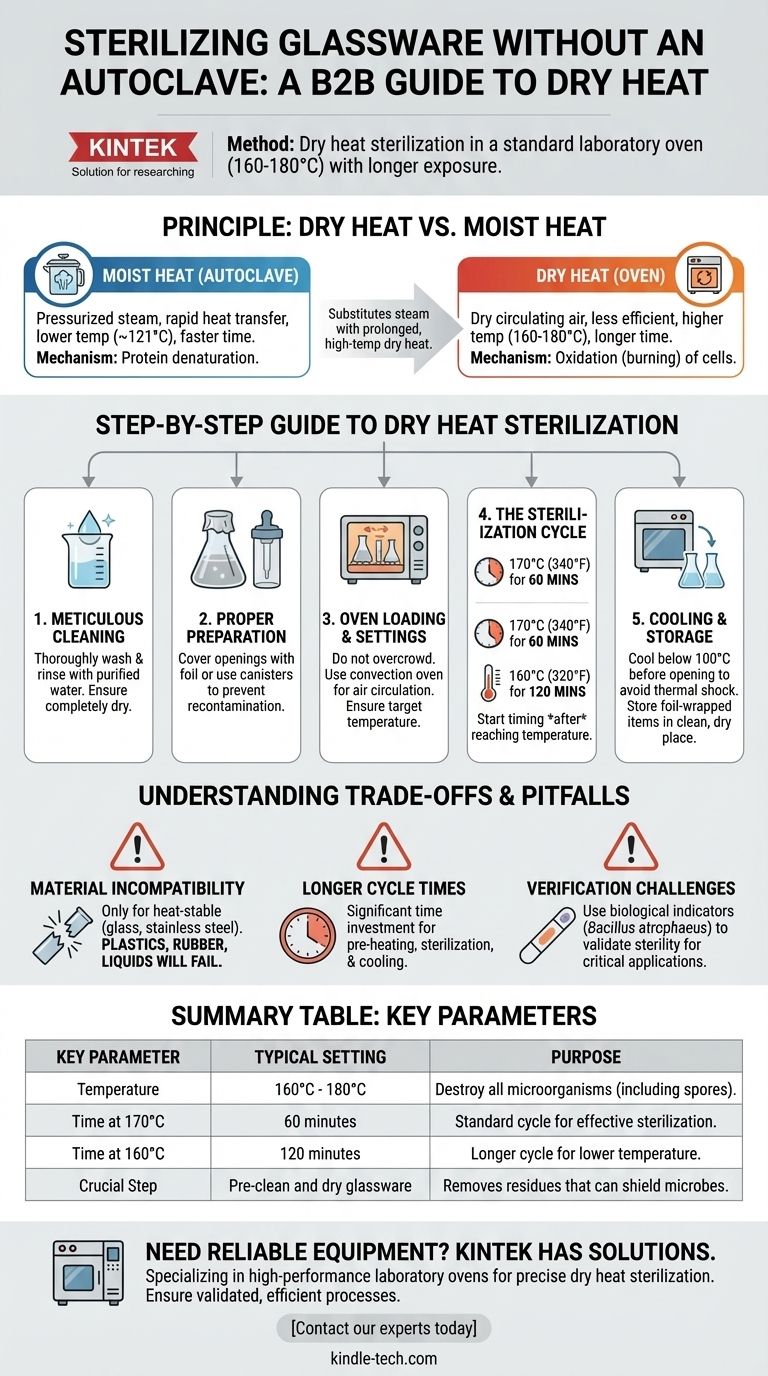
When an autoclave is unavailable, the primary and most reliable method for sterilizing glassware is dry heat sterilization using a standard laboratory oven. This process leverages higher temperatures (typically 160-180°C) and longer exposure times compared to an autoclave to effectively destroy all microorganisms, including resilient bacterial spores.
The core principle is substituting the pressurized steam of an autoclave with prolonged, high-temperature dry heat. While effective for glassware, this method requires stricter parameters—higher temperatures for longer durations—because dry heat transfers energy less efficiently than the moist heat of steam.

The Principle: Dry Heat vs. Moist Heat
Why an Oven Isn't a Direct Substitute
An autoclave uses pressurized steam to rapidly transfer thermal energy, allowing it to sterilize at lower temperatures (around 121°C) in shorter times.
