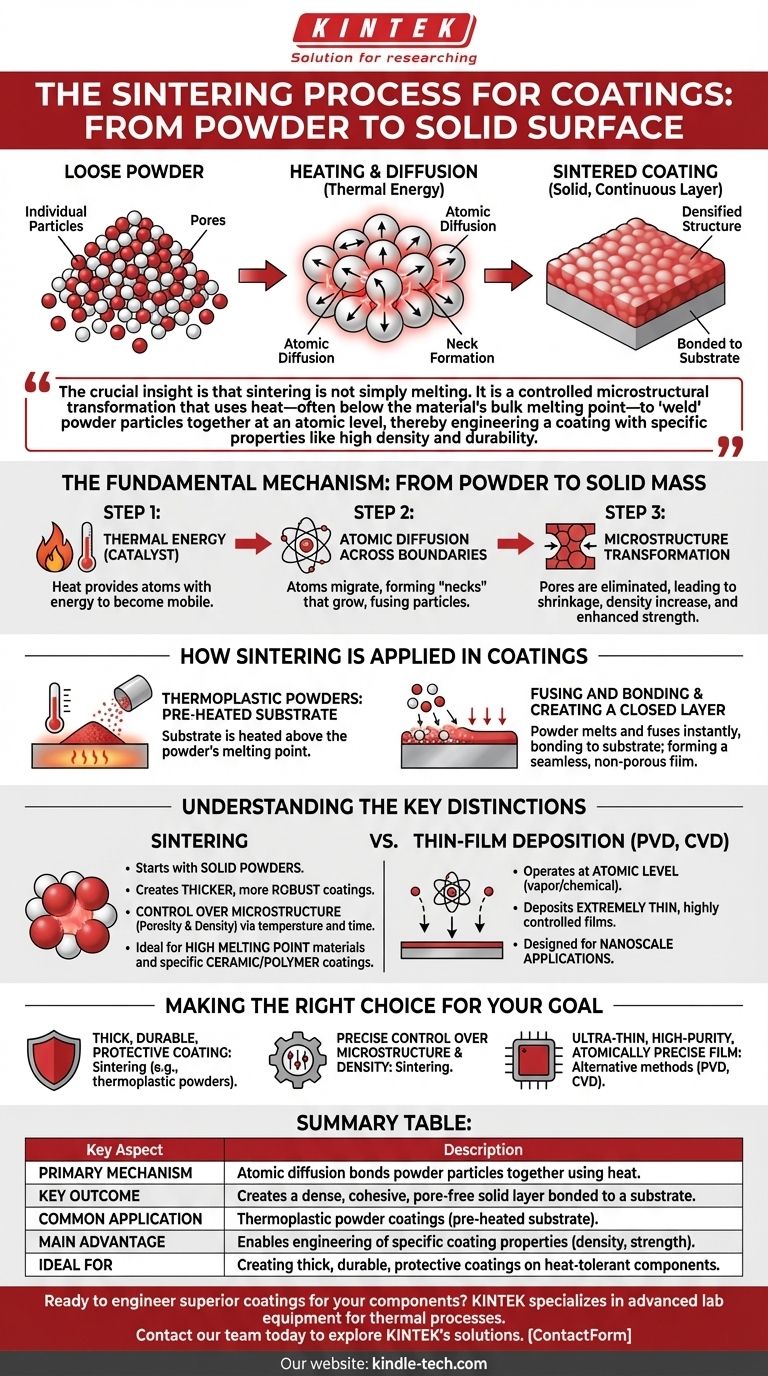
At its core, the sintering process for coatings is a thermal treatment that transforms a layer of loose powder into a solid, continuous, and dense surface. The components are heated to a specific temperature, causing the individual powder particles to bond and fuse together through atomic diffusion. This process compacts the material, eliminates the pores between particles, and creates a strong, cohesive layer bonded to the substrate.
The crucial insight is that sintering is not simply melting. It is a controlled microstructural transformation that uses heat—often below the material's bulk melting point—to "weld" powder particles together at an atomic level, thereby engineering a coating with specific properties like high density and durability.
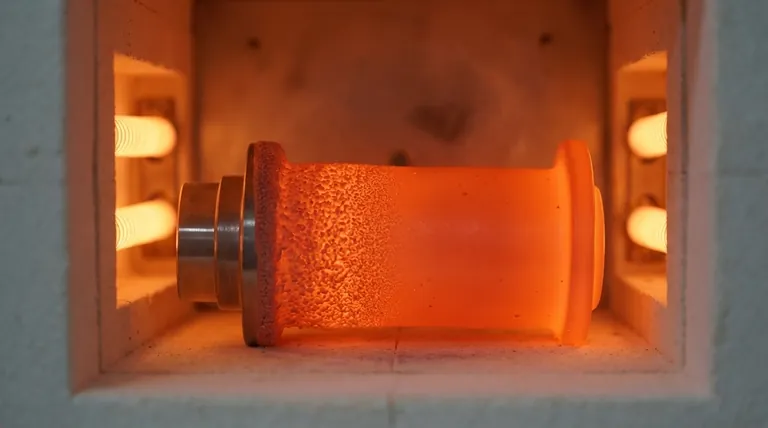

The Fundamental Mechanism: From Powder to Solid Mass
Sintering is a process of material transformation driven by thermal energy. It's the method by which a collection of individual grains becomes a single, solid piece without necessarily being melted into a liquid state.
