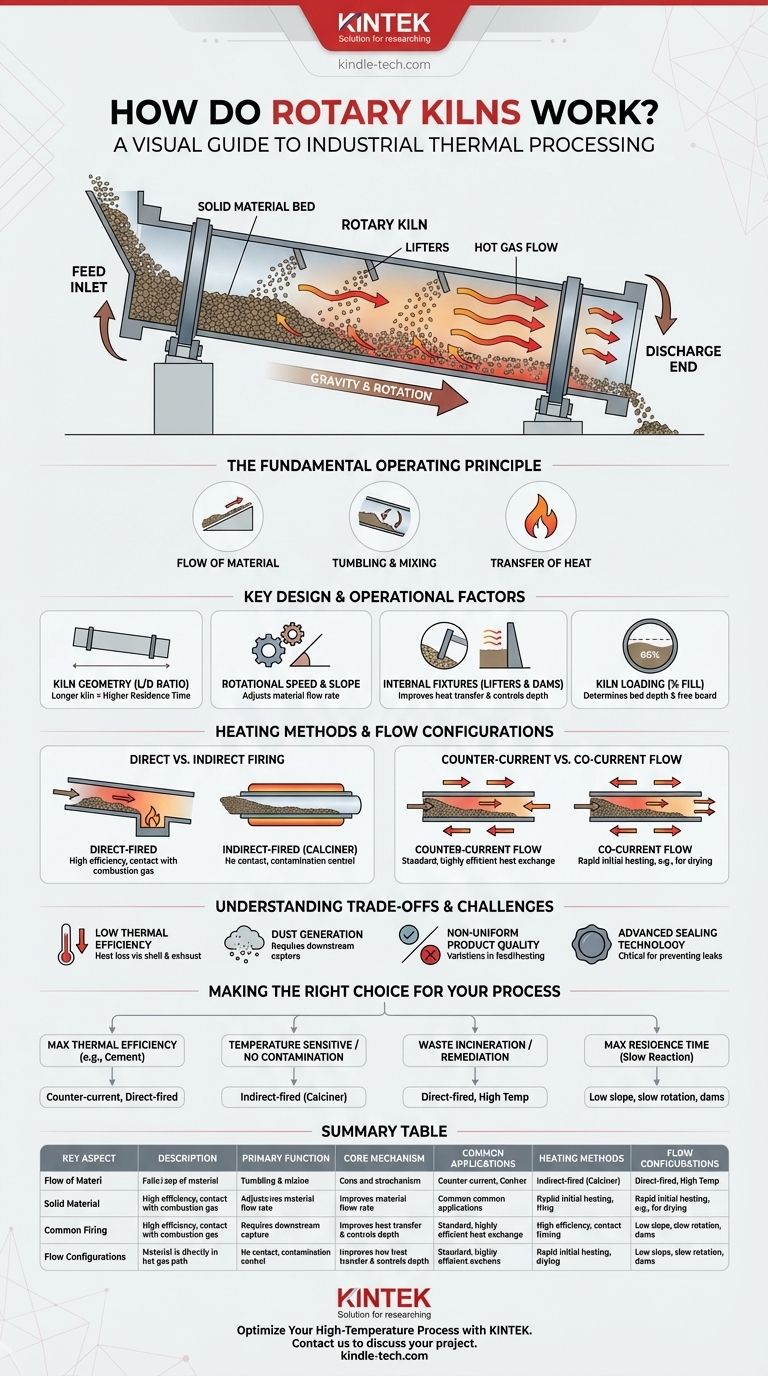
At its core, a rotary kiln is a large, rotating industrial furnace used to process solid materials at very high temperatures. Material is fed into the elevated end of a slightly sloped, rotating cylinder. As it tumbles and slides down the length of the kiln due to gravity and rotation, it is heated by hot gas to induce a desired chemical reaction or physical change, such as calcination, sintering, or incineration.
Industries need a reliable method to continuously and uniformly heat large volumes of granular solids. Rotary kilns solve this by combining rotational tumbling, gravitational flow, and controlled heating, making them versatile and powerful workhorses for processes ranging from cement manufacturing to hazardous waste disposal.
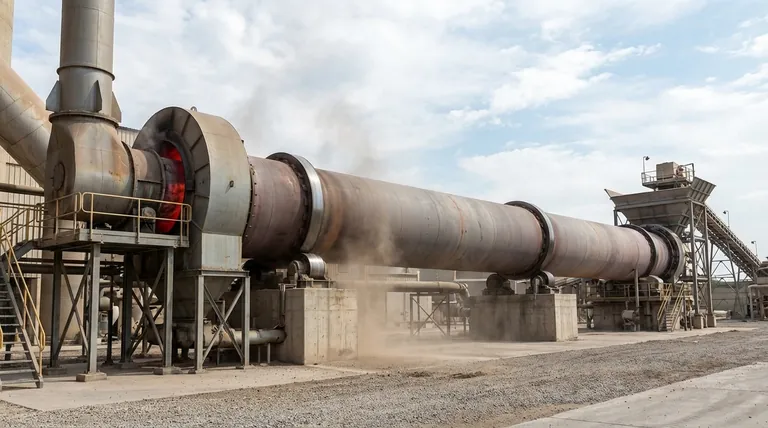

The Fundamental Operating Principle
A rotary kiln functions as a continuous heat exchanger, moving material through a controlled thermal environment. Its operation is defined by the interaction of material flow, mixing, and heat transfer.