A standard oven uses dry, circulating air. Air is a far less efficient conductor of heat than steam, meaning you must compensate with more intense conditions to achieve the same result.
The Mechanism of Dry Heat
Dry heat sterilization works by oxidizing cellular components, essentially burning microorganisms to death. This is a slower process than the protein denaturation caused by moist heat in an autoclave, which is why the time and temperature requirements are significantly higher.
Step-by-Step Guide to Dry Heat Sterilization
Step 1: Meticulous Cleaning
Sterilization can only be achieved on a clean surface. Any residual organic matter can insulate microbes, shielding them from the heat and compromising the process.
Wash glassware thoroughly with an appropriate detergent, rinse multiple times with purified water (e.g., deionized water), and ensure it is completely dry before proceeding.
Step 2: Proper Preparation and Wrapping
To maintain sterility after the cycle, items should be prepared correctly.
Cover the openings of flasks, beakers, and bottles with aluminum foil. For items like pipettes, you can place them in a metal canister or wrap them entirely in foil. This barrier prevents recontamination once the oven door is opened.
Step 3: Oven Loading and Settings
Do not overcrowd the oven. Proper air circulation is critical for ensuring all surfaces reach and maintain the target temperature. Leave adequate space between all items.
The oven used must be capable of maintaining a consistent high temperature. A convection oven, which uses a fan to circulate air, is highly recommended for this purpose.
Step 4: The Sterilization Cycle
The time and temperature for sterilization are inversely related. The clock starts only after the oven has reached the target temperature.
- 170°C (340°F) for 60 minutes
- 160°C (320°F) for 120 minutes
For larger or densely packed loads, extending the time is a prudent safety measure to account for heat transfer lag.
Step 5: Cooling and Storage
Do not open the oven door until the cycle is complete and the temperature has dropped below 100°C. A rapid temperature change can cause glassware to crack.
Once cooled, the foil-wrapped, sterile glassware can be stored in a clean, dry, and dust-free environment until needed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Material Incompatibility
Dry heat is only suitable for heat-stable materials like glass and stainless steel.
Plastics, rubber seals, and some types of caps will melt or degrade at these high temperatures. Always verify that every component of the item being sterilized can withstand the heat.
Not Suitable for Liquids
Dry heat sterilization is completely inappropriate for liquids, media, or agars. The process would simply boil away the liquid long before sterility is achieved. These items require an autoclave or sterile filtration.
Longer Cycle Times
The entire process, including pre-heating, the sterilization cycle itself, and the cooling period, is significantly longer than a typical autoclave run. This requires careful planning in any workflow.
Verification Challenges
Just as with an autoclave, simply running a cycle does not guarantee sterility. For critical applications, biological indicators (spore strips containing Bacillus atrophaeus) should be included in the load to validate that the process was successful.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you use the correct method, assess your specific materials and objectives.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing standard borosilicate glassware (flasks, beakers, bottles): Dry heat sterilization in a convection oven is your most effective and accessible method.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing items with plastic components (like filter funnels or caps): You must avoid dry heat. Explore chemical sterilization or acquire autoclavable versions of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids or biological media: Dry heat is not an option; you must find access to an autoclave or use pre-sterilized filtration systems.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently achieve reliable glassware sterility, even without an autoclave.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Typical Setting | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 160°C - 180°C | To destroy all microorganisms, including spores. |
| Time at 170°C | 60 minutes | Standard cycle for effective sterilization. |
| Time at 160°C | 120 minutes | Longer cycle for lower temperature. |
| Crucial Step | Pre-clean and dry glassware | Removes residues that can shield microbes. |
Need reliable equipment for your sterilization protocols? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory ovens and consumables designed for precise dry heat sterilization and other critical lab workflows. Ensure your processes are validated and efficient with our trusted solutions. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the RF frequency for sputtering? Unlocking the Standard for Insulating Materials
- What is ashing in chemistry? Enhance Analytical Accuracy with Ashing Techniques
- What is the sintering process of coating? Building Durable, Solid Layers from Powder
- What equation do you use to calculate the heat required to melt a sample? Master the Heat of Fusion Formula



















