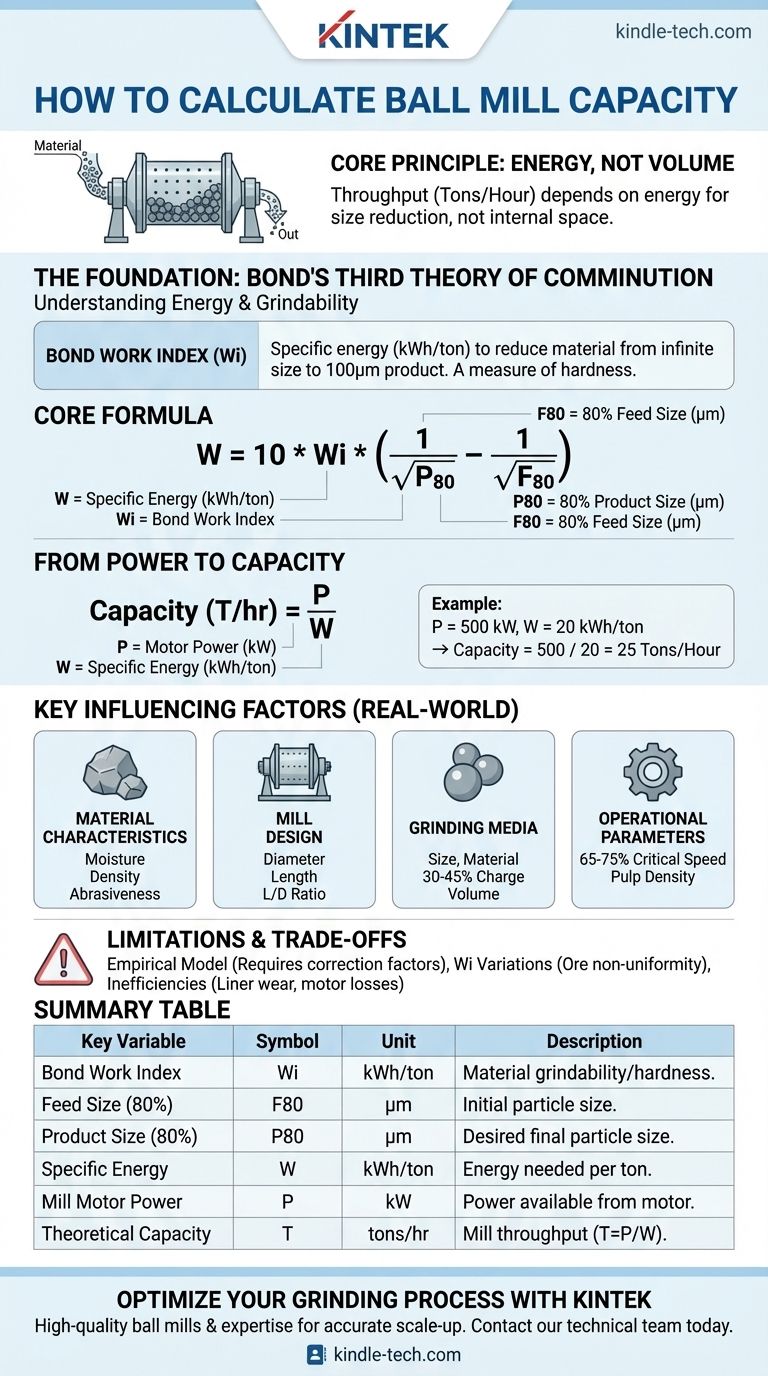
Calculating ball mill capacity is not a simple measure of volume, but rather an engineering calculation to determine its throughput in tons per hour. The industry-standard method relies on Bond's Third Theory of Comminution, which calculates the specific power (kWh/ton) required to grind a specific material from a given feed size to a desired product size. From this required power, you can derive the mill's capacity based on the motor's power rating.
The core principle is this: Ball mill capacity is not determined by how much material fits inside it, but by the energy required to achieve a specific particle size reduction for a particular material. This energy requirement is the limiting factor that dictates the feed rate in tons per hour.
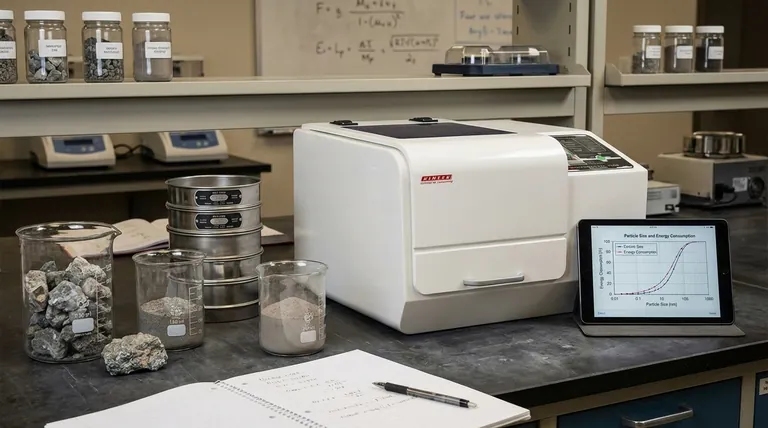

The Foundation: Bond's Third Theory of Comminution
To accurately estimate capacity, you must first understand the relationship between energy, material hardness, and particle size. Bond's formula provides the framework for this.
What is the Bond Work Index (Wi)?