The Flow of Material
Material is continuously fed into the upper end of the inclined cylinder. The combination of the kiln's slope and its slow rotation causes the material to gradually advance toward the lower discharge end. This creates a continuous, automated process.
The Tumbling and Mixing Action
As the kiln rotates, the solid material inside is constantly lifted and tumbled. This action, similar to a large-scale clothes dryer, is critical for ensuring that all particles are uniformly exposed to heat. This well-mixed "bed" of material promotes consistent reactions and a homogenous final product.
The Transfer of Heat
The primary function is to transfer energy from a hot gas phase to the solid material bed. This heat drives the end-use process, whether it's drying moisture, burning off organics, or causing a high-temperature chemical transformation. The kiln's ability to reach temperatures up to 2273 K (2000 °C) makes it suitable for demanding applications.
Key Design and Operational Factors
The performance of a rotary kiln is dictated by a combination of its physical design and how it is operated.
Kiln Geometry (L/D Ratio)
The length-to-diameter (L/D) ratio is a fundamental design parameter. A longer kiln with a higher L/D ratio increases the time the material spends inside, known as the residence time, which is crucial for ensuring complete reactions.
Rotational Speed and Slope
Operators can adjust the rotational speed and, in some designs, the kiln's slope. Increasing speed or slope will decrease the residence time by moving material through the kiln faster. These are the primary controls for managing the process on a day-to-day basis.
Internal Fixtures (Lifters and Dams)
Many kilns include internal structures to control material flow. Lifters are flights that pick up material and shower it through the hot gas stream, significantly improving heat transfer efficiency. Dams are used to increase the depth of the material bed, thereby increasing residence time.
Kiln Loading (% Fill)
The percentage of the kiln's cross-section filled with material is its loading. This determines the depth of the material bed and the size of the free board—the open space above the material where process gases flow.
Heating Methods and Flow Configurations
How heat is introduced and how it interacts with the material are critical design choices that define the kiln's application.
Direct vs. Indirect Firing
A direct-fired kiln is the most common type. Hot combustion gases flow directly through the kiln and make contact with the material. This is highly efficient for transferring heat.
An indirect-fired kiln, also called a calciner, is heated externally. The rotating shell gets hot and radiates heat to the material inside, without any contact between the material and the combustion gas. This is used for processes where contamination must be avoided or the atmosphere must be tightly controlled.
Counter-Current vs. Co-Current Flow
Counter-current flow is the standard configuration. Material enters the high end and moves down, while hot gas enters the low end and moves up. This opposing flow creates the most efficient heat exchange, as the hottest gases meet the most-processed material.
Co-current flow is less common. Both material and hot gas enter at the same end and travel in the same direction. This is typically used for applications like drying, where rapid heating of the incoming wet feed is desired.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While incredibly useful, rotary kilns are not without their operational complexities and limitations.
Low Thermal Efficiency
Rotary kilns are large, hot systems that can lose a significant amount of heat through their shell and exhaust gases. This can result in relatively low thermal efficiency, making them energy-intensive to operate.
Dust Generation
The tumbling action that makes kilns excellent mixers also creates fine particulate matter, or dust. This dust becomes entrained in the process gas and must be captured by downstream equipment like baghouses or cyclones to prevent pollution.
Non-Uniform Product Quality
While the goal is uniformity, achieving it perfectly can be challenging. Variations in feed rate, particle size, or heating can lead to slight inconsistencies in the final product quality, requiring robust quality control.
Advanced Sealing Technology
Sealing the rotating kiln at both the feed and discharge ends is critical to prevent cold air from leaking in or hot, dusty gas from escaping. Modern kilns use advanced sealing systems, but maintaining these seals is a constant and vital maintenance task.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The specific configuration of a rotary kiln is always tailored to its intended industrial process.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency for high-temperature reactions (like cement clinker or ore sintering): A counter-current, direct-fired kiln is the standard and most effective configuration.
- If your primary focus is processing temperature-sensitive materials or avoiding contamination from combustion gases: An indirect-fired kiln (calciner) is the necessary choice to protect your product.
- If your primary focus is waste incineration or soil remediation: A direct-fired kiln provides the robust, high-temperature environment needed to ensure complete destruction of contaminants.
- If your primary focus is maximizing material residence time for a slow reaction: A design with a low slope, slow rotation speed, and internal dams is the ideal approach.
Understanding these core principles allows you to view the rotary kiln not just as a piece of equipment, but as a precise and adaptable tool for material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Continuous high-temperature processing of solid materials. |
| Core Mechanism | Material tumbles down a sloped, rotating cylinder while being heated. |
| Common Applications | Cement production, ore sintering, hazardous waste incineration, calcination. |
| Heating Methods | Direct-fired (efficient) or Indirect-fired (for contamination control). |
| Flow Configurations | Counter-current (standard, efficient) or Co-current (for rapid heating). |
Optimize Your High-Temperature Process with KINTEK
Whether you are developing a new material, processing ores, or managing waste, the right thermal processing equipment is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory and industrial heating solutions, including rotary kiln systems tailored to your specific needs.
We provide the equipment and expertise to help you achieve precise temperature control, uniform heating, and efficient production. Let our team help you select the perfect system for your application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing



