The Role of Thermal Energy
Heat is the catalyst for sintering. Applying high temperatures provides the atoms within the powder particles with enough energy to become mobile and move across the boundaries of adjacent particles.
Atomic Diffusion Across Boundaries
This atomic movement, known as diffusion, is the central mechanism of sintering. Atoms migrate to the points of contact between particles, forming "necks" that grow over time. These necks gradually pull the particles closer together, effectively fusing them into a single, solid structure.
The Transformation of Microstructure
The result of this atomic bonding is a profound change in the material's internal structure. The empty spaces, or pores, between the original powder particles are gradually eliminated. This process leads to volume shrinkage, a significant increase in density, and enhanced material strength.
How Sintering Is Applied in Coatings
While the underlying principle of atomic diffusion remains the same, the practical application for coatings involves specific steps to create a fused layer on a component's surface.
A Common Application: Thermoplastic Powders
One widely used technique involves thermoplastic powder coatings. In this method, the substrate (the component to be coated) is heated to a temperature above the melting point of the powder.
The Fusing and Bonding Step
When the thermoplastic powder granules are applied to the pre-heated component, they touch the hot surface, melt, and immediately fuse together. This rapid process ensures the particles bond not only to each other but also to the substrate itself.
Creating a Closed, Cohesive Layer
The ultimate goal is to form a closed coating—a seamless, non-porous layer that completely seals the underlying substrate. The sintered particles are no longer distinct but have merged into a uniform and protective film.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
Sintering is a distinct process with characteristics that set it apart from other common coating technologies. Understanding these differences is critical for selecting the right method for an application.
Sintering vs. Thin-Film Deposition
Sintering should not be confused with processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
PVD and CVD operate at an atomic level, vaporizing a material or using chemical precursors to deposit an extremely thin, highly controlled film onto a substrate. Sintering, by contrast, starts with solid powders and is typically used to create thicker, more robust coatings.
Control Over Porosity and Density
The parameters of the sintering process—namely temperature and time—give engineers direct control over the final coating's microstructure. Incomplete sintering can be used to create porous structures for applications like filters, while full sintering aims to achieve maximum density for strength and protection.
Material Suitability
The process is especially valuable for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or molybdenum, where melting them completely would be impractical. It is also a foundational process for creating specific ceramic and polymer coatings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a coating process depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final product. Sintering offers a unique set of capabilities for specific engineering challenges.
- If your primary focus is a thick, durable, and protective coating: Sintering is an excellent method, especially when using thermoplastic powders on heat-tolerant substrates.
- If your primary focus is precise control over microstructure and density: The sintering process provides direct levers to engineer the final properties of the coating, such as its strength and porosity.
- If your primary focus is an ultra-thin, high-purity, or atomically precise film: You should investigate alternative methods like PVD or CVD, as they are specifically designed for these nanoscale applications.
Ultimately, understanding sintering allows you to see it not just as a coating method, but as a powerful tool for building a material’s final properties from the powder up.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Atomic diffusion bonds powder particles together using heat, often below the melting point. |
| Key Outcome | Creates a dense, cohesive, and often pore-free solid layer bonded to a substrate. |
| Common Application | Thermoplastic powder coatings, where a pre-heated substrate melts the powder for fusion. |
| Main Advantage | Enables engineering of specific coating properties like density, strength, and porosity. |
| Ideal For | Creating thick, durable, protective coatings on heat-tolerant components. |
Ready to engineer superior coatings for your components?
The sintering process is key to achieving durable, high-performance surfaces. At KINTEK, we specialize in the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect thermal processes like sintering for your R&D and production needs.
Our experts can help you select the right tools to control temperature, time, and atmosphere for optimal results. Let's discuss your specific coating challenges and goals.
Contact our team today to explore how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your coating capabilities and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do you sterilize glassware without an autoclave? A Step-by-Step Guide to Dry Heat Sterilization
- What role does a high-temperature box furnace play during the re-austenitization of 17-4 PH? Transform SLM Performance
- What is the importance of precise programmed temperature control in a high-temperature furnace? Master Co-Sintering
- Why is a muffle furnace or oven used for thermal annealing after silver nanowire deposition? Unlock Peak Conductivity
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer



















