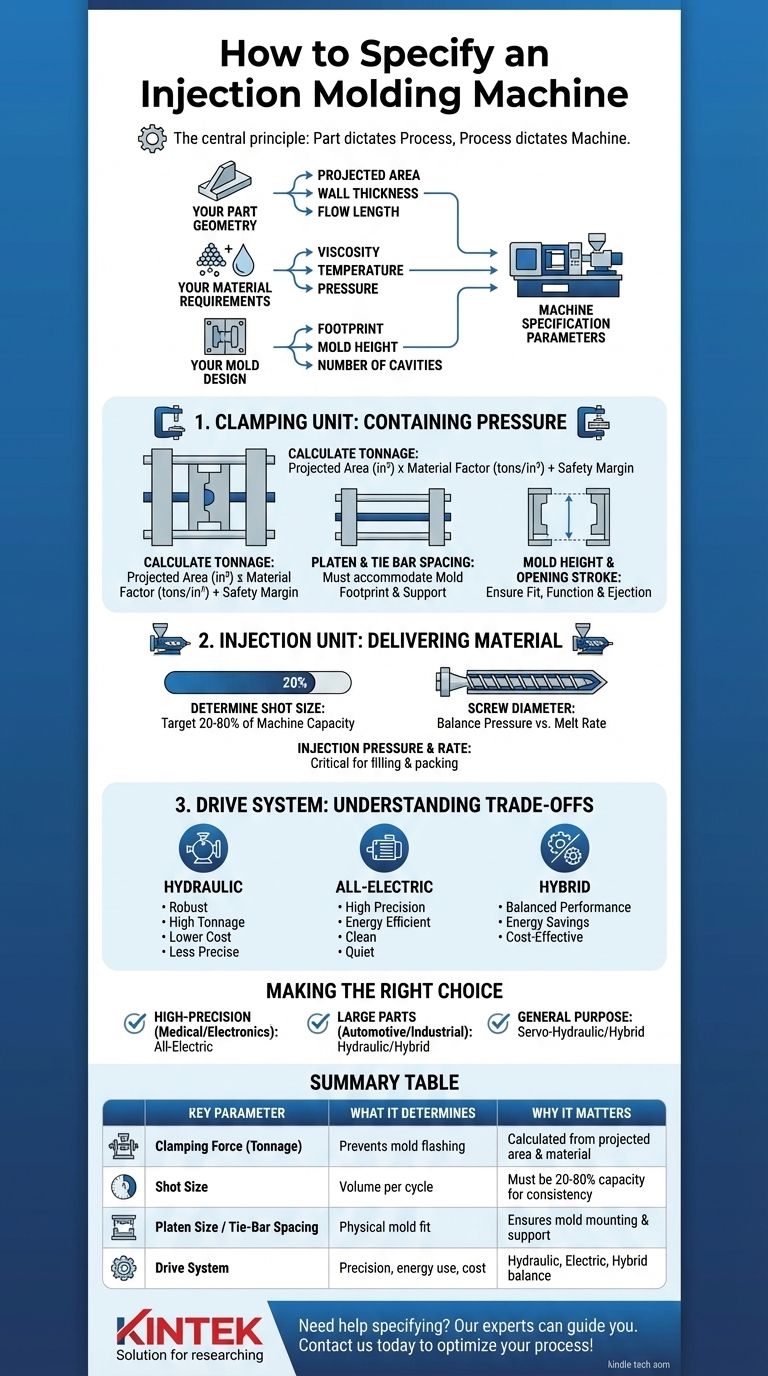
To specify an injection molding machine, you must define four primary parameters driven by your part and mold design: clamping force (tonnage), shot size, platen size/tie-bar spacing, and the type of drive system (hydraulic, electric, or hybrid). These specifications ensure the machine can physically hold your mold, inject the right amount of plastic, and produce parts that meet your quality, cost, and volume requirements.
The central principle of machine specification is that the part dictates the process, and the process dictates the machine. You cannot select the right machine without first performing a detailed analysis of your part's geometry, the plastic resin you will use, and the design of the mold itself.

The Foundation: Part and Mold First, Machine Second
Before you can even look at a machine catalog, you must have a clear understanding of the component you intend to produce. Every machine specification flows directly from the demands of your specific application.
Analyzing Your Part's Geometry
The physical shape and size of your part are the primary drivers. Pay close attention to its projected area—the total area of the part's shadow when looking at it from the direction of the clamp opening. This is the single most important factor in calculating required clamp force.
Also, consider the part's wall thickness and flow length. Thin-walled parts or those with long, complex flow paths require higher injection pressures and speeds to fill completely before the plastic freezes.
Understanding Your Material's Requirements
Different plastic resins behave differently. A high-viscosity material like polycarbonate (PC) requires significantly more injection pressure to fill a mold than a low-viscosity material like polypropylene (PP).
Each material also has a specific processing window for temperature and pressure, which the machine's injection unit must be capable of maintaining consistently.
Considering Your Mold Design
The physical size of the mold, or its footprint, determines the required platen size. The mold's thickness dictates the mold height range the machine must accommodate.
Furthermore, the number of cavities in the mold directly impacts both the required clamping force (more cavities = larger projected area) and the necessary shot size.