The Bond Work Index (Wi) is the central variable in the calculation. It represents the specific energy, measured in kilowatt-hours per ton (kWh/ton), required to reduce a material from a theoretically infinite size down to a product size of 100 micrometers.
This value is a fundamental property of the material itself—a measure of its hardness or "grindability." It is determined through standardized laboratory tests on a representative sample of the ore or material you intend to grind.
The Core Formula
The Bond equation calculates the specific energy (W) needed for a grinding task:
W = 10 * Wi * (1/√P80 - 1/√F80)
W= The work input required, in kWh per metric ton.Wi= The Bond Work Index for the specific material.P80= The particle size that 80% of the product passes through, in micrometers (μm).F80= The particle size that 80% of the feed material passes through, in micrometers (μm).
This formula tells you exactly how much energy you need to expend for every ton of material processed.
From Power to Capacity (Tons Per Hour)
Once you know the energy required per ton (W), you can calculate the theoretical capacity (T) of a mill with a known motor power (P).
Capacity (T/hr) = P / W
P= The total power drawn by the mill motor, in kilowatts (kW).W= The specific energy requirement calculated from the Bond formula (kWh/ton).
For example, if your mill motor draws 500 kW and your material requires 20 kWh/ton (W), your theoretical capacity is 25 tons per hour (500 / 20).
Key Factors Influencing Real-World Capacity
The Bond formula provides a robust theoretical baseline. However, actual operational capacity is influenced by several mechanical and operational factors.
Material Characteristics
Beyond the Work Index, properties like moisture content, density, and abrasiveness can impact grinding efficiency and material flow through the mill, affecting the final throughput.
Mill Design and Dimensions
The diameter and length of the mill are critical. A larger diameter provides greater impact force for breaking coarse particles, while the length-to-diameter ratio influences the material's residence time inside the mill.
Grinding Media
The size, material, and charge volume of the grinding balls are crucial. The ball size must be matched to the feed particle size. The charge volume—the percentage of the mill filled with balls—is typically optimized between 30-45% to maximize grinding action without wasting energy.
Operational Parameters
A mill's rotational speed is set relative to its "critical speed" (the speed at which balls would centrifuge). Most mills operate at 65-75% of critical speed to create the ideal tumbling and cascading motion for efficient grinding. Similarly, pulp density (the solids-to-water ratio in wet grinding) must be optimized to ensure proper particle coating and energy transfer.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
Relying solely on the formula without understanding its context can lead to inaccurate projections.
The Formula is an Empirical Model
Bond's equation is an excellent and widely trusted empirical model, but it is not a perfect law of physics. It works best for a specific range of particle sizes and may require correction factors for different conditions, such as dry grinding, open vs. closed-circuit operation, and oversized feed.
The Work Index is a Snapshot
The Bond Work Index is determined from a lab sample. However, ore bodies in a mine are never perfectly uniform. Variations in ore hardness will cause the actual Wi to fluctuate, leading to changes in mill throughput day-to-day.
Mechanical and Operational Inefficiencies
The calculated capacity is a theoretical maximum. Real-world inefficiencies from liner wear, motor and drive losses, and sub-optimal pulp density will always result in an actual capacity that is slightly lower than the calculated value.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Use these calculations to guide your specific goal, whether you are in the design, operation, or troubleshooting phase.
- If your primary focus is sizing a new mill: Use the Bond formula with a lab-determined
Wifrom a representative sample to calculate the required mill power, then select a mill that can deliver that power with an appropriate safety margin. - If your primary focus is optimizing an existing mill: Compare your actual energy consumption (kWh/ton) to the calculated Bond value (
W) to benchmark your grinding circuit's efficiency and identify areas for improvement. - If your primary focus is troubleshooting a capacity shortfall: Re-evaluate your key variables—has your feed size (
F80) become coarser, or has the material's hardness (Wi) increased, thus demanding more energy per ton than the system was designed for?
Ultimately, calculating ball mill capacity is about understanding the energy balance between your equipment's power and your material's resistance to being ground.
Summary Table:
| Key Variable | Symbol | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bond Work Index | Wi | kWh/ton | Material grindability/hardness. |
| Feed Size (80% passing) | F80 | μm | Initial particle size. |
| Product Size (80% passing) | P80 | μm | Desired final particle size. |
| Specific Energy | W | kWh/ton | Energy needed per ton (W = 10 * Wi * (1/√P80 - 1/√F80)). |
| Mill Motor Power | P | kW | Power available from the mill motor. |
| Theoretical Capacity | T | tons/hr | Mill throughput (T = P / W). |
Optimize Your Grinding Process with KINTEK
Accurately calculating ball mill capacity is the first step toward maximizing your laboratory or production efficiency. Whether you are sizing new equipment, troubleshooting a throughput issue, or seeking to benchmark your current operation's performance, having the right tools and expertise is critical.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including robust ball mills designed for reliable performance and accurate scale-up data. Our experts understand the intricacies of comminution and can help you select the perfect mill for your specific material and capacity requirements.
Let KINTEK empower your grinding process. Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation to ensure your operations are running at peak capacity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in the preparation of NASICON-type solid electrolytes like LATP and LAGP?
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill for Fe-Cu composites? Optimize Particle Distribution & Conductivity
- What is the primary function of a planetary high-energy ball mill? Master Mechanical Alloying for Nickel Nanoparticles
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in Al-LLZ lithium garnet preparation? Optimize Solid-State Electrolyte Synthesis
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis



















