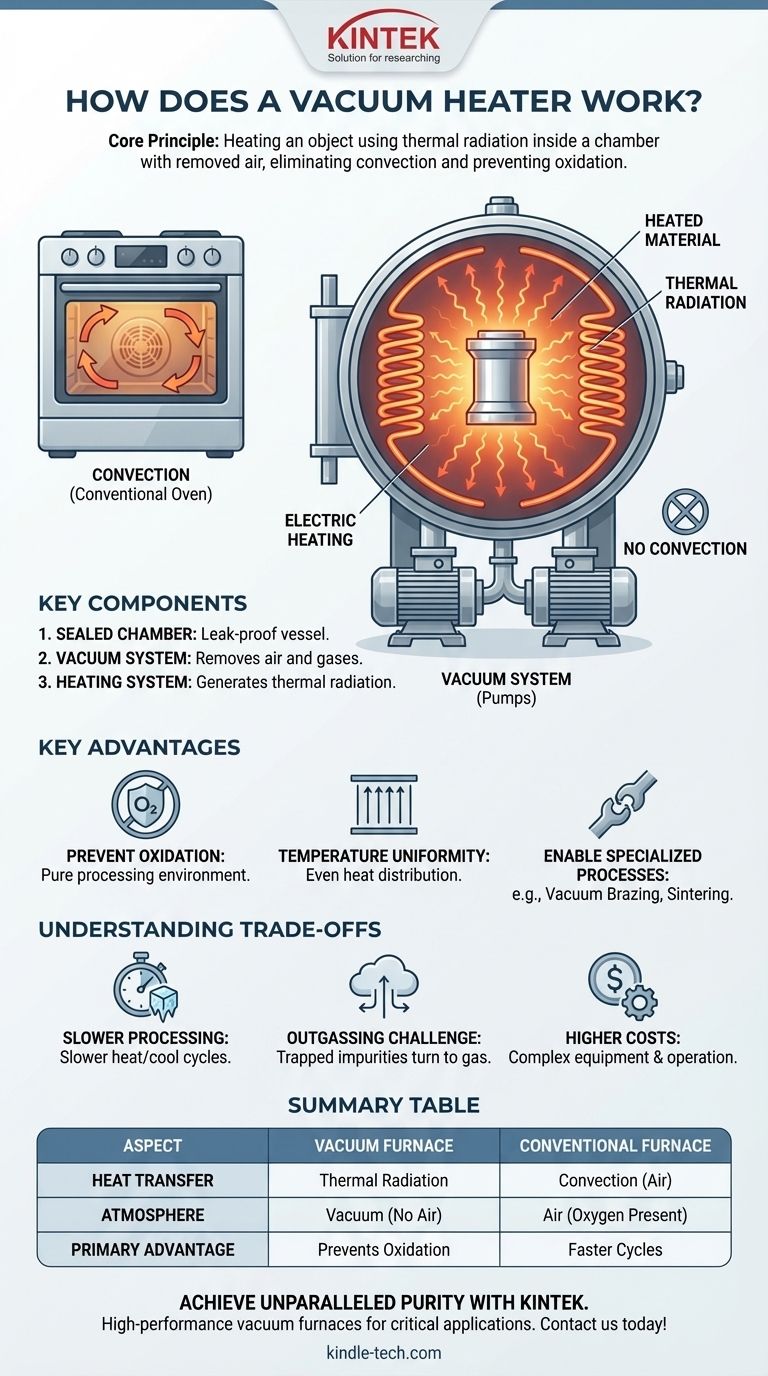
At its core, a vacuum furnace works by heating an object using thermal radiation inside a chamber from which all air has been removed. By creating a vacuum, the system eliminates heat transfer through air (convection) and prevents the heated material from reacting with gases like oxygen, which would cause oxidation or contamination. The heat source, typically electric heating elements, glows and radiates energy directly to the part, similar to how the sun heats the Earth through the vacuum of space.
A vacuum furnace isn't about heating a vacuum; it's about heating a material within a vacuum. The primary goal is to control the environment, preventing unwanted chemical reactions and contamination by removing the air, forcing the heat transfer to occur purely through radiation.