Specifying the Clamping Unit: Containing the Pressure
The clamping unit's job is to hold the two halves of the mold shut against the immense force generated by the injection unit.
Calculating Clamping Force (Tonnage)
This is the headline specification for any machine. Insufficient tonnage will allow the mold to flash, creating defective parts and potentially damaging the tool.
The basic calculation is Projected Area (in²) x Material Factor (tons/in²). The material factor is a general rule of thumb, typically ranging from 2 to 8 tons per square inch depending on the material's viscosity and the part's complexity. For example, a simple PP part might need 2-3 tons/in², while a thin-walled PC part may need 5 tons/in² or more.
Always add a safety margin of at least 10-20% to your calculated tonnage.
Matching the Mold Footprint: Platen Size & Tie Bar Spacing
The mold must physically fit within the machine. The tie bars are the four large posts that connect the stationary and moving platens. The distance between tie bars (horizontal and vertical) defines the maximum mold dimensions that can be mounted.
The overall platen size is also important, as it must be large enough to properly support the entire mold base.
Ensuring Fit and Function: Mold Height and Opening Stroke
Mold height is the machine's ability to handle a specific range of mold thicknesses. Your mold's thickness must fall between the machine's specified minimum and maximum.
The opening stroke is the maximum distance the moving platen can travel. This stroke must be large enough to allow the finished part to be ejected and cleared from the mold, often by a robot.
Specifying the Injection Unit: Delivering the Material
The injection unit is responsible for melting the plastic resin and injecting it into the mold cavity with precision and power.
Determining Shot Size
The shot size is the maximum volume (often expressed as weight in ounces or grams for a specific material like Polystyrene) of plastic the machine can inject in one cycle.
Your total shot weight (part(s) + runner system) should ideally fall between 20% and 80% of the machine's maximum shot capacity. Using less than 20% can lead to resin degradation from excessive residence time in the barrel. Using more than 80% risks inconsistent shots and poor process control.
The Role of Screw Diameter
The screw is the heart of the injection unit. A smaller diameter screw can generate higher injection pressure but has a lower melt rate. A larger diameter screw provides a higher melt rate and plasticizing capacity but at lower maximum pressures. The choice is a balance based on your material and cycle time needs.
Injection Pressure and Rate
Maximum injection pressure is the force the machine can exert to push the material into the mold. As mentioned, high-viscosity materials and thin-walled parts require higher pressures.
Injection rate (or speed) is how quickly that material can be delivered. This is critical for parts where the plastic could cool and solidify before the mold is fully packed out.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hydraulic vs. Electric vs. Hybrid
The drive system is a fundamental choice that impacts precision, energy use, and cost.
The Case for Hydraulic Machines
Hydraulic machines are the traditional workhorses of the industry. They offer very high clamping forces, are robust, durable, and have a lower initial purchase price. They are excellent for larger, less complex parts where ultimate precision is not the primary concern.
The Precision of All-Electric Machines
All-electric machines use high-precision servo motors instead of hydraulics. This provides exceptional repeatability, accuracy, and energy efficiency. They are also much quieter and cleaner, making them the standard for medical, electronics, and other high-precision applications.
The Balanced Approach: Hybrid Machines
Hybrid machines combine technologies, typically using an electric screw drive for precision melting and injection, paired with a hydraulic clamp for powerful and cost-effective tonnage. They offer a compelling balance of performance, energy savings, and price.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a machine is a process of aligning capabilities with your specific manufacturing objectives.
- If your primary focus is high-precision medical or electronics parts: An all-electric machine is the superior choice for its unmatched repeatability and clean operation.
- If your primary focus is large automotive, appliance, or industrial parts: A hydraulic or large hybrid machine will provide the necessary clamping force and durability in a cost-effective package.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose molding with a balance of cost and performance: A modern servo-hydraulic or a hybrid machine offers an excellent blend of energy efficiency and capability.
By starting with your part and systematically defining these parameters, you transform machine selection from a guess into a precise engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | What It Determines | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Clamping Force (Tonnage) | Prevents mold flashing | Calculated from part's projected area and material |
| Shot Size | Volume of plastic per cycle | Must be 20-80% of machine capacity for consistency |
| Platen Size / Tie-Bar Spacing | Physical mold fit | Ensures the mold can be mounted and supported |
| Drive System | Precision, energy use, cost | Hydraulic (robust), Electric (precision), Hybrid (balanced) |
Need help specifying the perfect injection molding machine for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and reliability. Our experts can guide you through the selection process to ensure you get a machine that matches your part geometry, material, and volume requirements. Contact us today to optimize your injection molding process and achieve superior part quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Lab Infrared Press Mold
- No Demolding Lab Infrared Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- How do you do the KBr pellet method? A Step-by-Step Guide to Perfect FTIR Sample Preparation
- Why we use KBr pellets in IR? Unlock Clear Sample Analysis with Infrared-Transparent Matrix
- What is the KBr method in IR spectroscopy? A Guide to Solid Sample Analysis
- Why use KBr to make the pellet? Achieve Clear, Accurate IR Spectroscopy Results
- What is the size range of pellets? From 1mm to 25mm, Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application



















