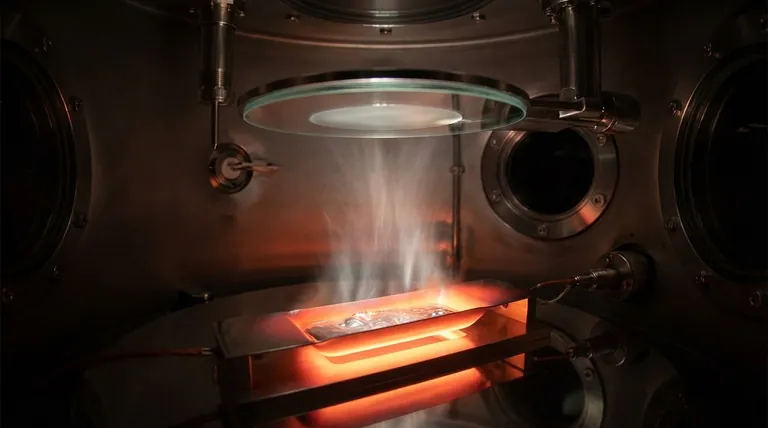
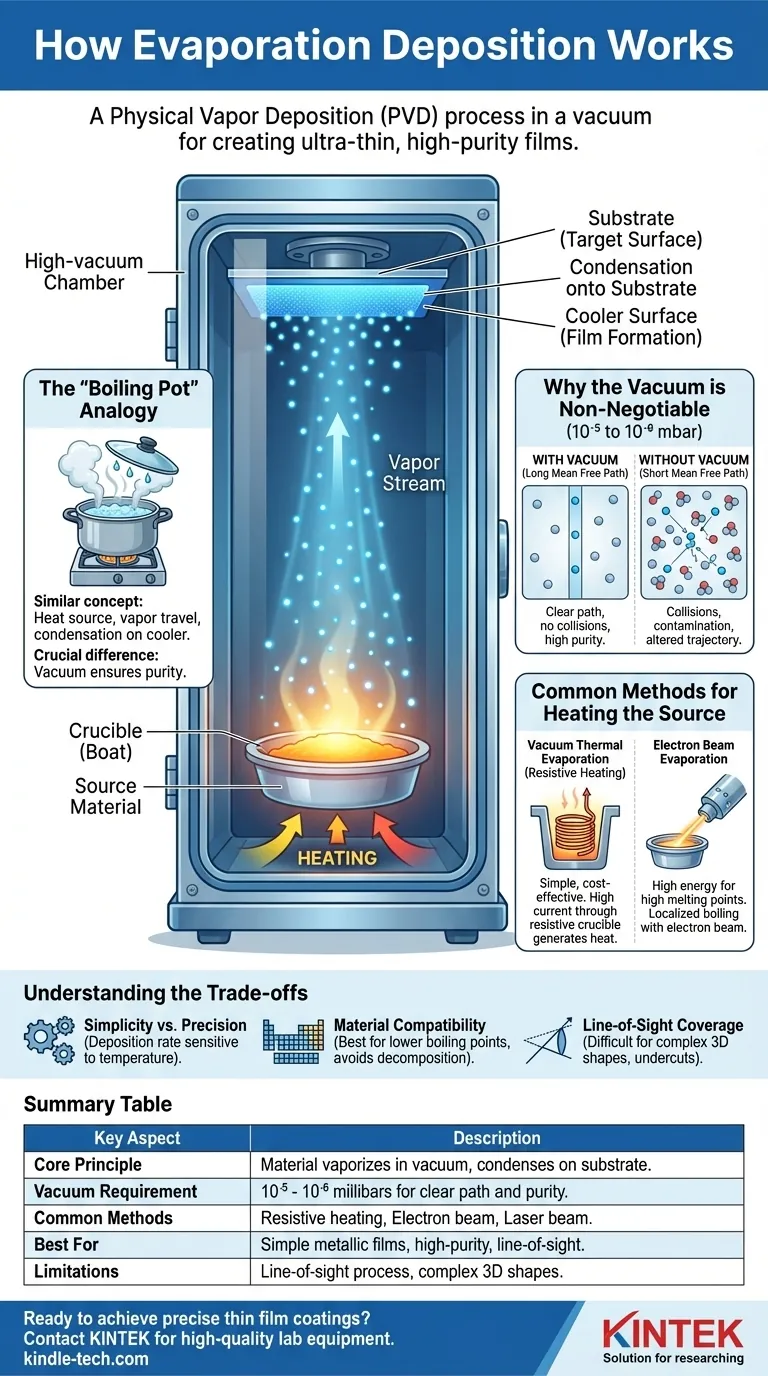
At its core, evaporation deposition is a physical process for creating ultra-thin films by boiling a material in a vacuum and allowing its vapor to condense onto a target surface. The source material is heated in a high-vacuum chamber until its atoms gain enough energy to evaporate. These vaporized particles then travel through the vacuum and settle onto a cooler substrate, forming a pure, uniform coating.