The Core Principle: Heating Without Air
Conventional ovens rely heavily on convection—hot air circulating and transferring thermal energy to the object. A vacuum furnace operates on a fundamentally different principle.
Eliminating Convection
The first step in any vacuum furnace process is to pump the air out of a sealed chamber. By removing the air molecules, you eliminate convection as a method of heat transfer.
This also prevents heat loss from the product via convection, allowing for highly controlled and efficient energy use once the target temperature is reached.
The Dominance of Thermal Radiation
With no air to carry heat, the furnace must use another method: thermal radiation. Inside the furnace, powerful electric heating elements (often made of graphite or molybdenum) are heated until they glow.
These elements emit infrared radiation, a form of electromagnetic energy. This energy travels unimpeded through the vacuum and is absorbed by the surface of the material being processed, causing its temperature to rise.
The Key Components
A vacuum furnace consists of three critical systems working together:
- A Sealed Chamber: A robust, leak-proof vessel that can withstand both high external atmospheric pressure and high internal temperatures.
- A Vacuum System: A series of pumps that remove air and other gases to achieve the required level of vacuum.
- A Heating System: The internal heating elements and heat shields that generate and direct the thermal radiation.
Key Advantages of Vacuum Heating
Removing the atmosphere creates an incredibly pure processing environment, which is the primary reason for choosing this technology.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, most metals and alloys react readily with oxygen, forming oxides (rust or scale) that can ruin a part's surface finish, integrity, and mechanical properties. A vacuum removes the oxygen, ensuring the material remains pristine.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
Without unpredictable air currents from convection, heat distribution from radiation can be exceptionally uniform. The heating elements surround the part, providing even, direct energy from all sides, which is critical for complex geometries.
Enabling Specialized Processes
Certain manufacturing processes are only possible in a vacuum. For example, vacuum brazing requires an atomically clean surface for the filler metal to flow and create a strong bond, something an oxygen-free environment guarantees. Similarly, sintering powdered metals to form a solid part requires a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heating is not the solution for every application. It comes with a specific set of operational considerations.
Slower Processing Cycles
Heating via radiation can be slower than convection, especially in the initial ramp-up phase. More significantly, cooling can be extremely slow since there is no air to carry heat away. To speed this up, many furnaces use a "gas quench" process where an inert gas like argon or nitrogen is rapidly backfilled into the chamber.
The Challenge of Outgassing
When materials are heated in a vacuum, trapped impurities, moisture, or other volatile compounds on their surface can turn into gas. This process, known as outgassing, can contaminate the vacuum environment and the part itself if not managed properly through careful cleaning and process control.
Higher Equipment Costs
Vacuum furnaces are complex machines. The vacuum-tight chamber, sophisticated pumping systems, and high-temperature seals make them significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the material requirements and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is surface purity and preventing oxidation: A vacuum furnace is the superior and often the only choice, especially for reactive materials like titanium or high-alloy steels.
- If your primary focus is rapid, low-cost bulk heat treatment: A conventional atmospheric furnace is typically more time- and cost-effective for simple processes where a bit of surface oxidation is acceptable or can be cleaned off later.
- If your primary focus is joining complex parts with maximum integrity: Vacuum brazing is the industry standard for aerospace, medical, and high-performance applications where joint reliability is non-negotiable.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is an investment in achieving a level of material purity and process control that is impossible in a normal atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Furnace | Conventional Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Method | Thermal Radiation | Convection (Air) |
| Atmosphere | Vacuum (No Air) | Air (Oxygen Present) |
| Primary Advantage | Prevents Oxidation & Contamination | Faster Heating Cycles |
| Ideal For | High-Purity Processes (e.g., Brazing, Sintering) | General Purpose Heat Treatment |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity and precision in your lab processes?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance vacuum furnaces and lab equipment designed for critical applications where contamination control is paramount. Our solutions are ideal for laboratories in aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and advanced materials research.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can enhance your results and reliability. Let's talk about your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing



