The critical principle is not the heating, but the vacuum. A high-vacuum environment is essential because it removes unwanted gases, ensuring the evaporated particles travel directly to the substrate without collisions, which is the key to achieving a high-purity, uncontaminated thin film.

The Fundamental Two-Step Process
Evaporation deposition works through a straightforward sequence of physical state changes, all conducted within a highly controlled environment.
Step 1: Evaporation of the Source Material
A source material, the substance you wish to deposit, is placed into a container called a crucible or "boat" inside a vacuum chamber. This crucible is connected to a power source that heats it, and consequently, the material within it.
As the material's temperature rises to its melting and then boiling point, its surface atoms gain enough thermal energy to break their bonds and escape as a vapor.
Step 2: Condensation onto the Substrate
This vapor stream travels upward through the vacuum chamber. Positioned above the source is the substrate, which is the object or surface to be coated.
Because the substrate is significantly cooler than the vapor, the gaseous particles lose energy upon contact and condense back into a solid state, building up layer by layer to form a thin film.
The "Boiling Pot" Analogy
The process is conceptually similar to seeing water droplets form on the cool lid of a boiling pot of water. In both cases, a substance is heated to a vapor, travels a short distance, and condenses on a cooler surface.
The crucial difference is that evaporation deposition occurs in a near-perfect vacuum instead of a gaseous kitchen environment, ensuring unparalleled purity.
Why the Vacuum is Non-Negotiable
The success of the entire process hinges on maintaining a high-vacuum environment, typically at pressures between 10⁻⁵ and 10⁻⁶ millibars.
Creating a Clear Path
The vacuum removes virtually all air and other gas molecules from the chamber. This creates a long "mean free path" for the evaporated source particles.
This means the particles can travel in a straight line directly from the source to the substrate without colliding with background gas. Such collisions would alter their trajectory and could contaminate the final film.
Ensuring Material Purity
By evacuating the chamber, any reactive gases like oxygen or water vapor are removed. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions with the hot vapor stream, guaranteeing that only the pure source material is deposited onto the substrate.
Common Methods for Heating the Source
While the principle remains the same, different techniques can be used to provide the thermal energy required for evaporation.
Vacuum Thermal Evaporation (Resistive Heating)
This is the most common method. A high electrical current is passed directly through the crucible, which is made of a resistive material like tungsten. The crucible's resistance to the current generates intense heat, which is transferred to the source material.
Electron Beam Evaporation
In this more advanced technique, a high-energy beam of electrons is fired at the source material. The kinetic energy of the electrons is converted to thermal energy upon impact, causing localized boiling of the material. This allows for higher temperatures and the deposition of materials with very high melting points.
Other Advanced Techniques
Methods like laser beam evaporation (using a high-power laser) and inductive heating (using RF-induced eddy currents) offer alternative ways to supply the necessary energy, each with specific advantages for certain materials and applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, evaporation deposition is a line-of-sight process with specific limitations that are important to recognize.
Simplicity vs. Precision
Thermal evaporation is relatively simple and cost-effective, but precisely controlling the deposition rate can be challenging. The rate is highly sensitive to temperature, which can be difficult to regulate perfectly.
Material Compatibility
The process is best suited for materials with relatively low boiling points. Attempting to evaporate materials with extremely high boiling points, or compounds that decompose when heated, can be difficult or impossible with standard thermal methods.
Line-of-Sight Coverage
Because the vapor particles travel in a straight line, the process can only coat surfaces that have a direct, unobstructed view of the source. This makes it difficult to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or hidden surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct approach depends entirely on your material requirements and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is depositing a simple metallic film (like aluminum or gold) for applications like mirrors or basic electrodes: Standard thermal evaporation is an excellent, cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing materials with very high melting points or achieving ultra-high purity films: Electron beam evaporation provides the necessary energy and control.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D object uniformly: You should consider alternative deposition methods, such as sputtering, that do not have line-of-sight limitations.
Understanding this foundational technique is key to appreciating how many of today's advanced electronic and optical components are manufactured.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Physical vapor deposition (PVD) in a vacuum chamber |
| Core Principle | Material is heated to vaporize, then condenses on a cooler substrate |
| Vacuum Requirement | 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ millibars for clear particle path and purity |
| Common Heating Methods | Resistive heating, Electron beam, Laser beam |
| Best For | Simple metallic films, high-purity coatings, line-of-sight surfaces |
| Limitations | Line-of-sight process, challenging for complex 3D shapes |
Ready to achieve precise thin film coatings for your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality evaporation deposition systems and lab equipment. Whether you need to deposit simple metallic films or work with high-melting-point materials, our solutions ensure purity, efficiency, and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your research and production processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition



















